
Research Article Volume 1 Issue 2
Self sustained oscillations for square cavities at yaw
Kuan Huang Lee,1 Keh Chin Chang,1 Kung-Ming Chung2
Regret for the inconvenience: we are taking measures to prevent fraudulent form submissions by extractors and page crawlers. Please type the correct Captcha word to see email ID.

1Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan
2Aerospace Science and Technology Research Centre, National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan
Correspondence: Kung Ming Chung, National Cheng Kung University, 2500 Section 1, Chung-Cheng South Road, Guiren district, Tainan, 711, Taiwan
, Tel 886-62392811
Received: July 20, 2017 | Published: August 22, 2017
Citation: Lee KH, Chang KC, Chang KM. Self sustained oscillations for square cavities at yaw. Aeron Aero Open Access J. 2017;1(2):76-79. DOI: 10.15406/aaoaj.2017.01.00010
Download PDF
Abstract
An experimental study was conducted to determine the characteristics for a compressible turbulent flow over square cavities at yaw. Flush-mounted dynamic pressure transducers for mean and fluctuating pressure measurements were installed along the chordwise direction. The self-sustained oscillation phenomenon was examined by spectral density function. For a fixed yaw angle, the ratio of the incoming boundary layer thickness to the depth of the cavity has an evident influence near the rear corner of cavity, including the trailing-edge expansion and the maximum pressure fluctuations.
Keywords: yawed cavity, self-sustained oscillations, pressure fluctuations, critical length, transitional cavity, mach number, gaussian distribution
Introduction
Cavities that are exposed to surface bounding flows are of high interest in both fundamental aspects and engineering applications due to the inherent complex flow structure and induced drag. Self-sustained oscillations lead to fluctuating load on airframes and generate enormous noise. Lawson & Barakos1 reviewed the numerical simulations on cavity flows from 1955 to 2009. Cavity flows are influenced by free stream conditions and cavity geometry. The most remarkable parameter is the ratio of length to depth, L/H. Charwat2 showed the critical length of a cavity flow, which is the length between the leading edge of the cavity and the attachment of shear layer, is dependent on the state of incoming boundary layer (laminar or turbulent). For a shallow cavity, Plentovich et al.3 found that there are three types of cavities, namely, an open, a transitional or a closed cavity. For supersonic cavity flows, a transitional cavity can be further split into a transitional-open or a transitional-closed cavity. In addition, for a compressible flow, the boundary between an open and a transitional cavity is at L/H of 8–10 and that between a transitional and a closed cavity is at L/H of 9–14 .4,5 The critical L/H for a transitional cavity decreases as L increases and is more apparent for higher M
For an open cavity, the flow essentially bridges the cavity and a shear layer is formed over the cavity. There is an almost uniform distribution of static pressure along the cavity floor. The impingement of the shear layer on the rear wall of the cavity leads to high fluctuations and acoustic tones.6 A yawed rectangular cavity means the flow are parallel to the planform of a cavity, but the chordwise direction of the cavity has an angle,
, with respect to the freestream direction.7 An asymmetric flow pattern inside the cavity was observed.8 Lada & Kontis9 showed the yaw angle either disturbs the shear layer or changes the flow type, resulting in attenuation of self-sustained oscillations. The incoming boundary layer thickness to depth ratio,
, is another critical parameter. Increasing
could smooth out the pressure gradient near the rear corner of a cavity.2 The effect of
was also noted by Sinha et al.10 A laminar incoming boundary layer generates strong vortex inside the cavity and the vortex is a more localized phenomenon near the rear face.11
Experiments were conducted to characterize a compressible turbulent flow for square cavities at yaw. The effect of
on the chordwise distribution of the mean and fluctuating pressure is determined. The distribution of the power spectral density near the rear face is also reported to characterize self-sustained oscillations.
Experimental setup
Experiments were conducted in the blowdown type transonic wind tunnel at Aerospace Science and Technology Research Center, National Cheng Kung University (ASTRC/NCKU). The tunnel has a constant area test section of 600 × 600 mm2 and 1500 mm in length. The test section is assembled with solid side walls and perforated top/bottom walls. The freestream Mach number, M, is 0.64, 0.70 and
, and the corresponding unit Reynolds number is 12.9, 15.1 and 17.2 × 106 per meter, with a naturally developed turbulent boundary layer over a flat plate. The stagnation pressure p0 and stagnation temperature were maintained at
kPa (25
0.15 psia) and room temperature, respectively. The boundary-layer thickness,
, at 25 mm upstream of the cavity was approximate 7 mm.12
The test model consisted of a 4° sharp leading-edge flat plate and an interchangeable instrumentation plate, as shown in Figure 1. The flat plate was 450 mm × 150 mm and was supported by a single sting that mounted on the bottom wall of the test section. The instrumentation plate with a square cavity was 195 mm × 150 mm × 25 mm. For a fixed yawed angle
, the geometry of cavities is summarized in Table 1. The length was 31, 43, 59 mm and the depth ranged from 2.2 to 9.7 mm, corresponding to L/H of 4.43-21.50 and
of 0.73-3.50.
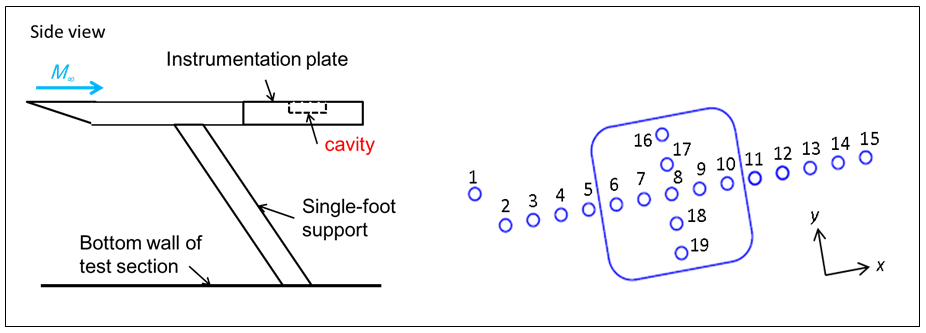
Figure 1 A schematic drawing of test configuration and location of pressure transducers.
Cavity |
L, mm |
H, mm |
L/H |
|
1 |
31 |
5 |
6.2 |
1.4 |
2 |
2.2 |
14.09 |
3.18 |
3 |
43 |
9.7 |
4.43 |
0.72 |
4 |
7 |
6.14 |
1 |
5 |
5 |
8.6 |
1.4 |
6 |
3.5 |
12.29 |
2 |
7 |
3 |
14.33 |
2.33 |
8 |
2 |
21.5 |
3.5 |
9 |
59 |
9.6 |
6.15 |
0.73 |
10 |
4.2 |
14.05 |
1.67 |
Table 1 Geometry of the square cavities.
Dynamic surface pressure (Kulite XCS-093-25A, B screen) measurements were conducted for the cavity models. The outputs of the pressure transducers were recorded by using a National Instruments (NI-SCXI) system, with a sampling rate was
. The uncertainties for the static surface pressure coefficient Cp and the surface pressure fluctuation coefficient
were 2.4% and 0.4%, respectively.
Results and discussion
The effect of yaw angle on chordwise pressure distributions is shown in Figure 2 where M = 0.83 and L/H = 4.43 and 8.60. For a given value of L/H, there is less expansion near the rear face when
. Lee et al.7 also indicated that the yaw angle has an evident effect on the amplitude of
near the rear face for open and transitional cavities. Regarding the effect of δ/H on square cavities at yaw, Figure 3 presents the results of mean surface pressure of open and transitional cavities for M = 0.83 in chordwise direction. For the open cavities (Figure 3(a)), little variation is observed upstream and along the floor of the cavity. Increasing
results in a suppression of trailing edge expansion downstream of the cavities. For the transitional cavities (Figure 3(b)), despite the existences of suppressions downstream of the cavities as
increases, the values of Cp along the rear half of the cavity (x/D = 0.5–1.0) for
are higher than those for
and 3.18. Figure 4 shows the variations in trailing-edge expansion with
for square cavities at yaw. For both open and transitional cavities, the expansion downstream of the cavities is suppressed by increasing
. Note that the effect of Mach number is minimal.
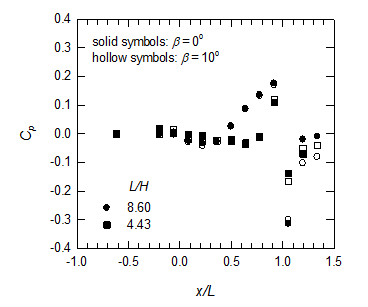
Figure 2 The chordwise static surface pressure distributions for M = 0.83 at
and
.
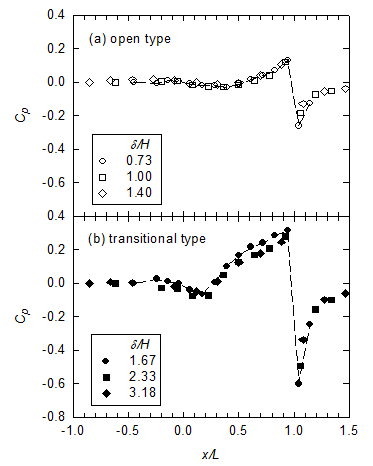
Figure 3 The chordwise static surface pressure distributions for M = 0.83.

Figure 4 Trailing-edge expansion.
Figure 5 shows the results of pressure fluctuations for the open and transitional cavities for M = 0.83 in chordwise direction. For open cavities, a similar trend is evident in the distributions of
with different values of
; in contrast,
immediately downstream of the cavities decreases as
increases. For transitional cavities, the distributions of
exhibit a similar trend with those for open cavities, and the
amplitude demonstrates a slight drop with increasing
. The effect of δ/H on
is shown in Figure 6. Increasing
tends to reduce the strength of pressure fluctuations near the rear face of a cavity. Furthermore, this phenomenon is more pronounced for open cavities at low values of M.

Figure 5 The chordwise fluctuating pressure distributions for M = 0.83.
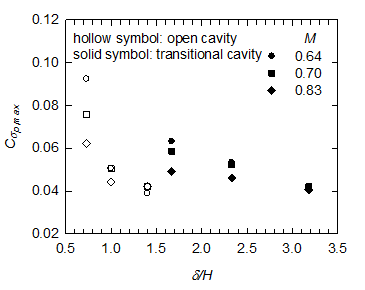
Figure 6 Peak pressure fluctuations.
Flow unsteadiness is associated with deviation of higher order moments (Skewness,
, and flatness,
, coefficients) with respect to the Gaussian distribution, in which the values of
and
are 0 and 3, respectively.13
represents the asymmetry of the probability density function and the deviation in
shows the presence of more large amplitude events. The effect of
on
and
for open and transitional cavities at x/L = 1.058 is presented in Figure 7. For either open or transitional cavities,
has a subtle influence on
. On the other hand, with increasing
, the value of
for the open cavity increases but that for the transitional cavity decreases.
at M = 0.64 and
is less than that at
, this requires further study. The variation of
with
for the open cavity is more evident at larger M.

Figure 7 Skewness and flatness coefficients at x/L = 1.058.
Periodic vortex shedding and acoustic disturbance result in self-sustained oscillations in a cavity. The distributions of power spectral density for M = 0.83 with varying
are presented in Figure 8. For an open cavity
, the peak frequencies of self-sustained oscillations decrease with increasing L. For example, the peak frequencies of the first mode are 2197, 1660, 1172 Hz for L = 31, 43, 59 mm, respectively. Although the second mode dominates for all three cases, the sound pressure levels (SPLs) of these peaks for
(L = 59 mm) are higher than those for
and 1.40 (L = 43 and 31 mm, respectively). For a transitional cavity
, both the peak frequencies and their associated amplitudes are nearly the same. However, the level of energy in low-frequency range (1000–4000 Hz) observed for
(L = 59 mm) is higher than those observed for
and 3.18 (L = 43 and 31 mm, respectively). The effect of
on the PSD distributions for M = 0.70 and 0.64 for a given L/H(≈ 6.15 and 14.05) shows a similar trend.
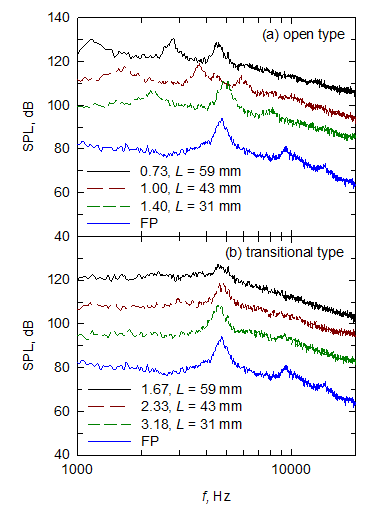
Figure 8 Power spectral density.
Conclusion
This experimental study determines the characteristics of square cavities at yaw
for a compressible turbulent flow. For a given value of M, an increase in
results in a suppression of trailing edge expansion downstream of the cavities. The effect of Mach number is minimal. Further, increasing
reduces the strength of pressure fluctuations near the rear face of a cavity and this phenomenon is more pronounced for open cavities at low values of M. For self-sustained oscillations, the peak frequencies decrease with an increase in the cavity length. The SPLs of these peaks are higher at a lower value of
.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 103-2923-E-006-006-MY3).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- Lawson SJ, Barakos GN. Review of numerical simulations for high speed turbulent cavity flows. Progress in Aerospace Sciences. 2011;47(3):186‒216.
- Charwat AF, Roos JN, Dewey FC, et al. An investigation of separated flow. Part 1. The pressure field. J Aerospace Science. 1961;28(6):457‒470.
- Plentovich EB, Stallings RL, Tracy MB. Experimental cavity pressure measurements at subsonic and transonic speeds. NASA Technical Paper. 1993;3358:1‒80.
- Stallings RL, Wilcox F. Experimental cavity pressure distributions at supersonic speeds. NASA Technical Paper. 1987;2683:1‒77.
- Tracy MB, Plentovich EB. Cavity unsteady-pressure measurements at subsonic and transonic speeds. NASA Technical Paper. 1997;3669:1‒78.
- McGregor OW, White RA. Drag of rectangular cavities in supersonic and transonic flow including the effect of cavity resonance. AIAA J. 1970;8(11):1959‒1964.
- Lee KH, Chung KM, Chang KC. The effect of yaw Angle on a compressible rectangular cavity flow. Inter J Aero Eng Article. 2017. p. 13.
- Czech M, Savory E, Toy N, et al. Flow regimes associated with yawed rectangular cavities. The Aero J. 2001;105(1045):125‒134.
- Lada C, Kontis K. Experimental studies of open cavity configurations at transonic speeds with flow control. J Aircraft. 2011;48(2):719‒724.
- Sinha SN, Gupta AK, Oberai M. Laminar separating flow over backsteps and cavities. II cavities. AIAA J. 1982;20(3):370‒375.
- Grace SM, Dewar WG, Wroblewski DE. Experimental investigation of the flow characteristics within a shallow cavity for both laminar and turbulent upstream boundary layers. Experiments in Fluids. 2004;36(5):791‒804.
- Chung KM. Investigation on transonic convex-corner flows. Journal of Aircraft. 2002;39(6):1014‒1018.
- Kim J. On the structure of pressure fluctuations in simulated turbulent channel flow. J Fluid Mech. 1989;205:421‒451.

©2017 Lee, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the,
which
permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.


