Journal of
eISSN: 2574-8114


Research Article Volume 11 Issue 3
1Department of Fashion Design & Technology (FDT), Sonargaon University (SU), Bangladesh
2Department of Apparel Manufacture & Technology (AMT), Sonargaon University (SU), Bangladesh
Correspondence: Md. Ahshan Habib, Department of Fashion Design & Technology (FDT), Sonargaon University (SU), Dhaka, Bangladesh
Received: June 22, 2025 | Published: July 3, 2025
Citation: Habib A, Rahaman S, Adnan MAR. Understanding consumer demand and merchandising strategies for knit basics in the RMG industry of Bangladesh. J Textile Eng Fashion Technol. 2025;11(3):158-165. DOI: 10.15406/jteft.2025.11.00418
This study sheds light on the current state of Bangladesh’s knitwear industry in relation to consumer demand, merchandising, sustainability, and issues facing micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs). Prime among the findings are that price, comfort and quality continue to be the primary consumer demands, and that sustainable production is beginning to emerge, especially in export markets. Timely sampling, cost management, and quality control as well as branding and effective merchandising all play a significant role in enhancing global competitiveness. The study also finds an increasing application of technologies such as 3D virtual design, as well as predictive modeling with AI, to help more efficient and sustainable product development. MSMEs face challenges in accessing finance, branding opportunities and digital infrastructure and therefore are behind on leveraging such innovations. Nevertheless, the implementation of circular economy practices is still scarce. The research ultimately points towards the role of innovation and technology accessibility for the country’s MSMEs as a way to remain ahead and points to the need for supportive policies that focus on inclusive and environmental sustainability within the sector as imperative for achieving sustainable growth for the knitwear industry in Bangladesh.
Keywords: RMG industry, knit basics, consumer demand, merchandising, MSME challenges, sustainability, export marketing, digital transformation, technological innovation
Background
The Ready-Made Garments (RMG) industry is the backbone of Bangladesh’s economy, contributing over 81.29% in the year of 2023/2024 and 84.21% in year of 2018-19 the country’s total exports and providing employment to more than four million people.1 Within this sector, knit basics such as T-shirts, tank tops, undergarments, leggings, lightweight sweaters, and loungewear form a significant segment, offering both domestic and international market opportunities. The industry’s rapid growth over the past decades has positioned Bangladesh as a global leader in knitwear exports, with the knitwear segment alone adding up to 19282.15 million USD in the year of 2023-2024 whereas total export Bangladesh's Apparel Export to World 36151.31 Million USD.1 Figure 1 the blue line & Dots illustrates the export value of Ready-Made Garments (RMG) sector from Bangladesh, reflecting a regular rising trend over the years. The green line and cross represents the total export earnings of the country, covering all sectors. The red dotted line and squares shown the percentage share of RMG in total exports, emphasizing the sector’s dominant role in Bangladesh’s export economy.
However, this growth is convoyed by growing consumer demands, shifting global fashion trends, and increasing competition, demanding a deeper understanding of consumer behavior and effective merchandising strategies. Price, style, comfort, quality, availability, and other attentions all play a part in Bangladesh's rising consumer demand for knit necessities. Due to the fact that various consumer groups have different tastes and purposes, demographic and psychographic segmentation also has an impact on purchase decisions.2 Because customers are seeking out new designs and trends every few weeks due to the growth of micro-seasonal fashion and styles, conventional seasonal cycles have been disrupted, forcing manufacturers to rapidly adjust to fast shifting consumer tastes.3 Additionally, there is a growing segment of consumers who value eco-friendly and sustainable apparel, although their purchasing behavior is often constrained by price sensitivity and limited product availability.4,5
Knitwear Merchandising Strategies in a Vibrant Market to remain competitive, RMG manufacturers and retailers in Bangladesh have adopted a range of merchandising strategies. These include diversifying product offerings, investing in technology and innovation, and enhancing sustainability practices to meet both domestic and international markets consumers.3,5 Market segmentation and targeted fashion marketing strategies are crucial for capturing different consumer segments and expanding market share, both domestically and globally.2 The adoption of digital marketing platforms and the alignment of product quality and affordability with consumer expectations have emerged as key drivers of success.5 Sustainability has become a major concern in the knit wear industry and it is motivated by increasing consumer awareness and international demand for ethical products.4 While a significant percentage of consumers express positive attitudes toward environmentally sustainable products, actual purchasing decisions are often influenced by cost, price and quality considerations.5 The integration of sustainability into merchandising strategies presents opportunities for brand differentiation and long-term profitability.5
The RMG industry in Bangladesh has shown outstanding growth. Nonetheless, it faces several encounters, including infrastructure limitations, skill shortages, and the need for improved productivity and market and product diversification.6 The pressure to deliver high-quality products quickly and efficiently, especially in response to micro-seasonal fashion trends, requires ongoing investments in technology, supply chain management, and workforce training.3 Addressing these challenges through cooperative efforts and positive branding is essential for sustaining the industry’s competitive edge.6 Market segmentation is essential for understanding and meeting consumer demand for knit basics.2 By identifying and targeting specific demographic and psychographic segments, businesses can design their product offerings and marketing messages to better align with consumer preferences.2 This approach not only improves customer satisfaction but also increases the effectiveness of merchandising strategies in both domestic and international markets. The digital transformation of the RMG industry has opened new avenues for engaging consumers and streamlining merchandising operations.5 The use of digital marketing platforms enables businesses to communicate their sustainability efforts, showcase new product lines, and respond rapidly to changing consumer trends.5 By utilizing market segmentation, embracing sustainability, and investing in digital innovation, industry stakeholders can navigate the challenges of a dynamic market and capitalize on emerging opportunities. The integration of consumer insights into merchandising practices will be key to sustaining growth and maintaining Bangladesh’s position as a global leader in knitwear exports.
Rationale of the study
The RMG sector is Bangladesh’s most important industry; it is the principal sector of the economy, and Bangladesh is an internationally well-known exporter of knitwear products. Knit basics, including t-shirts, tanks, underpinnings, leggings, lightweight sweaters, and loungewear, are particularly popular in both local and international markets within this category. But, consumer preferences based on affordability, quality, style, sustainability, and the rise of micro-seasonal trends are changing fashion retail and merchandising practices. But, little is known about consumer demand or merchandising techniques for knit basics in Bangladesh. Especially in micro small and medium enterprises (MSMEs), the sub-sector experiences issues with price sensitivity, infrastructure gaps, and low awareness of sustainable fashion, often without access to more modern tools and insights into the market. This study seeks to overcome these gaps by conducting a secondary data analysis looking at consumer behavior, the influence of sustainability on purchasing, and the effectiveness of merchandising strategies specifically digitally and segmenting. The findings can help to develop more conscious, customer oriented and sustainable practices that will improve Bangladesh’s competitiveness in the global market for knitwear.
Research objectives
Literature review
Overview of Bangladesh’s RMG sector and the rise of knit basics
The Ready-Made Garments (RMG) industry is a cornerstone of Bangladesh’s economy, contributing more than 81.29% to export revenues and employing millions, with a significant proportion being women.1 Bangladesh’s knitwear sector or knit basics, particularly in essential items like different kind of T-shirts, tank tops, and leggings, dresses and under garments has experienced exceptional growth driven by production efficiency and rising global demand for knitwear’s. Figures 2–5 depicts a collection of knit basics flat sketches showcasing a variety of knits basics/garments including tank tops, t-shirts, sweatshirts, leggings, jackets, knit dresses, under garments and shorts.

Figure 2 A collection of basic knitwear flat sketches (Collected by the author from Barnali Textile & Printing Industries Pvt. Ltd.)

Figure 3 A collection of basic knitwear flat sketches (Collected by the author from Barnali Textile & Printing Industries Pvt. Ltd.).

Figure 4 A collection of basic knitwear flat sketches (Collected by the author from Barnali Textile & Printing Industries Pvt. Ltd.)

Figure 5 A collection of basic knitwear flat sketches (Collected by the author from Barnali Textile & Printing Industries Pvt. Ltd.).
Knit garments now serve as a vital segment of both domestic and international apparel markets. According to BKMEA, knitwear exports increased from US$12.05 billion in FY 2013–14 to US$25.74 billion in FY 2022–23, with an average annual growth rate of 10.23%. Figure 6 Bangladesh’s Apparel Export to the World, illustrates the export value of ready-made garments into two segments; woven garments (blue line) and knit garments (orange line) as well as total RMG (green line indicates the total export value calculated by adding the values of woven and knit garments). The data set is in million USD and follows the calendar year from 1993 to 2024. Knitwear has started to close the gap with woven garments since 2010 and in fact exceeded them in a couple of years, like 2021 and 2022. This trend reflects not only the growing world demand for knitwear but also it is shows a growing of production and efficiency of the knit sector. Over the last three decades the export of RMG from Bangladesh has exponentially grown, particularly knit garments that at some points has even exceeded the export value of woven garments.
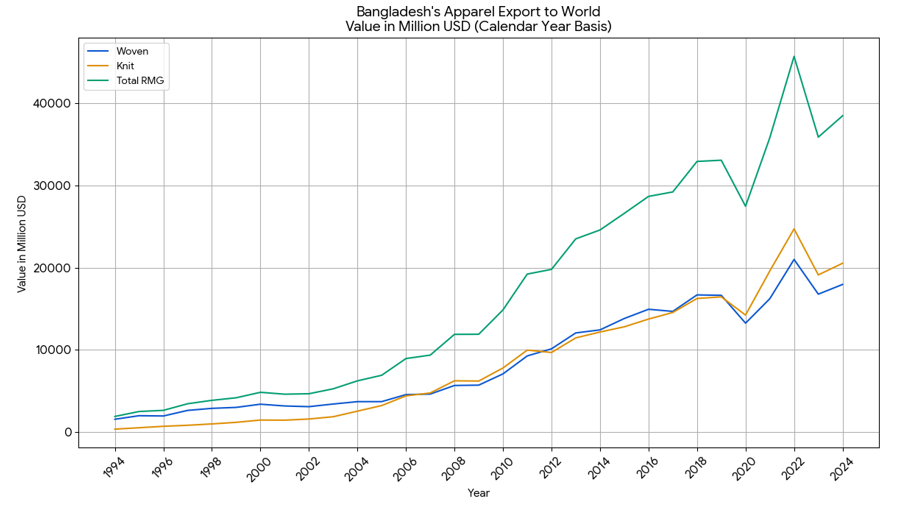
Figure 6 Bangladesh’s Apparel Export to the World presents the export values of three categories: woven garments (blue line), knit garments (orange line), and total RMG exports.
For over two decades, the sector has been central to Bangladesh’s economy, now representing the largest export-earning segment. In FY 2022–23, it contributed 5.67% to GDP and accounted for 46.34% of national exports. The sector also supports forward linkages such as banking, insurance, and logistics. Since the late 1970s, knitwear manufacturing has generated 1.9 million direct and 0.5 million indirect jobs. It has significantly contributed to poverty alleviation, reducing national poverty by 9.10% in FY 2022–23. Notably, women constitute 65% of the workforce, most of whom come from underprivileged backgrounds, promoting economic empowerment and inclusive development. A key strength of the sector is its robust backward linkage, enabling a vertically integrated production process from cotton to finished garments. This system contributes to 75% domestic value addition and enhances Bangladesh’s competitive position in the global market. Several factors further reinforce this advantage: high-quality diversified products; duty- and quota-free access to markets such as the EU, Canada, Australia, and Japan; and increasing capacity in the woven sector. The industry is characterized by socially and environmentally compliant, child labor free factories certified by ISO, WRAP, OKETEX, and others. Sustainability initiatives include green factory practices, clean production mechanisms (CPM), quality assessment processes, and compliance with global labor and safety standards set by ILO, ACCORD, and ALLIANCE positioning Bangladesh as a global leader in responsible apparel manufacturing. Most factories were inspected by Bangladesh University of Technology and Engineering (BUET), thus ensuring structural safety for the importers of the world.7 Specific Advantages of Knitwear Sector of Bangladesh: Knitwear is a self-sufficient sector in all respects; currently, the sector is supplying 90% of the knit fabric requirements. Local yarn suppliers provide a large sum of yarn demand for the industry. Many garments have their dyeing and finishing units. A separate dyeing and finishing industry also has grown up over the time to support the sector More than 200 composite factories. Bangladeshi Knitwear is almost unbeatable in price advantages in the world. Bangladesh provides not only a cheap labor force in respect to other competitive countries, which is unbeatable but also they are peerless in stitching capability. Knitwear is exported to 157 countries of the world. Strong backward linkage facilities. A long experience of apparel business and a created value chain across the globe. More than 2100 knitwear factories.7,8 These attributes have made knitwear the preferred category among fast fashion retailers.
Understanding consumer demand for knit basics
Consumer purchasing behavior for knit garments is shaped by price sensitivity, quality assurance, comfort, and growing interest in sustainability. An emerging dimension in demand patterns is sustainability. Bangladesh’s apparel exports to the European Union began 2025 with a remarkable 60.9% increase, reaching €1.91 billion in January, compared to €1.19 billion in the same month a year ago.9 Of these, knitwear exports surged by 64.2%, while woven apparel exports increased by 56.3%, according to data from Eurostat, the statistical office of the EU, released on Tuesday (20 March). In terms of quantity, Bangladesh's readymade garment exports to the 27-nation economic bloc also witnessed a substantial surge in January 2025, increasing by 58.1% to 126.86 million kilograms from 80.25 million kilograms in the same month of the previous year. This strong growth solidifies Bangladesh's position as a key supplier to the European market, driven by competitive pricing, preferential trade facilities under Everything but Arms, and improvements in production capacity. The overall growth has been driven by increased capacity, efficiency, and productivity. Bangladesh remained the second-largest apparel exporter to the EU after China.9 Bangladesh’s apparel exports to the EU are dominated by knitwear items under the Harmonized System (HS) of product classification category 61, accounting for a share of about 57 per cent in 2017.10 About 21 per cent of total knitwear shipped from Bangladesh was destined for Germany in FY2018, followed by 12.5 per cent to the UK .Slightly less than 10 per cent is exported to the USA. While Bangladesh is developing capacity in making relatively high-priced garment products sold by many global brands, until now it has mainly been known as a source of low-cost garment items in bulk.10 Comfort and fabric feel also rank high among consumer considerations. Knit basics are favored for their stretch ability and breathability, particularly in tropical climates .Additionally, the rising influence of social media on fashion choices has increased the visibility and desirability of minimalist, functional knit garments.
Merchandising strategies in the knitwear segment in Bangladesh
The knitwear sector of the Bangladesh textile industry is very competitive and export oriented, necessitating effective merchandising in order to prepare products according to international merchandising standards, satisfy customers, and remain profitable. Merchandising entails aspects such as cost, quality control, delivery, and responding to market trends.
Core merchandising strategies
Sample development & approval: Timely development of samples is key both to securing bulk orders as well as to meeting the expectations of foreign buyers. Merchandisers must also ensure technical accuracy while minimizing the cost of production and speed is especially of the essence in the production of kids’ and ladies’ knitwear because of the tight deadlines imposed by customers.11
Quality control & timely delivery: Successful merchandising also tends to rely on high quality control and on-time delivery. While sometimes complicated by the changing prices of raw materials and labor struggles, this type of work engenders customer loyalty and repeat business.12
Cost-effective sourcing: Exploring alternative sourcing options for raw materials and implementing advanced technologies for production monitoring can help control prices and improve productivity.12
Marketing and consumer-focused approaches
Market segmentation: Understanding local and international customer segments allows for targeted marketing and product development. Demographic breakdown and promotion of local textile trade can help expand market share.2
Visual merchandising: In retail settings, visual merchandising elements such as store design, product display, and window design significantly influence customer buying behavior and can attract new clients.13
Brand identity & innovation: Creative merchandise offerings, exclusive product collections, and innovative strategies for example themed collections, storytelling, and exclusivity can help strong consumer-brand relationships and enhance brand loyalty.14
Sustainability and green practices
Sustainable merchandising: Integrating sustainability into merchandising through environmental friendly materials, recycling, and responsible production can expand brand competitiveness and appeal to environmentally sensible buyers.15,16
Green business strategies: Adopting green business practices not only reduces environmental impact but also provides a competitive edge in the global market.16 In terms of merchandising, the Bangladesh knitwear industry specializes in fast sample turn-around; tight quality control; cost control; market segmentation; and sustainability. They all provide competitiveness, consumer matching and adaptation to global trends for the products. More importantly, they contribute to the export growth of knitwear by affecting product quality, expanding markets, and improving customer satisfaction. Another area with a direct link to export performance in the sector is merchandising and marketing.
Key influences of merchandising strategies
Market research & segmentation: Exporters who invest in market research and segment their customers, are able to better match their products with international buyer preferences, and become more competitive and increase their exports. This strategy enables them to recognize market trends, customize offers, and form better relationships with buyers in the global market.2
Branding & promotion: Units that develop their own brands or engage in marketing activities such as trade fairs, and international certification, tend to be more visible and credible in global markets. This increased reputation will help not only buyer´s confidence to procure from this source, but it also plays an important role in more stable and continued export growth.
Buyer-merchandiser relationships: Buyer-merchandiser communication and faith, along with effective production quality checks and visual merchandising, are also critical to successful export. They help assurance that product quality and delivery times will be consistent and that the product will meet buyer expectations, which can strengthen future trade relations.17
Continuous learning & innovation: Ongoing learning from international markets, adoption of new technologies, and organizational improvements help knitwear exporters adapt to changing demands and sustain long-term growth.18
Integrated marketing strategies: Combining traditional marketing with innovative approaches such as creative merchandise offerings, unique product assortments, and storytelling strengthens brand identity and attracts international buyers.14 Merchandising plays a vital role in growing new knitwear exports by enabling exporters to understand market demand, build a strong and consistent brand image, and substitute long-term buyer relationships. When applied together, these strategies help knitwear exporters realize sustainable international growth and maintain a competitive advantage in the global market.
Knitwear export marketing strategies
Export marketing is vital for the success of knitwear firms exporting to competitive international markets. Through exploring insights derived from the case studies research surfaces common strategies including branding, certification, digitization, and market segmentation that amplify international presence, deepen buyer relationships, and foster export expansion.
Branding and certification
Brand Ownership vs. Private Label: Branding strategies vary significantly across regions. For example, in Ludhiana, most knitwear exporters own their brands, whereas in Tirupur, the majority focus on producing for buyers’ brands or private labels, showing less interest in developing their own brand identity.19
Certifications: Obtaining international certifications such as ISO 14000 and OekoTex Standard-100 is a common strategy used by knitwear exporters to build credibility and fulfill with buyer requirements in global markets. These certifications increase trust, prove obligation to quality and sustainability, and often open doors to new business opportunities.19
Promotion and market entry
Trade Shows and Events: Participation in seminars, meetings workshops, and international trade shows is a top tactic for gathering market intelligence and connecting with buyers. These events facilitate networking, help understand emerging trends, and enhance business opportunities in global markets.
Promotional budgets: Exporters allocate different levels of budget to promotional activities, with some investing heavily to boost visibility and expand their market reach. Such investments often lead to stronger brand recognition and improved access to international buyers.19
Digital marketing: The use of web existence and e-commerce platforms allows knitwear exporters to overcome traditional obstacles, reach new markets, and connect directly with international buyers.21
Market research and segmentation
Investment in market research: Many exporters share part of their export sales revenue to market research, enabling them to better understand buyer likings, track market trends, and categorize new business opportunities. This investment supports more informed decision-making and enhances their competitive position in global markets.2
Consumer segmentation: Demographic and market segmentation strategies allow exporters to supply product and promotional efforts to particular groups of international consumers, improving relevance and capturing share of the market. Attention on specific niches helps to satisfy diverse customer needs and increases competitiveness.2
Value-added services and innovation
Full-service models: Major exporters also add value to overseas retailers by offering design, sourcing materials, finishing, and logistics as full-service private label contracts. This full package approach also strengthens client relations and competitiveness in global markets.21
Innovation and adaptation: Knitwear exporters who have been successful, focus on product design, technology and are sensitive to and anticipate changing market demand. Their marketing approaches generally combine branding, certifications, presence at fairs, market investment research, segmented markets, online marketing, and value added services. Collectively, these approaches construct credibility, help flexibility, and extend global reach resulting in gradual increases in exports and competitive advantage over the long term.
The role of MSMEs and challenges in knit garment merchandising
Micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) form the essence of production, employment and innovation within the Bangladesh knitwear value chain. As subcontractors to local brands or larger exporters, they suffer from weak strategy planning, lack of funding, low supply chain visibility and minimal merchandising skills. These problems stunt their development and competitiveness in the global market.22 In the knitwear industry in Bangladesh, MSMEs tend to respond to trends rather than anticipate them due to a lack of official trend reports and market research. Branding, packaging and consumer communications deficiencies also prevent them from charging higher prices. But, the use of digital platforms, particularly e commerce platforms relevant for knitwear MSMEs has been successful in widening markets, managing products and facilitating transactions to increase competitiveness and business performance.23 virtual exhibitions and online marketing becoming vital alternatives for product promotion and customer engagement.24 These helps MSMEs stay relevant during the disruptions and improve their digital literacy for business purposes. In the end, ingenuity in marketing, using technology and the capacity to respond to market changes are critical for MSMEs to succeed in knitting apparel merchandising.23
Sustainability trends in knitwear merchandising
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a focus of the knit merchandising industry in Bangladesh due to environmental, economic, and social concerns. Additional trends include minimizing environmental impact and green business practices and resource efficiency as well as placing technology at the center of developing more sustainable and less opaque supply chains. The knitwear sector faces its greatest sustainability challenges in environmental areas, such as pollution, resource use, and waste management, with environmental vulnerability rated higher than economic or social concerns.25 Water and energy consumption, as well as greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, are major concerns. Cotton processing, yarn spinning, and wet treatments are particularly high in carbon emissions, while water use in dyeing is substantial but can be reduced through improved processes and technology.26 Sustainable Practices and Innovations covers the Green Business Strategies, Adoption of green business models and corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives is increasing, providing competitive advantages and aligning with global buyer expectations.16 Circular Economy and Design is a growing emphasis on circular design, sustainable manufacturing, and life cycle assessment to minimize waste and promote reuse and recycling.28 Industry 4.0 Technologies is Advanced digital technologies, green supply chain management, and circular economy practices are being integrated to enhance sustainability performance across the supply chain.28
Technological innovations in knit merchandising
The use of 3D virtual technology is streamlining and enhancing the accuracy and creativity of knit merchandising, design, and production. Knitted fabrics can now be realistically simulated, seen and assessed from a design perspective using advanced simulation technology. This simplifies the design and approvals process, lessens the dependence on physical samples and speeds time to market.29,30 3D virtual technologies are changing knit merchandising and helping to eliminate waste by allowing for body scans and digital knitting. The digital designs are then quickly and easily processed into seamless, knit structures through automation. Online 3D visualization tools help speed and collaboration across disciplines. Combined, they increase efficiency, creativity, and sustainability, and redefine the future of knitwear design.29 Digital transformation is changing the merchandising of knitwear via technologies like 3D visualization, virtual sampling, and AI trend forecasting. These tools are now commonplace in developed markets, as they minimize fabric waste, quicken product development time, and allow for more accurate product targeting to consumers.
Research design
The following study utilizes a qualitative research design, primarily sourced from secondary data examining consumer demand and selling strategies for knit basics within Bangladesh’s RMG industry. The methodology calls for a study of current market papers, scholarly writings, business case studies and sustainability reports to help understands changing consumer behavior and merchandising practices.
Data sources
Secondary data will be collected from a variety of reputable sources. Selection criteria include credibility (e.g., peer-reviewed or institutionally published), relevance to the knitwear and RMG sectors preferably within the past 2-3 decades, and contextual alignment with Bangladesh’s apparel industry. These criteria ensure the data used is both reliable and meaningful to the research objectives.
Sources will include:
Data analysis
Collected data will be systematically reviewed using thematic content analysis. This involves thoroughly reading and coding relevant information from secondary sources, then grouping similar codes into key themes. Thematic analysis will help identify:
Through this structured process, the analysis will highlight successful practices, existing challenges, and opportunities for improvement in current merchandising approaches, providing practical insights for industry stakeholders.
Limitations
Since this research uses secondary data, the results can be limited to what is found or reported in existing literature and documents. Future studies could further supplement this by gathering primary data to gain deeper consumer insights.
Knitwear’s expanding role in Bangladesh’s RMG sector
The analysis confirms that knitwear has become a leading segment of the ready-made garments industry in Bangladesh due to solid backward linkages, cost advantages, and growing international demand for casual and comfortable apparel. Also, exports of knitwear have been growing at twin digit numbers thanks to vertically integrated production with preferential treatment on exports. It is also a substantial contributor to GDP as well as employment, and has interesting implications for the economic empowerment of women.
Consumer behavior and market orientation
Knit basics are mostly driven by the affordability and comfort and overlook the quality of the fabric. Sustainability is starting to become an important buyer’s preference issue, especially in major export markets such as the European Union. Knitwear is lightweight, stretchy, and breathable, making it ideal for hot, tropical weather, while minimalist aesthetics promoted on social media have grown in popularity among urban consumers.
Merchandising strategies and competitive advantage
Merchandising activities such as sample-making in a timely manner, quality control, sourcing at competitive prices and delivering on time are essential for remaining competitive. Firms also aim to enhance buyer satisfaction and loyalty through visual merchandising, market segmentation, and brand positioning and product innovation. The use of sustainable merchandising practices like greening certifications and the use of sustainable materials is presenting itself as a competitive differentiator.
Export marketing and digital engagement
Knitwear exporters gradually highlight brand development, contribution in international trade fairs, and loyalty to global certification standards. Investments in publicity activities and digital platforms have expanded global reach and improved buyer engagement. Market research and consumer segmentation enable bespoke product offerings, enhancing effectiveness and export performance.
Challenges and potential of MSMEs
MSMEs continue to play an important role in the knitwear value chain but have weaknesses in access to finance, branding, supply chain visibility, and merchandising expertise. These restrictions inhibit their participation in higher value market opportunities. Digital platforms and e-commerce also present new opportunities for MSMEs to organize production and connect with buyers and market presence, with virtual exhibitions and online marketing helping to mitigate challenges during the market disruptions.
Sustainability trends in knitwear merchandising
Sustainability is becoming a priority but varies in its implementation. Issues like water and energy use, waste production, and greenhouse gas emissions, continue to plague these crops. But, there is increasing uptake of circular designs, cleaner production processes and corporate social responsibility practices that bring the sector in line with regulatory and global buyer standards.
Technological innovations and digital transformation
Digital sampling, 3D virtual design and AI forecasting have the potential to transform merchandising, pulling back even further on physical samples, shrinking time to market, and decreasing waste. Although the digitalization process is mainly driven by large companies, as a result of resources and technical capabilities available to them, MSMEs also find themselves in need of targeted support and digitalization capacity building.
It finds the Bangladesh knitwear industry to be an important component of the Ready-Made Garments, or RMG, sector that has spurred export growth, economic development and job creation in Bangladesh, especially for women. This can be attributed to competitive prices, good backward linkages and increasing global market for this product. But consumer preferences especially in key export markets such as the EU are changing as sustainability is gaining as one of the purchasing factors along affordability, comfort, and quality.
In order to compete these changes will require the industry to move away from a low cost high volume industry and towards product differentiation, innovations and branding. Merchandising practices are also fundamental; timely development of samples, quality control and costing continue to underpin competitiveness. But, changing demands also call for greater visual merchandising, brand positioning, and even digital engagement, as these have become necessary for market differentiation and appealing to buyers.
Larger businesses have made progress in both but MSMEs face a number of barriers that exclude them from engaging in these changes within the sector. Their financial constraints limit them from investing in new technologies or more sustainable modes of production. Also, MSMEs are not skilled in branding and digital marketing, which restricts them from conveying value to buyers around the world. Access to advanced technologies such as virtual 3d design, and AI powered forecasting is low, resulting in a widening technology gap that threatens to leave MSMEs behind from higher value and more sustainable market segments.
The results highlight the need for MSME empowerment programs. Capacity building programs in digital merchandising, sustainable production practices and branding development are key. Collaborative efforts in technology hubs or industry clustering could help MSMEs to overcome the scale challenges and achieve affordable access to innovation and possibly to market intelligence. Policy support plays a crucial role in enabling these changes. Government and industry bodies should prioritize subsidized access to digital tools and sustainable technologies for MSMEs, alongside dedicated training and green financing options. Incorporating MSMEs into national digitalization and circular economy strategies will foster more inclusive growth and improve the overall sustainability and competitiveness of Bangladesh’s knitwear sector. By addressing these challenges, the industry can ensure that MSMEs remain active contributors to export growth and economic empowerment while aligning with global sustainability goals.
This study firmly establishes the pivotal position of the knitwear industry in Bangladesh’s RMG sector as a leader of export growth, economic development and employment for women. Though cost competitiveness and good backward linkages remain important pragmatically speaking as a characteristic of the industry, in terms of global markets and consumer trends, preferences are shifting toward sustainable practices in addition to affordability, comfort and quality. In order to remain competitive the industry needs to embrace product differentiation and innovation and branding. Other key challenges for MSMEs is the lack of access to funds, branding know-how, and technological advancements like 3D design and AI-based forecasting. Without targeted support these barriers risk excluding MSMEs from value-added activities and sustainable transformation. Growth of MSMEs will thus need support in the form of policy. This includes subsidized access to digital and sustainable technologies, training on branding and merchandising digitally, and green finance initiatives. Incorporating MSMEs into national digitalization and circular economy programs, will help foster more inclusive and sustainable development. If these challenges are met and MSME’s are strengthened in a deliberate manner, Bangladesh’s knitwear industry has the potential be more competitive in the global market; as well as inclusive and sustainable in its growth.
None.
None.
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.

©2025 Habib, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.