Journal of
eISSN: 2373-4310


Review Article Volume 8 Issue 6
1Department of Microbiology, Assam down town University, India
2Department of Microbiology, Assam down town University, India
3Department of Botany, University of Chittagong, Bangladesh
4Department of Pharmacy, Assam downtown University, India
Correspondence: Avra Pratim Chowdhury, M Phil. researcher, Department of Microbiology, Assam down town University, India
Received: October 27, 2018 | Published: December 6, 2018
Citation: Chowdhury AV, Thakuria N, Uddin B, et al. A review on home yard medicinal plants commonly used in diabetic treatment. J Nutr Health Food Eng. 2018;8(6):494-502. DOI: 10.15406/jnhfe.2018.08.00316
Bangladesh is a land of tropical forests and boggy jungle. As boasted with floral genetically plantation of herbs made it an excellent source of medicinal plants. The modern analysis of herbal plants designed with highly esteemed source of medicine to treat Diabetes mellitus. On these consequences the researcher illustrated the local application of raw medicinal products of herbs as a remedy of controlling diabetes. Herbal practitioner in Bangladesh both registered and nonregistered traditionally use some of the herbal plants and active chemical constituents which have a role in the management of Diabetes including type 1 and type 2. The research protocols is subjected as local implementation of home yard medicinal plant to control diabetes in a minimal cost reviewing for its anti diabetic activity without side effects.
Keywords: amyline antagonism, cAMP, diabetes mellitus, insulinotropic, phytomedicine, herbal practitioner
Bangladesh created own environmental support for tree plantation due to its monsoon effects. The concern of isolation and identification of phytomedicinal plants based on tropical rain forest area in Bangladesh is subjected on these global effects. For this reason, the research work has been carried out at Chittagong metropolitan and rural based area in Bangladesh. Here the reviewers tried to follow up differentiate implementation of raw herbal products for the treatment of Diabetic patient collected from home yard ground. Inexpensive and easily accessible nature of the traditional medicines made it an integral part of public health services in Bangladesh. Diabetes mellitus is metabolic diseases characterized in group of patterns incorporate with high blood sugar (glucose) levels that result from insufficient insulin secretion.1 Phyto medicines have been highly esteemed source are widely used today indicating that herbs usually inconsideration growing part of modern Bio tech application.2 Home yard herbal plants with active chemical constituents play a vital role in the treatment of Diabetes mellitus type 1 and type 2 maintaining blood sugar level in normal 70 to 100, or less than 140 mg/100ml.3,4 The Ayurvedic village prescribers were compiled along with their specific treatment and authentic suggestion as use this raw medicine discussed in this review.
The herbal practitioner suggested comfortless and effective ways to practice medicine for diabetic treatment depending on home yard source.5 Natural home yard plants, crops, seeds, leaves considered as performing potent candidates with pharmaceutical synthetic oral medicines.6 So steps should be taken from root label to optimize a procedure for ant diabetic screening of different plant extracts isolating new bioactive compounds for the discovery of home yard available herbal anti diabetic drugs.7 Herbal village practitioner chose Fenugreek (Trigonellafoenum-graecum L., family Leguminasae) seeds due to its active components 4-HI (4-hydroxyisoleucine), this potential active compound is applied on diabetic patient in a successive patterns. Another available source of application is chosen by the ayurvedic doctors Neem (Azadirachtaindica, mahogany family).8 The present study evaluated the long term hypoglycemic effect of Black cumin (Nigella sativa) holy basil (Ocimum sanctum), Cherotha (Swertiachirayita), Seeds of Mehogone (Swieteniamacrophylla), Bitter gourd (Momordicacharantia L.) to treat as yard plenty ailments based on activities regarding anti diabetic application. The in vitro application of aqueous extract of aloevera (Aloe barbadensis) leaves examined for its anti diabetic activities against alloxan induced diabetic mice. But aloevera maintains a long term hypoglycemic effect accordance with observational studies of village herbal practitioner,9,10 proved the basic fundamentals need of diabetic patient.11
Isolation and Identification of home yard anti diabetic plants:
Plants name |
Scientific identity |
Active initiator compounds |
Aloe vera |
Aloe barbadensis |
Methylenecycloartanol. |
Garlic |
Allium sativum |
Diallyldisulphide oxide(allicin) |
Onion |
Allium cepa |
Mehtyl cysteinesulphoxide |
Neem |
Azadirachtaindica |
Oleic& stearic acids. (50%, 20%) |
Noyontara |
Catharanthus roseus |
Vinculin alkaloids |
Telacucha |
Capparisdeciduas |
Phenyl propanoid, thymol (24.4%) |
Bitter gouard |
Momordicacharantia |
Glycosides momordin, charantosides,charantin. |
Holy basil |
Ocimum sanctum |
Eugenol 4,5,Cinnamyl acetate 5 and Beta-elemene 5. |
Cherotha |
Swertiachirayita |
Ophelic acid |
Black berry |
Syzygiumcumini |
Kaempferol-3-O-β-D glucuronopyranoside |
Seeds of Mehogony |
Swieteniamacrophylla |
Limonoids |
Fenugreek |
Trigonellafoenumgraecum |
Trogonelline, and Coumarin |
Collection of authentication
The plant used in this study was collected from the stand at the courtyard around the Dean’s Office, Botanical garden, Home yard garden of ayurvedic doctor and Faculty of Biological Sciences, University of Chittagong. The specimens were authenticated by Dr. Shaikh Bokhtear Uddin, a botanist in the Department of Botany, University of Chittagong



Azadirachtaindica Momordicacharantia Aloe barbadensis



Catharanthus roseus Capparisdeciduas Ocimum sanctum


Terminaliachebula, Allium cepa, Allium sativum. Swieteniamacrophylla
Field survey
A total of twenty Herbal practitioners have been interviewed. They have age group between 35-50. In this contrary approaching honored by at least 10 to 25years experience. So following nine practitioners were selected for their logical arguments and also for effective prescriber.
Preparation of anti diabetic suspension
Saturate solution of Neem leaves (over night): 250 ml
Fenugreek: 20gm
Alovera gel: 10gm
Seeds of Mehogone: 5gm
Natural resources considered as potent candidates for drug discovery and are playing a pivotal role in drug development programs. Moreover, many medicinal herbs provide a rich mine for bioactive chemicals that are markedly free from undesirable side effects and of powerful pharmacological actions.12–14
Twenty Herbal practitioners have been interviewed remedies the herbs as medicine. They have age group between 35-50. In this contrary approaching honored to them by at least 10 to 25years experience. So following nine practitioners (Table 1) were selected for their logical arguments as for effective prescriber. A total of 17 species have been found to be used for the treatment of diabetes in 16 /genera under six Families and subjected to Herb, shrub, tree and climber. From the analysis of herbal formularies, it has been observed that the percentage of use of plant parts contain 37% leaves, 17% entire plant, 16% seed, 14% Fruit, 6% Flower, 4% Bulb, 6% Bark (Figure 1). Than the researcher and associates selected twelve home yard phytomedicinal plants and their remedies upon patient for three months (Table 2). The ayurvedic village doctor practices their home made medicines where as their patient became cure from their outdoor suggestion (Figure 2).
Herbal Practitioners (Ayurvedic or Unani medicine) Name, Designation and Locality |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 1 Herbal Practitioners and their prescribed remedies of diabetic patient
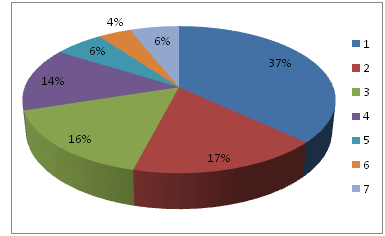
Figure 1 Analysis of remedies obtained from different plant parts for Diabetes Mellitus 1. L - Leaves, 2. EP - Entire plant, 3. S - Seed, 4. F - Fruit, 5. FL - Flower, 6.B - Bulb, 7. BR – Bark.
Plants Used. |
Mode of application |
|
|
Aloe barbadensis (Aloe vera), |
Leaves |
Grinding in juice and used as syrup. |
Once daily up to one year. |
Allium cepa: (onion) |
Root crops, Bulbs, stem, tops. |
Grinding in juice and used as pulpy syrup. |
Two times daily up to one year |
Allium sativum: (garlic) |
Root crops Bulbs, stem, tops |
Grinding in juice and used as pulpy syrup. |
Two times daily up to one year. |
Azadirachtaindica: (Neem), |
Leaves, Flowers |
Grinding in juice and used as syrup. |
Once daily up to one year. |
Catharanthus roseus (Noyontara) |
Flowers |
Grinding in juice and used as syrup. |
Once daily up to six months |
Capparisdeciduas (Telakucha), |
Leaves |
Grinding in juice then boiled and used as syrup |
Two times daily up to one year. |
Swieteniamacrophylla ( Seeds of Mehogone), |
Seed |
Dried and grinding form to use as powder. |
Once daily up to six months |
Momordicacharantia: (bitter gourd) |
Fruit |
Grinding pulp and its juice. |
Once daily up to one year. |
Ocimum sanctum: (holy basil) |
Leaves |
Grinding in juice and used as syrup. |
Once daily up to six months |
Swertiachirayita(Cherotha) |
Stem and Bark |
Dried and wet. |
Once daily up to six months |
Trigonellafoenumgraecum: (fenugreek) |
Seed |
Dried and grinding form to use as powder |
Once daily up to one year. |
Syzygiumcumini: (Black berry) |
Fruit |
Dried and grinding form to use as powder |
Once daily up to one year. |
Table 2 Herbal prescribed remedies and its mode of application
The research survey continued with daily assessment of history in diabetic and non diabetic patients being with administered specific isolated plant medicine by respective doctor. Medicinal plants that have been shown to improve the diabetic state without apparent enhancement of insulin secretion tested for effective constituents of raw alkaloids properties suggested by Ayurvedic village doctors (Figure 3 & Figure 4). The constituents and active properties regarding hypoglycemic effect and antibiotic sensitivity has been studied and observed by researcher from several blood reports of patients in a collective profile (Table 3). From this group study and research survey, the outcomes resulted about self home remedies for diabetic patient in regular practice at a minimal cost. Garlic, onion and fenugreek (48.57%, 60% and 76.73% curability rate) is very much effective to maintain hypoglycemic level in both diabetic and non diabetic patients. Blackberry, hollybasil and aloevera cultivation is the good source for home yard cultivation due to antibiotic and antidiabetic effects on patients without having any discomfort for its own chemical components. These include eugenol, linalool, estragole, limonene, citral, methylchavicol, and methyl cinnamate. The more distinctly scented varieties boast a predominant volatile compound that out-competes the rest, producing a characteristic aroma.


Figure 3 Ayurbedic village doctor Md. Najmul Hasan showed home yard medicinal plants, and home made medicinal ingredients from leaves, bark, fruits and roots.


Figure 4 Ayurvedic village doctor Mr. Ghandhi Das showed home yard medicinal plants and its fruits with roots.
Plants name |
Mode of action |
History of curability (%) according to patient registry, December-February (2015-2016) |
Result |
|
Type 1 |
Type 2 |
|||
Aloe barbadensis (Aloevera) |
As medicine, it is used and suggested to the patient in syrup suspension of Aloevera for 4 - 14weeks. The outcome is resulted significant by hypoglycemic effect both clinically and experimentally. Scientifically it is proved Aloevera gel is used in reducing sugar in diabetes under studying prescription of Ayurvedic village doctors. |
Total no. 40, |
Total no. 12 Cure: 7 |
61.67% |
Allium sativum (garlic) |
2.4gm garlic tablet is administered for patient containing 31.2mg allicin in high dose. The actual dose is used to control and regulate hyperglycemic effect after 5 h of administration. |
Total no. 25 |
Total no. 14 |
48.57% |
Allium cepa (onion) |
The control of hyperglycemic effects regarding the systemic routine studies showed that oral administration of the ethanol extract of onion regulated the blood-sugar level, normalizing the activity of both liver hexokinase and glucose-6- phosphatase. |
Total no. 10 |
Total no. 8 |
60% |
Azadirachtaindica(Neem) |
The ingradients suggested by doctors followed in suppressing digestion and absorption at intestinal and hepatic cells. The raw contents prepared homemade medicine is used to decrease of carbohydrate. This suggestion includes with no risk of hypoglycemia,hyperinsulineia and undesirable weight gain.But carries hyper risk of stomach ache. |
Total no. 56 |
Total no. 44 |
58.93% |
Capparisdeciduas (Telakucha), |
Village Ayurvedic doctors suggest the raw juice of telakucha. The activity for α-glucosidase was assessed according to the method of enzyme inhibition directly. Patients were administered pasted juice for three weeks, and the outcomes were fruitful from patient registry. |
Total no. 9 |
Total no. 4 |
45.84% |
Catharanthus roseus(Noyontara) |
The active compound vinculin alkaloids decrease the hyperglycemic levels by increasing anti cytotoxic factors in liver. |
Total no. 39 |
Total no. 13 |
64.10% |
Momordicacharantia |
It is widely used and administered to type 1 diabetic patient suffering from obesity. The hypolipidemic and hypoglycemic effects comes out by synthesis of active compound momordin and cucurbitacin B. The potential rate of medicinal extract is highly potent on the field basis application. |
Total no. 65 |
Total no. 38 |
56.44% |
Swieteniamacrophylla |
Seeds of extracted medicine in oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is administered for exhibiting (60% reduction) in blood glucose level. The outcomes of treated patient resulting after 12 consecutive days of oral treatment (300mg/kg). It is also potent antibiotic active compound against gangrenous bacteria. |
Total no. 19 |
Total no. 10 |
61.58% |
Ocimum sanctum: |
Leaves of holy basil produced alcohol extract. In ayurvedic treatment pasted syrup was administered orally which significantly reduced glycemia and enhanced exogenous insulin action. |
Total no. 70 |
Total no. 85 |
71.68% |
Swertiachirayita (Cherotha) |
The insulin levels are maintained on the treatment of 200mg/kg from extracted ethanols. The treatment of diabetic patient was compared to the diabetic control from abnormal glucose homeostasis. The result was subjected to leading part on type I diabetes due to selective and progressive destruction of pancreatic β-cells was about to cure. |
Total no. 122 |
Total no. 74 |
75.11% |
Syzygiumcumini: |
The juice and pasted seed and leaves extract are the medicinal source of hydrolyzed tannins. This compound is the active source of transforming growth factor beta1, Fibrinoactin and growth factor of connective tissue in pancreatic islets. It contains Plasminogen activator which inhibits the active site of renal cortex in type 2 diabetic patient. |
Total no. 15 |
Total no. 8 |
74.17% |
Trigonellafoenumgraecum: (fenugreek) |
The fenugreek is a complete diet for regular practices of diabetic or non diabetic patient. Studying consecutive patient history the result of fenugreek significantly awesome to reduce fasting blood sugar. The case study was improved glucose tolerance test in type 2 after urine analysis. |
Total no. 106 |
Total no. 48 |
76.73% |
Table 3 Synchronized percentages in curability of diabetic patient
Momordin, Ophelic acid and Stearic acid produced acidity in stomach accelerating the receptor of hydrogen antagonistic to probiotic production. Indigestion may result if generic Compound is administered in fasting condition of patient. So the raw juice of Neem (58.93%curability rate) leaves, Cherotha and Bitter gourd (56.44% curability rate) should be suggested in 200ml daily considerable in age 35-55. This medicine should not be prescribed to complete insulin dependent patient. So the curability rate comes out as best suggestive for Bitter gourd for type 1 and Cherotha is suggestive for type 2. But as regular practice to control sugar label as preventive medicine, Cherotha (75.11%curability rate) is the best selection for practitioner. Telakucha and Noyontara is less effective than others and it may also cause ulceration to intestine of immune suppressed patient. So the ayurvedic practitioners suggest as observing the history and blood report of diabetic patients. The graphical presentation Figure 5–8 showed the diagrammatic points of view that already been described in noted discussion.
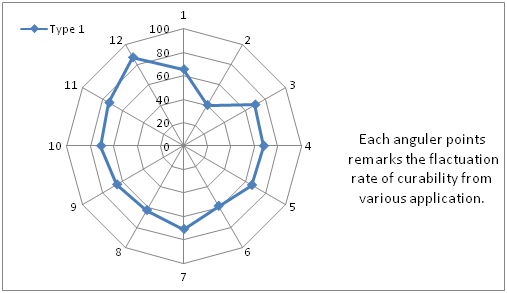
Figure 6 Fluctuation points are noted as curability percentages among isolated plants in Type1 diabetes patients.
The phytomedicinal condition of different samples and their safety assessment revealed that most of the raw medicinal residues as a treatment were acceptable. The implemented safety of the samples depend not only the environmental conditions but also on the personal medication and doctors suggestion. Detailed study is required concerning more areas, increasing more sampling sites and their numbers for better growth of home yard medicinal plants. Storage duration of home yard phytomedicinal plants plays an important vital role and long storage duration favors more carcinogenic and chemical toxin degrading gradually their remedies potency. Therefore storage of processed raw medicine for long time should always be avoided and prohibited. As most of the plants constituents are able to produce toxins, it is necessary to monitor strictly medicinal products and then certify them for human consumption after performing a dose to patient.
None.
The authors declare that there is no conflicts of interest.

©2018 Chowdhury, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.