MOJ
eISSN: 2574-9773


Mini Review Volume 1 Issue 5
Sakarya University, Faculty of Technology, Turkey
Correspondence: Huseyin Unal, Sakarya University, Faculty of Technology, Esentepe kampusu, Sakarya, Turkey
Received: October 17, 2017 | Published: November 30, 2017
Citation: Unal H, Mimaroglu A, Ozel A. Friction and wear performance of glass fiber reinforced poly-ether-ether-ketone composite against different polymer counterparts. MOJ Poly Sci. 2017;1(5):188-190. DOI: 10.15406/mojps.2017.01.00030
In this study, the friction and wear performance of 30wt.% glass fiber reinforced poly-ether-ketone (PEEK+30%GF) composite materials against poly-ether-imide (PEI) polymer blend and poly-phenylene-sulphide (PPS) polymer composite materials under dry sliding condition were evaluated. Friction and wear tests were carried out on a pin-disc arrangement at the sliding speed of 0.5m/s and under 0.707, 1.41, and 2.12(N) applied loads condition. 10wt.% poly-tetra-fluoro-ethylene (PTFE) filled poly-ether-imide polymer blend (PEI+10%PTFE) and 40wt.% glass fiber reinforced poly-phenylene-sulphide (PPS+40%GF) composite counter-face disc materials were used. The results show that the coefficient of friction and specific wear rates for PEEK+30%GF polymer composites against steel, polymer blend and polymer composite material increases slightly with the increment of applied pressure values. Finally, the specific wear rates for PEEK polymer composite against PTFE filled PEI polymer blends and glass fiber reinforced PPS composite under dry sliding conditions are in the order of 10-14m2/N and 10-14m2/N, respectively. The results suggested that it is more convenient to use PEEK+30%GF composite against steel for tribological applications.
Keywords: PEEK, PEI, PTFE, polymer, wear, composite
PEI, poly-ether-imide; PPS, poly-phenylene-sulphide; PTFE, poly-tetra-fluoro-ethylene; PEEK, poly-ether-ether-ketone
In tribological applications, because of the corrosive problems of the metals in water applications, poly-ether-ether-ketone (PEEK) and its composites are preferred for rubbing materials. As it is known PEEK is a high performance semi-crystalline thermoplastic polymer and has received significant attention in recent years. This is due to its high mechanical strength and elastic modulus, high toughness, chemical inertness, high melting temperature, easy processing, and wear resistance. Therefore, poly-ether-ether-ketone polymer material plays a more important role as a bearing and sliding material.1,2 Lots of studies on the tribological properties of PEEK have been reported.3-11 Most studies published in the literature were in the friction and wear of polymers sliding against steels in dry conditions. The coefficient of friction can, generally, be reduced, and the wear resistance can be improved by selecting the right material combinations.12,13 Usually, tribological phenomena lead to a loss of mechanical efficiency. So, the accurate knowledge of the influence of applied load, sliding speed and contact temperature on the friction and wear is extremely important.14 The purposes of this investigation are to clarify the tribological characteristics of 30 wt. % glass fiber reinforced poly-ether-ether-ketone composite sliding against poly-tetra-fluoro-ethylene (PTFE) filled poly-ether-imide (PEI) blend and 40% glass fiber reinforced PPS composite under dry sliding conditions. Tribological tests versus PTFE filled PEI blend and 40% glass fiber reinforced PPS composite were carried out on a pin-on-disc arrangement. Tribological tests were at room temperature under 0.707MPa, 1.42MPa and 2.12MPa applied pressure and at 0.5 m/s sliding speed. The specific wear rates were realized from mass loss and were reported.
In this study, the pin material used is 30% glass fiber reinforced PEEK composite. The glass fiber reinforced PEEK composite with trade name Ketron GF30 is supplied by Quadrant Engineering Plastics, Istanbul. PTFE blended PEI with granule form is supplied by GE Engineering Plastics, Istanbul. PPS+40%GF engineering polymer with granule form purchased from Chevron Phillips Chemical Co. Istanbul. Samples of six mm in diameter flat-ended pins of PEEK+30%GF composite were machined by a revolver machine. The 5 mm in thickness and 100 mm in diameter disc materials that are PPS composite reinforced with 40 wt. % glass fiber and PEI blend with PTFE were produced by ordinary injection molding machine. For friction and wear tests, a pin-on-disc rig connected to a computer is used. During the tests, a transducer mounted on the loading arm measured the friction force. The readings are taken as the average of 30 readings every 60 second. For this purpose a microprocessor controlled data-acquisition system is used. Each test was carried out for a sufficient time period (33 minute) within the steady-state region. Furthermore, to ensure the reliability in the results, each test is repeated three times. After each test, the mass loss in pin was measured. The scatter in the results is small. Therefore, the average values are taken into consideration, which eliminate the essential evaluation of the sensitivity of the obtained data.
Table 1 illustrates the tribotest process parameters used in the study. Figure 1 shows the variation of coefficients of friction with contact pressure for 30% glass fiber reinforced PEEK composite against 10%PTFE filled PEI blend and 40% glass fiber reinforced PPS composite discs under dry sliding conditions, respectively. It is clear from this figure that the coefficients of friction values of 30% glass fiber reinforced PEEK composite are influenced by the change in applied pressure and different rubbing surface materials.
Process Parameters |
Experimental Conditions |
Applied pressure (MPa) |
0.707, 1.41, 2.12 |
Sliding speed (m/s) |
0.5 |
Temperature (°C) |
22±2 |
Humidity (%) |
59±2 |
Sliding distance (m) |
1000 |
Surface roughness (Ra, μm) |
0.35-0.40 |
Table 1 The test conditions from pin-on-disc tribo test
The average friction coefficient of 30% glass fiber reinforced PEEK composite rubbing against 10%PTFE filled PEI blend discs is between 0.23 and 0.30. In rubbing against 30% glass fiber reinforced PPS composite, the coefficient of friction values for PEEK composite are between 0.28 and 0.36. As seen in Figure 1, the coefficient of friction values of PEEK composite increases with the increment of applied load values against PEI blend and PPS composite materials. There are about 30% and 28% increase in coefficient of friction with the increase in applied pressure from 0.707 to 2.12 MPa for 30% glass fiber reinforced PEEK composite against PEI blend discs and 30% glass fiber reinforced PPS composite disc, respectively. It is known that tribological performance of polymer and polymer composites can be associated to their visco-elastic and temperature-related properties. It is known that the sliding contact of two materials results in heat generation at asperities and hence increases in temperature. The amount of rises in temperature is influenced by the amount of heat flow. If the increase in surface temperature is high in comparison to heat deformation temperature of the material, this influences the visco-elastic property which causes softening of the materials. This causes the rubbing of glass fibers of faced materials or fiber against polymer; therefore reflect the friction and wear performance of materials. Therefore, the increase in the coefficient of friction occurs as rubbing polymer composite with polymer composite.
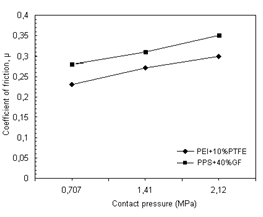
Figure 2 illustrates the variation of specific wear rate with applied pressure values for 30% glass fiber reinforced PEEK composite against 10%PTFE filled PEI blend and 40% glass fiber reinforced PPS composite discs under dry sliding conditions, respectively. The specific wear rate value of 30% glass fiber reinforced PEEK composite are influenced by applied pressure value and counter-face material.
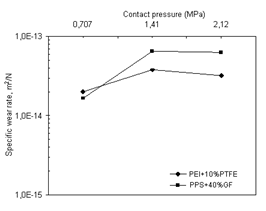
In case of rubbing against PTFE filled PEI blend and 40% glass fiber reinforced PPS composite, glass fiber reinforced PEEK composite have shown sensitivity to change in applied pressure values. The average specific wear rate values for glass fiber reinforced PEEK composite against PEI blend and PPS composite are 4.5.0x10-14 and 8.0x10-14 m2/N, respectively. Glass fiber reinforced PEEK composite/PTFE filled PEI blend combination shows the best tribological performance. The specific wear rate values increased with the increase in applied pressure. The increasing ratio in specific wear rate values for glass fiber PEEK composite against PEI blend and glass fiber PPS composite are 125% and 433% respectively. Glass fiber reinforced PEEK composite/PEI blend couple illustrates the best tribological performance for electrical contact breaker.
The study of friction and wear performance of 30% glass fiber reinforced poly-ether-ether ketone polymer composite in use in electrical applications showed that:
None.
The author declares no conflict of interest.

©2017 Unal, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.