MOJ
eISSN: 2381-179X


Case Report Volume 6 Issue 1
1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Osaki Citizen Hospital, Japan
2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Tokyo west Tokushukai hospital, Japan
Correspondence: Tatsuro Sasaji, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Osaki Citizen Hospital 3-8-1, Furukawa Honami, Osaki-shi, Miyagi, Japan, Tel l +81-229-23-3311, Fax +81-229-23-5380
Received: December 19, 2016 | Published: January 18, 2017
Citation: Sasaji T, Imaizumi H, Takano H, et al. Intradural-extramedullary metastatic tumor from lung cancer-a case report and review. MOJ Clin Med Case Rep. 2017;6(1):14-19. DOI: 10.15406/mojcr.2017.06.00147
A 62-year-old male presented with a thoracic intradural-extramedullary metastasis from lung cancer. He complained of walking difficulty and bilateral lower leg numbness. He had a past history of lung adenocarcinoma three years prior. Thoracic spine magnetic resonance imaging showed that the tumor occupied the right subarachnoid space and spinal nerve roots had shifted to the left side at Th12. He was diagnosed with cauda equina syndrome by an intradural-extramedullary tumor. Surgery was performed (Th12 laminectomy) and we opened the dura mater and arachnoid membrane. The tumor was in the right side and was removed. After the operation, his neurological condition soon improved and he could walk with a cane. By four moths postoperatively, a metastatic brain tumor occurred and he had to use a wheel chair. He died one year after surgery. Immunohistochemical staining was positive for thyroid transcription factor-1 in both the lung adenocarcinoma and intradural-extramedullary tumor. We diagnosed a metastatic tumor. Including the present case, 102 cases of a metastatic intradural-extramedullary tumor have been reported and, thus, the condition may not be rare. In more than twenty years there have only been two case studies, which recommended both operative and non-operative methods. We reviewed the validity of an operation base on the prognosis and surgical results of previous reports. The average life expectancy was 8.6months. The functional improvement rate was 78%. We recommend an operation for an intradural-extramedullary metastatic tumor because it improves the quality of a patients’ short life.
Keywords, metastatic tumor, intradural-extramedullary tumor, lung cancer, cauda equina syndrome, laminectomy
IEMT; intradural-extramedurally metastatic tumor, JOA; japanese orthopaedic association; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; TTF-1, thyroid transcription factor-1
Metastases are by far the most common skeletal tumors seen by orthopedists, and the spine is the most common site of skeletal involvement.1 A spinal epidural metastasis is the most common neoplastic myelopathy.2 In a total of 1215 cases of primary lung cancer in an autopsy study, 20(1.65%) revealed intradural parenchymal involvement.3 Among 200 patients treated for symptomatic spinal metastases, a localized intradural extramedullary tumor was discovered in 10 cases.4 Among 136 patients who underwent surgery for spinal metastases, an intradural extramedullary tumor was observed in two cases (1.5%).5 To our knowledge, Rogers et al.,6 were the first to report on an intradural-extramedurally metastatic tumor in 1958 since then, 101 cases have been reported in 66 articles.4–69 Including our case, the total number of reported cases is now 102. Many authors have described an intradural-extramedullary metastasis as a rare metastatic condition; however, we do not consider it to be rare given the number of reported cases.
Two types of treatment have been reported for an intradural-extramedullary tumor, the recommended operative and non-operative methods.4,18,31,38,45,63 In two case studies, Perrin et al.,4 recommended a non-operative method and Chow et al.,30 recommended an operation. Both reports had a small number of cases (n=10). There have been no reviews of many cases that were not limited to primary tumors and in more than twenty years since the two case studies were reported, medical technology has advanced. Surgery for a metastatic tumor is palliative and cannot extend the life expectancy. So, we consider that there is a need to review previous reports and examine the validity of surgery for an intradural-extramedullary metastatic tumor.
In this article, we report on a case of a thoracic intradural-extramedullary metastatic tumor from lung cancer. We further review previous reports and our case from the point of view of postoperative life expectancy and surgical results. The patient and his family gave consent to submit data for publication. The protocol for case report and review was approved by the Ethics Committee at Osaki Citizen Hospital (Osaki, Japan) (H28-Rinri-18).
In 2015, a 62-year-old female presented to our hospital with gait disturbance and numbness in the bilateral lower extremities. There was a past history of adenocarcinoma in the apical portion of left lung that had been treated with chemotherapy and radiation in 2012 (Figure 1). In 2013, a brain metastatic tumor from lung cancer occurred that was treated with an operation and gamma knife.
Upon neurological examination, the iliopsoas muscle strength was zero and quadriceps muscle and tibialis anterior muscle strengths were three (fair) in the right lower extremity using a manual muscle test. Muscle strength was graded on a 0 (zero) to 5 (normal) scale (arbitrary units).70 The patellar tendon and Achilles tendon reflexes could not be elicited. Sensory disturbance was detected in the right anterior femur. The patient was diagnosed with cauda equina syndrome. The Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA) score for lumbar disease was 7 out of 29.71 All laboratory findings were within normal limits.
Preoperative sagittal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed that the tumor was located in the dura mater at Th12 (Figure 2A–C). Compared with the spinal cord, the tumor had an iso-intensity signal in a T1-weighted MRI and high-intensity signal in a T2-weighted MRI (Figure 2A) (Figure 2B). The tumor was enhanced by Gadolinium with diethlenetriaminepentacetate (Gd-DTPA) (Figure 2C) (Figure 2D). The spinal nerve roots were compressed by the tumor, as observed on an enhanced T1-weighted axial image with Gd-DTPA (Figure 2D). The patient was diagnosed as having an intradural-extramedullary tumor and tumor resection surgery was performed to decompress the nerves.
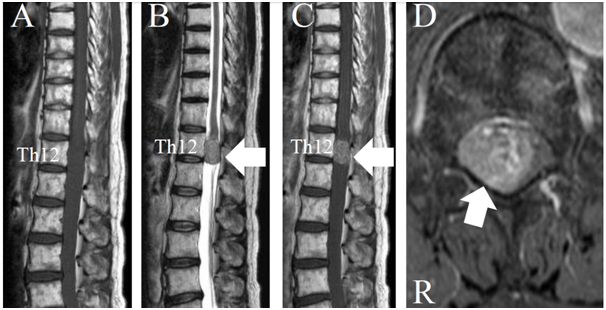
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance image of the thoracic spine. A. T1-weighted sagittal imaging. B. T2-weighted sagittal imaging. C. Gadolinium with diethlenetriaminepentacetate (Gd-DTPA) enhanced sagittal imaging. D. Gd-DTPA enhanced axial imaging. An intradural-extramedullary tumor can be seen at the 12th thoracic vertebral body level. The tumor has an iso intensity in T1-weighted imaging (A) and high intensity in T2-weighted imaging (B) compared with the spinal cord (white arrow). The tumor was enhanced by Gd-DTPA (white arrow) (C, D).
The thoracic spine was explored through a straight posterior midline approach. A laminectomy at Th12 revealed no extradural tumor. The dura mater and arachnoid membrane were exposed and the spinal nerve roots and conus medullaris were compressed by the tumor (Figure 3A). We scraped out and removed the tumor after which the spinal nerve roots and conus medullaris were decompressed (Figure 3B).
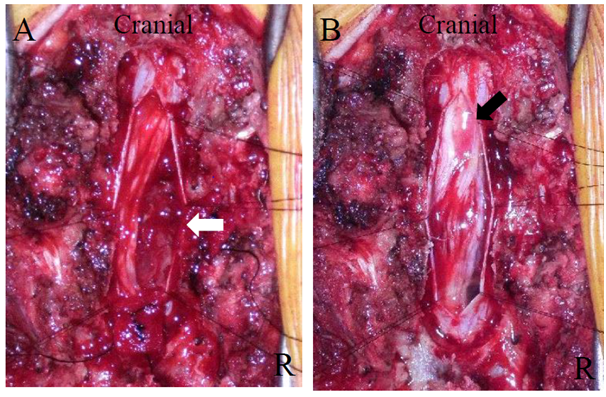
Figure 3 Intraoperative photograph. A. Before tumor resection. B. After tumor resection. Once the dura matter was opened, the tumor was can be seen in the left dura mater. The tumor adhered to spinal nerve roots (A). Following a tumor resection, the conus medulallis (black arrow) and spinal nerve roots were decompressed (B).
Muscle weakness in the right lower extremities improved soon after surgery. It was irradiated at 34Gy after the operation. Three months later, the patient complained of numbness in the right lower extremity. His muscle strength improved to normal and he could walk with a cane. The JOA score was 22 out of 29.71 Four months later, the brain metastatic tumor recurred and he could no longer walk and used a wheel chair. The patient died one year after surgery.
Lung cancer stained by Hematoxilin-eosin (HE) showed low differentiated adenocarcinoma (Figure 4A). The intradural-extramedullary tumor HE stained showed a moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (Figure 4B). Both the lung adenocarcinoma and intradural-extramedullary tumor were positive by immunohistochemical staining for thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) (Figure 4C) (Figure 2D). TTF-1 is a substance that is a specific stain for lung adenocarcinoma and thyroid cancer and is recognized as useful for the diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma.72,73 According to the above pathological findings, the pathological diagnosis was an intradural-extramedullary metastatic tumor from lung adenocarcinoma.
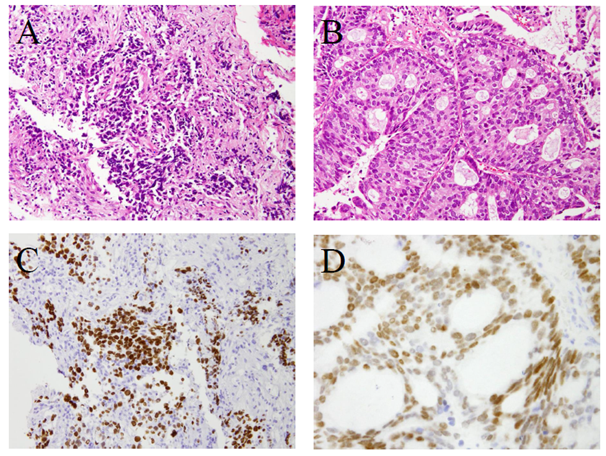
Figure 4 Histopathologic examination. A. Lung cancer (Hematoxilin and eosino stain). B. Intradural extramedullary tumor (Hematoxilin and eosino stain). C. Lung cancer (Thyroid transcription factor-1 stain). D. Intradural extramedullary tumor (Thyroid transcription factor-1 stain).
Lung cancer in the Hematoxilin-eosin (HE) stain showed a proliferation of atypical cells composed of a high nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio. This was low differentiated adenocarcinoma (A). An intradural-extramedullary tumor in the HE stain showed that atypical epithelial cells proliferated. This was moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (B). The antibody to thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) is a specific marker for lung adenocarcinoma and thyroid cancer. Both lung cancer and THE intradural-extramedullary tumor showed positive immunohistochemical staining for TTF-1 (C, D). The intradural-extramedullary tumor was diagnosed as a metastatic tumor from lung adenocarcinoma. Magnified 400times.
According to previous reports, the main primary tumors of intradural-extramedullary metastasis were lung cancer (24cases including ours), breast cancer (18cases) and renal cell carcinoma (15cases) (Figure 5).4–69 The average life expectancy of an intradural-extramedullary metastasis was 110days in lung cancer and more than one year in renal cell carcinoma.3,62 These reports were limited to each primary tumor. However, the primary tumor cannot be diagnosed before surgery and we need the general life expectancy for treatment. The general life expectancy of an unfamiliar condition, intradural-extramedullary metastasis, is still unknown. Therefore, we examined the postoperative life expectancy of all 65 cases, 64 cases previously reported plus the present case.5,6,8,10–14,16-18, 22, 24, 26–32,34,36–38,41,44–46,48,50–52,54,55,58,60–65,67–69 We excluded articles that had no description or a vague description about life expectancy. In cases where patients were alive at the last examination, we calculated as over the time until the last examination. We calculated one month as four weeks. The average life expectancy was more than 8.6months (1week~more than 63months) (Figure 6). The life expectancy of an intradural-extramedullary metastasis was considered to be not so long.
Lung cancer was 24 cases,4,5,9,15,22,31,51,55,56,59,63,67 present case. Breast cancer was 18 cases.4, 5,7,8,11,13,14,16,22,24,41,57,61 Renal cell cancer (including Wilm’s tumor and Grawitz tumor) was 15 cases.25,27,35,38,43,45–47,49,52,54,58,64–66 Occult primary cancer was 9 cases.10,13,14,16,17,22, 24,26,31 Ovarian cancer was 4 cases19,31,32,39 Prostate cancer was 4 cases.26,34,44,68 Malignant melanoma was three cases.4,18 Carcinoid was three cases.23,33,48 Chondrosarcoma was two cases.28,53 Uterine malignancy was two cases.4,20 Nasopharynx was two cases.21,31 Colorectal cancer was two cases.12,22 Neuroblastoma was two cases.13,60 There was once case each of adrenal gland cancer,6 gastric cancer,29 anal cancer,30 glioblastoma,36 sinonasal carcinoma,37 germinoma,40 submandibular gland carcinoma,82 papillary carcinoma of the thyroid,62 muscle,31 lymphoreticular system,31 lacrimal gland,31 and a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor.69
There were 10 cases of <1month, 18 cases between 1-3months, 12 cases between 3-6months, 15 cases between 6-12months, six cases between 1-2years, three between 2-3years, and one case between 3-6years. The average life expectancy was 8.6months and 84.6% patients died within one year.
Most reports about an intradural-extramedullary metastasis were case reports. Postoperative functions were reported in various ways and were not uniform so the general surgical results were unknown. According to Chow et al.,31 we evaluated the surgical results of each report by simple three grades, improved, unchanged, or worse. We defined the percentage of functional improvement as the number of improved cases divided by the total number of cases×100. We reviewed a total of 70 patients, 69 cases with descriptions about the postoperative function plus the present case.5,6,8,10,11,13,14,16–18,20,21,23–36,28–35,37–49,51,52,54,55,57,60–62,64–66,68,69 A total of 55 cases were improved (Figure 7). The overall functional improvement rate was 78%. An intradural-extramedullary metastatic tumor was expected to improve following surgery regardless of the primary tumor.
There were a total of 70 cases of which 55 were improved,5,6,8,10,11,13,14,16–18,20,23–25,28–33,35,37–41,44–49,52,54–59,61–69 eight remained unchanged8,21,26,31,51 and seven were worse.13,31,34,42,43,60 The postoperative functional improvement rate was 78%.
For the treatment of an intradural-extramedullary metastatic tumor, some reports recommended surgery18,31,45,63 and some recommended non-surgical methods.4,38 Of 102 cases, including ours, 94 received surgery. Non-surgical methods were used in eight patients because of a poor general condition.19,22,26,34 According to our review of an intradural-extramedullary metastasis, the life expectancy was more than 8.6months and a functional improvement was expected. So, we recommended an operation for the treatment of an intradural-extramedullary metastatic tumor to improve the quality of life, even though the life expectancy may be short.
This review has some limitations. This review included both old and recent reports that were under different medical conditions. Some reports had an inadequate or no description of the postoperative survival duration. All reports described postoperative function in different ways and the postoperative evaluation of this review was, therefore, inadequate. The functional improved duration was not described.
None.
The author declares no conflict of interest.

©2017 Sasaji, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.