Journal of
eISSN: 2373-4310


Research Article Volume 2 Issue 4
Department of Nutrition and Food Science, University of Kalamoon, Syria
Correspondence: Tony Abdullah, Department of Nutrition and Food Science, University of Kalamoon, Deir Atiah, Syria, Tel 00963944629298
Received: March 05, 2015 | Published: September 10, 2015
Citation: Abdullah T. Reduction of oil uptake in deep fat fried falafel. J Nutr Health Food Eng. 2015;2(4):114-117. DOI: 10.15406/jnhfe.2015.02.00059
The Arabic word )لفلاف( "Falafel" is the plural of )لفلف( "pepper". Falafel is a fried ball principally made of spiced fava beans and/or chickpeas. It is a popular form of fast food in the Middle East Brothwell & Brothwell.1 Falafel was invented some 1000years ago by the Egyptian Copts, who brought it with them to the rest of the Middle East originally made with fava beans. The dish migrated northwards to Syria and Palestine where chickpeas were introduced instead. The chickpea was used as a food item in the levant before 4000 BC Jodi K.2 Fat and calorie content of falafel are of concern to healthy consumers, Lefort et al.,3 Fats (lipids) are implicated in cardiovascular disease due to the fact that the product constitutes a major source of energy content (9Kcal/g); eating high fat diet is conducive to obesity Baur.4 Therefore, high oil content is a major factor affecting consumer acceptance of oil-fried products today, as well as low fat food products are becoming more popular, Bunger et al.,5 Saturated fat and trans-fat are the undesirable fats Allan.6
In many countries medical authorities have implicated a high fat diet as being one of the most conducive factors to cardiovascular disease Glew.7
During the last 10years, the American Heart Association and other health organizations have encouraged limitation of fats in foods to less than 30% of calories for most people.8,9
Reducing the oil content in falafel is also motivated by other several reasons; oil is a costly raw material and is an important determinant of the cost of product, as well as neither study was applied to determine the oil content of any kind of falafel, nor reducing their oil content. High oil content makes falafel balls greasy or oily. On the other hand it would be health-wise rewarding if it becomes possible to make falafel balls less greasy then healthier. However, there have been many techniques applied to reduce the fat content of frying products.
Numerous coating materials could be used. Gold10 disclosed the treatment with an aqueous hydrocolloid solution, which is methylcellulose, hydroxypropylcellulose, carboxymethylethyl cellulose (CMC).
Albert et al. experimented 11 hydrocolloid materials including gelatin, gellan gum, k-carrageenan- konjac-blend, locust bean gum, methyl cellulose (MC), microcrystalline cellulose, pectin (three types), sodium caseinate, soy protein isolate (SPI), vital wheat gluten, and whey protein isolate (WPI). These materials were compared for their film forming ability and suitability for fried foods, water and fat transfer properties.
Gelatin, wheat gluten, and sodium caseinate were not suitable in single material coating. The SPI, WPI, and MC were the best materials for coating to reduce fat uptake during frying. SPI/MC and SPI/WPI mixed coatings provided the highest index value (reduction in fat uptake/decrease of water loss), and reduced the fat uptake up to 99.8%, Albert et al.,11
Results obtained indicate that the ability to reduce oil uptake in this product decreases in the following order: gum Arabic>carrageenan>gum karaya>guar gum>carboxymethyl cellulose>hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose.
Hydrocolloids such as xanthan, gum ghatti, gum tragacanth, and locust bean gum were found to be ineffective (<10% reduction in oil content), Annapure et al.,12
Ferrero et al.,13 used methylcellulose (MC) and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) in coating formulations to reduce the oil uptake in deep-fat frying potato strips. MC coatings were more effective in reducing oil uptake than HPMC ones. The effect of plasticizer addition (sorbitol) was also evaluated. The best formulations were 1% MC and 0.5% sorbitol for fried potatoes. For these formulations, oil uptake reduction was 40.6% for potato strips compared to the uncoated samples. Non-significant differences in texture of coated and uncoated samples were observed.
Materials
Methods
Immersion treatments were as follows
Spraying treatments were as follows
The results presented in Table 1 show that CMC immersion resulted in reduction of oil uptake in fried falafel balls of 25.2% compared by 14.2% attained by the spraying treatment.
|
Control |
CMC Immersion |
CMC Spraying |
Pectin Immersion |
Pectin Spraying |
Gum Arabic Immersion |
Gum Arabic Spraying |
Average Oil Content |
21.80% |
16.30% |
18.70% |
* |
18.40% |
* |
* |
Average Oil Decrease |
- |
-25.20% |
-14.20% |
* |
-15.60% |
* |
* |
Table 1 CMC immersion resulted in reduction of oil uptake in fried falafel balls of 25.2% compared by 14.2% attained by the spraying treatment
*: Couldn’t be analyzed due to technical problems and foaming related to its nature.
Spraying with a pectic dispersion, while it would be impractical to adopt at present time, showed results that were very close to CMC spraying treatment (Figure 3).
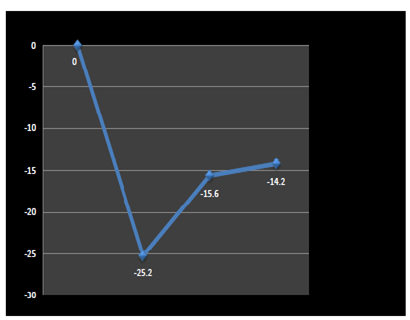
Figure 3 % oil uptake reduction in three treatments.
0%: Control; -25.2%: CMC immersion; -15.6%: Pectin spraying; -14.2%: CMC spraying
The mechanism of action of hydrocolloid derivatives is attributed to formation of an oil resistant barrier film, an alteration in surface hydrophobicity of the product being fried, and the thermal gelation.
To all who participated and gave a hand to make this project possible……Tony D. Abdullah February 2009.
Author declares that there is no conflict of interest.

©2015 Abdullah. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.