eISSN: 2379-6367


Review Article Volume 7 Issue 2
Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacy, World University of Bangladesh, Bangladesh
Correspondence: AK Mohiuddin, Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacy, World University of Bangladesh, 151/8, Green Road, Dhanmondi, Dhaka–1205, Bangladesh, Tel +8801716477485
Received: February 20, 2019 | Published: March 22, 2019
Citation: Mohiuddin AK. Natural Foods and Indian herbs of cardiovascular interest. Pharm Pharmacol Int J. 2019;7(2):60-84. DOI: 10.15406/ppij.2019.07.00235
Since the start of human development, herbs have been an essential piece of society, esteemed for both their culinary and medicinal properties. Cardiovascular malady is the main executioner in the United States. Diet and way of life assume an imperative job in avoiding and switching heart infection, and certain herbs and supplements can help in bringing down hazard for heart ailment and treat heart conditions. Contrasted and customary prescriptions, herbal drugs don't require clinical investigations previously their showcasing or formal endorsement from administrative organizations, and thus their viability and wellbeing are once in a while demonstrated. Herbal medications have been utilized in patients with congestive heart disappointment, systolic hypertension, angina pectoris, atherosclerosis, cerebral inadequacy, venous deficiency, and arrhythmia, CHF, since hundreds of years. Be that as it may, numerous herbal cures utilized today have not experienced cautious logical appraisal, and some can possibly make genuine lethal impacts and real medication tranquilize cooperation’s. In spite of the greater part of these herbs demonstrating an impact on organic components identified with the cardiovascular system, information on their clinical impacts are inadequate. Conceivably applicable reactions, including expanded danger of medication connections, are portrayed, and the likelihood of tainting or substitution with different meds speaks to a worry. Doctors ought to dependably evaluate the utilization of herbal meds with patients and talk about the conceivable advantages and symptoms with them. Multidisciplinary explore is as yet required to misuse the tremendous capability of these plants. Potential synergistic and unfriendly reactions of herb-medicate communications additionally should be considered. These methodologies will help in setting up them as solutions for cardiovascular sicknesses and incorporating them in the standard of healthcare system. In spite of the fact that it has for quite some time been demonstrated that nutrient D, ascorbic acid, and nutrient B12 are the way to treating unending ailments, including CVDs. Various regular carotenoids are available in new foods grown from the ground, and some have been concentrated widely in the counteractive action of coronary heart illness (CHD).
Keywords: anti-oxidant, hypertension, cholesterol, atherosclerosis, cardioprotective, stroke
The utilization of herbal medicine has soar in the course of the most recent 10 years, with wellbeing consumption assessed over 18% of the GDP in US in 2018 (Figure 1). In the traditional Indian system of medicine Ayurveda and Siddha different spices and herbs are portrayed to have medicinal properties, for example, being antithrombotic, hostile to atherosclerotic, hypolipidemic, hypoglycemic, calming, antiarthritic, and so forth. It has been accepted for quite a while that dietary factors assume a key job in the advancement of some human maladies, including cardiovascular sickness. A few herbs and spices of culinary origin were incorporated into the "endorsed" monographs, for example, caraway oil and seed, cardamom seed, cinnamon bark, cloves, coriander seed, dill seed, fennel oil and seed, garlic, ginger root, licorice root, mint oil, onion, paprika, parsley herb and root, peppermint leaf and oil, rosemary, sage, thyme, turmeric root, and white mustard seed. Spices are wealthy in cancer prevention agents, and a logical report recommends they are likewise strong inhibitors of tissue harm and irritation brought about by elevated amounts of glucose and coursing lipids. Aside from the treatment of cardiovascular hazard factors with pharmacological specialists and the utilization of antithrombotic drugs, there is developing attention to the job of dietary factors and herbal medicines in the anticipation of CVD and the likelihood of their utilization in treatment. Quite a bit of this intrigue focuses on the utilization of cancer prevention agent nutrients and the cell reinforcement properties of herbal materials, albeit some herbal materials may likewise enhance regular cardiovascular hazard factors or have antithrombotic impacts. Herb– tranquilize cooperation’s are probably going to be increasingly genuine with medications having a thin remedial file, for example, warfarin or digoxin. The utilization of supplements of essential micronutrients (EMNs) in universal medicinal practice stays questionable, albeit sufficient measures of these substances are known to be important for the upkeep of wellbeing like Carotenoids, Vitamins B, C, D, E and K, Flavonoids, Magnesium and Iron, L-Carnitine, Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Coenzyme Q10. Different advantageous cardiovascular impacts have been found with garlic, Danshen, Lingzhi, Maidenhair Tree, Foxglove, Ginseng and so on. The proof to help the utilization of these elective treatments from clinical preliminaries isn't yet verify, yet custom and practice make it likely that they will keep on being utilized for the aversion or treatment of CVDs, among different signs. Current patterns for heftiness the executives include numerous pharmacological procedures, including blocking supplement assimilation, adjusting fat digestion, directing fat flags, and balancing the satiety focus, additionally exists in the extent of cardiac administration. Dietary phytochemicals have as of late stimulated significant enthusiasm as the potential helpful operators for wellbeing advancement and to balance stoutness. Because of their substance assorted variety and capacity to follow up on different organic targets, plant items have for some time been a flourishing hotspot for the revelation of new medications, and these discover use among the most widely recognized reciprocal and elective medicine systems (Figure 2).

Figure 1 Acetylcholine and adenosine coronary vascular effects.
Acetylcholine and Adenosine Coronary Vascular Effects Acetylcholine (ACH) has double contradictory impacts on the coronary veins. By authoritative to muscarinic 3 (M3) receptors on the outside of vascular smooth muscle cells, it inspires (bolt and +) an intracellular arrival of calcium particles (Ca2+), prompting vasoconstriction, while endothelial M3 receptor– intervened Ca2+ discharge enacts the endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthase (eNOS, NOS III) through a calmodulin-subordinate pathway. NO is then discharged and, in vascular smooth muscle cells, actuates dissolvable guanylate-cyclase (sGC), which changes over (bended bolt) guanosine triphosphate (GTP) into cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). The resulting actuation of GMP-subordinate protein kinase (PKG) initiates a course of intracellular occasions with the last impact of diminishing (bolt and −) intracellular Ca2+ fixations, prompting vasodilation. Adenosine (ADE) ties to its receptors (A2a) on the outside of vascular smooth muscle cells, initiating adenylate cyclase (AC) and prompting an expansion in cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) focus and cAMP-subordinate protein kinase (PKA) enactment. The last outcomes in potassium (K+) channel opening, bringing about a hyperpolarization of vascular smooth muscle cells, hinders the passage of Ca2+ and furthermore initiates inducible NOS (iNOS) (NOS II), hence delivering vasodilation. ATP = adenosine triphosphate

Figure 2 Different manifestations of myocardial ischemia.
Stable angina occurs when myocardial ischemia is caused by fixed atherosclerotic narrowing of one or more epicardial coronary arteries. In some circumstances, the angina is associated with a coronary spasm and metabolic dysfunction. Vasospastic angina occurs when myocardial ischemia is caused by a coronary artery spasm with or without endothelial dysfunction. Microvascular angina refers to the absence of an obstructed epicardial coronary artery. Myocardial ischemia in this case can be caused by microvascular and/or endothelial dysfunction and inflammation.
Cardiovascular diseases include the blood vessels, the heart, or both.1 These incorporate various issues, a significant number of which are identified with a procedure called atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a condition that creates when a substance called plaque develops in the dividers of the conduits.2 Arrhythmia alludes to a strange heart beat.3 There are different kinds of arrhythmias. The heart can pulsate excessively moderate, excessively quick or sporadically. At the point when heart valves don't open enough to enable the blood to course through as it should, a condition called stenosis results. At the point when the heart valves don't close legitimately and consequently enable blood to spill through, it's called spewing forth. On the off chance that the valve flyers lump or prolapse again into the upper chamber, it's a condition called prolapse.4,5 Hypertension is another name for hypertension. It can prompt serious confusions and expands the danger of heart malady, stroke, and demise. Circulatory strain is the power applied by the blood against the dividers of the veins.6 Myocardial ischemia happens when blood stream to heart is diminished, keeping it from getting enough oxygen. The diminished blood stream is normally the consequence of a fractional or complete blockage of heart's conduits (coronary courses).7
Traditional hazard factors for CVD incorporate more established age, smoking, hypertension, being overweight or large, diabetes, elevated cholesterol, and a family ancestry of heart sickness.8 Instances of other "nontraditional" chance factors that are once in a while utilized for hazard evaluation incorporate the lower leg brachial file (ABI), high-affectability C-responsive protein (hsCRP) level, and the coronary corridor calcium (CAC) score. The ABI is determined by contrasting circulatory strain esteems estimated at the lower leg and the arm (brachial supply route). High-affectability CRP is a protein associated with aggravation that is estimated by its dimension in an individual's blood. The CAC score estimates the measure of calcium in the veins of the heart dependent on a figured tomographic sweep of the chest (Figure 3) (Table 1).9‒35

Figure 3 Chest pain evaluation algorithm.
An algorithm that integrates information from the above clinical decision rules with ECG findings. Low-risk patients are unlikely to have chest pain resulting from acute or chronic cardiac disease, although other serious causes (e.g., anxiety disorder, reflux disease, peptic ulcer, and pulmonary embolism) should be considered. Patients at high risk of CAD require urgent evaluation and, in many cases, hospitalization. For patients at moderate risk, ECG and clinical findings can be used to identify those who are at high or low risk. Cardiac troponin testing can be used for risk stratification if it is available (e.g., in urgent care settings). A normal troponin level at least six hours after the onset of chest pain in combination with normal or near-normal ECG findings is a good prognostic sign; only one in 300 patients with this combination of findings have a cardiovascular event within 30 days.9 Although this algorithm has not been prospectively validated, it is based on prospectively validated diagnostic data.
|
Heart failure |
One of the most common complications of heart disease, heart failure occurs when heart can't pump enough blood to meet body's needs. Heart failure can result from many forms of heart disease, including heart defects, cardiovascular disease, valvular heart disease, heart infections or cardiomyopathy. |
|
Heart attack |
A blood clot blocking the blood flow through a blood vessel that feeds the heart causes a heart attack, possibly damaging or destroying a part of the heart muscle. Atherosclerosis can cause a heart attack. |
|
Stroke |
The risk factors that lead to cardiovascular disease also can lead to an ischemic stroke, which happens when the arteries to brain are narrowed or blocked so that too little blood reaches brain. A stroke is a medical emergency-brain tissue begins to die within just a few minutes of a stroke. |
|
Aneurysm |
A serious complication that can occur anywhere in your body, an aneurysm is a bulge in the wall of your artery. If an aneurysm bursts, you may face life threatening internal bleeding. |
|
Peripheral artery disease |
Atherosclerosis also can lead to peripheral artery disease. When peripheral artery disease is developed in extremities, usually legs don't receive enough blood flow. This causes symptoms, most notably leg pain when walking (claudication). |
|
Sudden cardiac arrest |
Sudden cardiac arrest is the sudden, unexpected loss of heart function, breathing and consciousness, often caused by an arrhythmia. Sudden cardiac arrest is a medical emergency. If not treated immediately, it is fatal, resulting in sudden cardiac death. |
Table 1 Complications of heart disease14‒25
|
CVH Metric |
Ideal CVH definition (2 Points) |
Intermediate CVH definition (1 Point) |
Poor CVH definition (0 Point) |
|
Smoking |
Never smoker |
Former smoker |
Current smoker |
|
Body mass index, kg/m2 |
<25 |
25–29.9 |
>30 |
|
Physical activity |
≥150 min/wk moderate or |
1–149 min/wk moderate or 1– |
None |
|
≥75 min/wk vigorous or |
74 min/wk vigorous or 1– |
||
|
≥150 min/wk |
149 min/wk moderate+vigorous activity |
||
|
moderate+vigorous activity |
|||
|
Diet score, no. of componentsa |
4–5 |
2–3 |
0–1 |
|
Total cholesterol, mg/dL |
<200b |
200–239b or treated to goal |
≥240 |
|
Blood pressure |
<120/<80 mm Hgb |
SBP 120–139 mm Hgb and/or DBP 80–89 mm Hgb or treated to <120/<80 mm Hg |
SBP ≥140 mm Hg and/or DBP ≥90 mm Hg |
|
Fasting glucose, mg/dLb |
<100 |
100–125 |
≥126 |
|
aFruits and vegetables: ≥4.5 cups/d; fish: ≥2 3.5‐oz servings/wk (preferably oily fish); fiber‐rich whole grains (≥1.1 g of fiber per 10 g of carbohydrate): ≥3 1‐oz equivalent servings/d; sodium: <1500 mg/d; sugar sweetened beverages: ≤450 kcal (36 oz)/wk. bUntreated values. |
|||
Table 2 AHA's life's simple 7 CVH Score36
In 2014, US future positioned 43rd on the planet, despite the fact that the United States spent the most ($3.0 trillion) on human services, surpassing the middle sum spent by Organization for Economic Co-activity and Development nations by 35%.39 CVD was the main source of death in the United States in 2016, representing more than 900 000 deaths. Most CVD trouble in the United States is from atherosclerotic vascular infection, and 80% can be ascribed to realized causal hazard factors.30 Almost 1 of every 3 (around 80 million) grown-ups have some type of CVD, which confers a substantial financial weight, including assessed direct expenses of roughly $444 billion in US. The CVD expenses of consideration are proceeding to ascend, with the present expenses for treatment representing almost $1 of each $6 spent on social insurance.40 The proof on the monetary weight of CVD in LMICs stays rare. The expenses per scene for hypertension and nonexclusive CVD were genuinely homogeneous crosswise over investigations; extending somewhere in the range of $500 and $1500. Interestingly, for CHD and stroke cost assessments were commonly higher and progressively heterogeneous, with a few gauges in overabundance of $5000 per scene. Normal month to month treatment costs for stroke and CHD extended somewhere in the range of $300 and $1000 in China, Brazil, India and Mexico.41
Predominance of affirmed hypertension in youngsters to run somewhere in the range of 2% and 4%.26 In a few nations, up to 75% of more established grown-ups are hypertensive.27 87% of the grown-ups in the US who self-revealed having hypertension take part in at least two exercises to diminish pulse, for example, taking prescription, participating in physical action, evolving diet, and decreasing liquor utilization.28 In November 2017, new rules from the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) extended the meaning of hypertension, stretching out the mark to 46% of grown-ups in the United States.31 CHD is a noteworthy reason for death and handicap in created nations. Despite the fact that the mortality for this condition has slowly declined in the course of the most recent decades in western nations, regardless it causes around 33% of all passings in individuals more seasoned than 35 years.38 Atrial fibrillation is the most well-known continued arrhythmia, increments with age, and gives a wide range of manifestations and seriousness.32 The latest investigations have affirmed this discernment and demonstrated that the predominance of AF in the general grown-up populace of Europe is more than twofold that detailed only multi decade sooner, extending from 1.9% in Italy, Iceland, and England to 2.3% in Germany and 2.9% in Sweden.33 The assessed commonness is lower in ladies (373 for every 100,000) than in men (596 for each 100,000).
AF frequency has been appeared to increment lopsidedly with expanding age in the two ladies and men, coming to as high as 30.4 per 1000 man a very long time in ladies and 32.9 per 1000 man a long time in men by age 85- 89 years.34 Most investigations of intense myocardial localized necrosis (AMI) the study of disease transmission and treatment have concentrated on patients who experience the beginning of AMI outside of the emergency clinic. It is progressively perceived that AMI additionally happens among patients previously hospitalized for different conditions.35 All inclusive, stroke is the second driving reason for death and third driving reason for disability.1 More than 74% of the weight of stroke has been ascribed to smoking, less than stellar eating routine, and low physical movement, while over 72% has been credited to metabolic hazard factors (high plasma glucose, elevated cholesterol, hypertension, overweight and heftiness, and kidney ailment).37 Myocardial areas of localized necrosis (MIs) are among the main sources of dismalness and mortality in the United States and lead to >$11 billion in yearly hospitalization costs. Of people >45 years old who have a first MI, frequency of repetitive MI or deadly coronary heart illness inside 5 years extents from 17% to 20%, and heart disappointment rates are comparable, including further healthcare costs, which are anticipated to increment by practically 100% by 2030.36
Cardiometabolic illnesses are evaluated to cause more than 700,000 passings for every year in the US and about half of these passings are straightforwardly identified with eating routine.42 Way of life factors, including nourishment, assume a critical job in the etiology of CVD. CVD hazard in postmenopausal ladies seems, by all accounts, to be delicate to a change to a low-fat dietary example and, among sound ladies, incorporates both CHD advantage and stroke chance.43 Factors that impact people to devour a low-quality eating regimen are heap and incorporate absence of information, absence of accessibility, staggering expense, time shortage, social and social standards, promoting of low quality nourishments, and attractiveness.44 The medicinal writing is still brimming with articles contending contradicting positions. For instance, in 2017, after an audit of the proof, the AHA Presidential Advisory firmly embraced that "bringing down admission of immersed fat and supplanting it with unsaturated fats, particularly polyunsaturated fats, will bring down the rate of CVD". After three months, the 18-nation observational Prospective Rural Urban Epidemiology (PURE) Study finished up much the inverse: "Absolute fat and kinds of fat were not related with cardiovascular sickness, myocardial dead tissue, or cardiovascular illness mortality".45
Today, there keeps on being an enthusiasm for low-carb methodologies, for example, Atkins, Banting, ketogenic, and South Beach. While eats less carbs instigating weight reduction delivers a caloric shortage, the system of low-carb slims down stays in discussion. When bringing down starches from the eating regimen, the macronutrient admission of fat and protein by and large increments to make up for the decrease of sugars. One speculation of why low-carb approaches produces quick weight reduction contrasted with different eating regimens is that fats and protein increment satiety and produce less attendant hypoglycemia. This expansion in satiety and less bounce back hypoglycemia at that point decreases yearning and by and large nourishment admission and produces a caloric deficiency.46 Both high and low rates of sugar consumes less calories were related with expanded mortality, with insignificant hazard saw at 50–55% starch admission. Plant-inferred protein and fat admission, from sources, for example, vegetables, nuts, nutty spread, and entire grain breads, were related with lower mortality, proposing that the wellspring of sustenance quite adjusts the relationship between starch admission and mortality.47 The traditional Mediterranean eating routine is portrayed by the utilization of entire grains, vegetables, natural products, vegetables, nuts, fish and olive oil, wine with some restraint, and a moderate admission of meat, dairy items, prepared sustenance’s and desserts.48
Mediterranean eating routine decreased cardiovascular ailment mortality chance identified with long haul introduction to air contaminations in a vast forthcoming U.S partner. Expanded utilization of nourishments wealthy in cancer prevention agent compounds may help in decreasing the extensive ailment trouble related with encompassing air contamination.49 As appeared in a metaexamination of seven partner thinks about; a 2-point increment in adherence to the Mediterranean eating regimen was related with a noteworthy decrease of in general mortality.50 Furthermore, a meta-examination of 23 forthcoming accomplice investigations of 937,665 members and 18,047 CHD patients demonstrated that natural product utilization was contrarily connected with a danger of CHD.51 Second rate aggravation, instead of lipids, is probably going to be on the pathway of the communication among MD and statins towards mortality chance. MD brought down the danger of all-cause, cardiovascular and CAD/cerebrovascular mortality CVD patients, net of statins (Table 3).52
|
Food pattern |
Recommendations |
|
Low-fat diet |
Low-fat diet with restricted calories may present a healthy alternative to the typical Western diet. It may improve quality and life expectancy in healthy people, as well as in patients with overweight, diabetes, and CVD. |
|
Low carbohydrate Diet |
In the short-run, low-carbohydrate diets lead to a greater weight loss compared to low-fat diets. Some studies have shown that this advantage is retained at 2 years but not at longer follow-up periods Low-carbohydrate diets are preferable to a low-fat diet in reducing TG levels and increasing HDL-C blood levels. It should be emphasized that carbohydrates should preferably be replaced by unsaturated vegetable fats. Low-carbohydrate diets, which include 30%–40% of calories from carbohydrates and are low in saturated fat and high in monounsaturated fat, were found to be safe in healthy and overweight individuals at follow-up up to 4 years. |
|
Mediterranean Diet |
A Mediterranean diet with restricted calories may present a healthy alternative to the typical Western diet. It may improve quality and life expectancy in healthy people, as well as in patients with overweight, diabetes, and CVD. Mediterranean diets are preferable to a low-fat diet in reducing TG levels, increasing HDL-C blood levels, and improving insulin sensitivity. |
|
DASH Diet |
The DASH diet is recommended to prevent hypertension and lower blood pressure. The diet should be accompanied by lifestyle changes such as: weight reduction in overweight people, increased physical activity, sodium restriction, and alcohol avoidance. |
Table 3 Recommendations of dietary patterns in prevention of CVD50
Contrasted with refined grains, entire grains are higher in fiber, which may help diminish "terrible" LDL cholesterol and reduction the danger of heart infection.53,54 Berries are likewise wealthy in cell reinforcements like anthocyanins, which ensure against the oxidative pressure and irritation that add to the advancement of heart illness.55 Avocados are an incredible wellspring of heart solid monounsaturated fats, which have been connected to diminished dimensions of cholesterol and a lower danger of heart infection.56 Walnuts are an extraordinary wellspring of fiber and micronutrients like magnesium, copper and manganese. Of the unsaturated fats, oleic and linoleic acids speak to the greater part of the all out fat substance in pistachios. Pistachios are additionally a decent wellspring of vegetable protein (about 21% of all out weight), with an essential amino acid proportion higher than most other regularly devoured nuts (ie, almonds, walnuts, pecans, and hazelnuts), and they have a high level of expanded chain amino acids.57 Dull chocolate is wealthy in cancer prevention agents like flavonoids, which can help support heart wellbeing.58 Tomatoes are stacked with lycopene, a characteristic plant color with amazing cancer prevention agent properties.59 Almonds are likewise a decent wellspring of heart-solid monounsaturated fats and fiber, two essential supplements that can help secure against heart illness (Table 4).60
|
Fruit |
Subject |
Study Type |
Dose |
Main Effects |
|
freeze-dried grape powder |
SHR and Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats |
in vivo |
600 mg/day |
BP↓, arterial relaxation↑, vascular compliance↑, cardiac hypertrophy↓ |
|
GSPE |
SHR |
in vivo |
250 mg/kg/day |
arterial remodeling↓, ET-1↓, NO↑, SOD↑, CAT↑, MDA↓ |
|
GP-EE |
rat aorta and small mesenteric artery (SMA) segments |
in vitro |
0.3 and 10 μM |
endothelium- and NO-dependent vasodilatation↑, phenylephrine(Phe)-induced response in aortic rings↓, O2−↓, contraction elicited by ET-1↓ |
|
red grape skin and seeds polyphenols |
human endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) |
in vitro |
5, 50 and 150 µg/mL |
EPC viability and function↑, endothelial dysfunction↓, hyperglycemia effect↓, ROS production↓ |
|
GSPE |
ouabain induced hypertensive rats model |
in vivo |
250 mg/kg/day |
BP↓, aortic NO production↑ |
|
HUVECs |
in vitro |
10µg/mL |
eNOS expression↑ |
|
|
GPE |
endothelial (EA. hy926) cells |
in vitro |
0.068 and 0.250 µg/mL |
GCS levels↑, GST activity↑, antioxidant activity↑ |
|
GSE |
HUVECs |
in vitro |
1μg/mL |
platelet reactivity↓ |
|
red grape berry powder |
rats with metabolic syndrome |
in vivo |
200, 400 and 800 mg/kg/day |
BP↓, plasma TG↓, insulin↓ |
|
HUVECs |
in vitro |
20–1400 μg/mL |
ET-1↓ |
|
|
0.011,0.058, 0.29, 1.46 and 3.66 mg/mL |
eNOS level↑ |
|||
|
grape seed procyanidin extract |
hamster |
in vivo |
25 mg/kg/day |
body weight gain↓, adiposity index↓, weight of white adipose tissue depots↓, plasma phospholipids↓, plasma FFA↓, mesenteric lipid and triglyceride accumulation↓ |
|
grape polyphenols from Vitis vinifera grapes |
24-month-old obese rats |
in vivo |
90 mg/kg/day |
plasma HDL PON activity↑, LCAT activity↑, CETP activity↓ |
|
grape seed procyanidin extract |
SHR |
in vivo |
375 mg/kg |
SBP↓, DBP↓, GSH activity↑ |
|
GSE or black chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) extract |
human platelets incubated with Hcy (100µM) or HTL (1µM) |
in vitro |
2.5, 5, 10µg/mL |
platelet adhesion to collagen and fibrinogen↓, platelet aggregation↓, O2•− production in platelet↓ |
|
malvidin-rich red grape skin extract |
isolated and Langendorff perfused rat heart |
in vitro |
1–1000 ng/mL |
I/R damages↓, coronary dilation↑, active PI3K/NO/cGMP/PKG pathway, intracellular cGMP↑, eNOS, PI3K-AKT, ERK1/2, and GSK-3 β phosphorylation↑ |
|
GSSE |
a rat model of global ischemia |
in vivo |
2.5 g/kg |
brain damage size and histology↓, oxidative stress↓, transition metals associated enzyme activities↑ |
|
GSPE |
isolated rat hearts |
in vitro |
NA |
RA↓, Na+/K+-ATPase activity↑, Na+/K+-ATPase α1 subunit↑, free radical↓ |
|
GSPE |
a rat model of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) |
in vivo |
400 mg/kg/day |
thrombus length and weight↓, protecte endothelium integrity, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α↓ |
|
blueberry extract (Vaccinium ashei Reade) |
hypercholesterol emic rat |
in vivo |
25, 50 mg/kg |
aortic lesions↓, oxidative damage to lipids and proteins↓, TC↓, LDL-C↓, TG↓, activity of CAT, SOD and GSH-Px↑ |
|
freeze-dried blueberry powder |
rats fed a high-fat/cholesterol diet |
in vivo |
2% (w/w) |
SBP↓, aorta relaxation↑, endothelial dysfunction↓ |
|
7 phenolic acids of freeze-dried blueberry |
murine macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 |
in vitro |
NA |
TNF-α and IL-6 mRNA expression and protein levels↓, MAPK, JNK, p38, and Erk1/2 phosphorylation↓, mRNA expression and protein levels of scavenger receptor CD36↓, foam cell formation↓, expression and protein levels of ABCA1↑ |
|
PE |
SR-BI/apoE double KO mice |
in vivo |
307.5 µL/L in water |
aortic sinus and coronary artery atherosclerosis↓, oxidative stress and inflammation in the vessel wall↓ |
|
PE containing 40% punicalagin |
SHR |
in vivo |
150 mg/kg/day |
BP↓, cardiac hypertrophy↓, oxidative stress↓, antioxidant defense system↑, paraventricular nucleus inflammation↓, mitochondrial superoxide anion levels↓, mitochondrial function↑ |
|
PE containing 40% punicalagin |
heart of a high-fat diet-induced obesity rat model |
in vivo |
150 mg/kg/day |
mitochondrial biogenesis↑, oxidative stress↓, phase II enzymes↑, cardiac metabolic disorders↓ |
|
pomegranate seed extract |
CHI rat model |
in vivo |
100, 200, 400, 800 mg/kg/day |
motor and cognitive coordination↑ |
|
Bravo de Esmolfe apple |
male Wistar rats fed a cholesterolenriched diet (+2% cholesterol) |
in vivo |
20% (w/w) = 5g/rat/day (~2–3 apples/perso n/day) for 30 days |
serum TG↓, TC↓, LDL-C↓, oxLDL↓ |
|
Fuji apple peel Granny Smith apple peel |
CF-1 mice with MS apoE−/− mice |
in vivo |
20% (w/w) for 43 days 20% (w/w) for 10 weeks |
glycaemia↓, TC↓, HDL-C↓, LDL-C↓, ureic nitrogen↓, TG↓, insulin↓, ADMA↓ atherogenic progression↓, cholesterol accumulation area↓ |
|
HFC |
apoE−/− atherosclerotic mice with high blood lipid levels fed with a high cholesterol diet |
in vivo |
0.5 mL/day |
TG↓, LDL-C/TC ratio↓ |
|
HPPS |
the liver of high fat diet induced hyperlipidemic mice |
in vivo |
150 mg/kg |
weight gain↓, TG↓, lipid excretion in feces↑, mRNAs and activities of acyl-CoA oxidase, carnitine palmitoyltransferase I, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, and 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase↑, gene and protein expressions of PPAR-α↑ |
|
freeze dried hawthorn fruit (Crataegus pinnatifida) |
apoE−/− mice |
in vivo |
1% (w/w) |
atherosclerotic lesions↓, TC↓, TG↓, T-AOC values↑, SOD and GSH-Px activities↑, hepatic FAS and SREBP-1c mRNA levels↓, hepatic SOD1, SOD2, Gpx3 mRNA levels↑ |
|
sugar-free aqueous extract of hawthorn fruit (Crataegus pinnatifida var. Major) |
high fat diet fed rats |
in vivo |
72 and 288 mg/kg/day |
TC, TG and LDL-C↓, HDL-C↑, CRP, IL-1β, IL-8 and IL-18↓, ET, 6-keto-PGF1α and TXB2↑, pathological changes in the arteries↓, IMT↓ |
|
avocado pulp (Persea americana) extract |
male adult CD 1 mice |
in vivo |
25 mg/kg |
thrombus formation↓ |
|
|
platelet |
in vitro |
10 µL |
platelet aggregation↓ |
|
avocado oil |
rats ingested with sucrose |
in vivo |
7.5% (w/w) |
TG↓, VLDL↓, LDL↓, hs-CRP↓ |
|
freeze-dried mango pulp |
male C57BL/6J mice fed a highfat diet |
in vivo |
1% or 10% (w/w) |
epididymal fat mass↓, percentage of body fat↓, improve glucose tolerance, insulin resistance↓ |
|
methanolic extract of papaya (Carica papaya) |
SHR |
in vivo |
100 mg/kg (twice a day) |
BP↓, angiotensin converting enzyme(ACE) activity↓, cardiac hypertrophy↓, improve baroreflex sensitivity |
|
sour cherry seed kernel extract |
hearts from Sprague-Dawley rats |
in vitro |
30 mg/kg/day |
post ischemic cardiac functions↑, infarct size↓, heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1)↑, Bcl-2↑ |
|
total flavonoids of Guangzao (Choerospondias axillaris) |
I/R male Sprague-Dawley rats |
in vivo |
75, 150 and 300 mg/kg/day |
cardiac function↑, heart pathologic lesion↓, CAT↑, GSH-Px↑, SOD↑, MDA↓, TUNEL-positive nuclear staining↓, Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax)↓, caspase-3↓, Bcl-2↑, p38 MAPK activity↓, JNK activity↓ |
|
hydroalcoholic extract of acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) seeds |
male Wistar rats subjected to myocardial infarction |
in vivo |
100 mg/kg/day |
prevent the development of exercise intolerance, cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and dysfunction |
|
Acai pulp |
female Fischer rat of dietaryinduced hypercholesterol emia |
in vivo |
2% (w/w) |
TC↓, LDL-C↓, atherogenic index↓, HDL-C↑, cholesterol excretion in feces↑, expression of the LDL-R, ABCG5, and ABCG8 genes↑ |
|
Bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) anthocyanin-rich extract |
apoE−/− mice |
in vivo |
0.02% (w/w) |
improve hypercholesterolemia against atherosclerosis |
|
Unrefined black raspberry seed oils |
male Syrian hamsters fed high-cholesterol (0.12%), high-fat (9%) diets |
in vivo |
NA |
plasma and liver TG↓, hypertriglyceridemia↓ |
|
Polyphenols from sea buckthorn berry |
rats with hyperlipidemia |
in vivo |
7–28 mg/kg |
serum lipids↓, TNF-α↓, IL-6↓, antioxidant enzymes activity↑, eNOS, ICAM-1, and LOX-1 mRNA expression and proteins in aortas↓ |
|
Jujube (Zizyphus jujuba) fructus and semen extract |
human macrophages |
in vitro |
NA |
the foam cell formation induced by acetylated LDL↓, prevent atherosclerosis |
|
Methanol extract of blackberry (Rubus allegheniensis Port.) |
human monocyte-derived macrophages induced by acetylated LDL |
in vitro |
50μM |
foam cell formation↓ |
|
Yellow passion fruit pulp |
SHR |
in vivo |
5, 6 or 8 g/kg/day |
SBP↓, GSH↑, thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS)↓ |
|
Proanthocyanidins in boysenberry seed extract |
SHR |
in vivo |
100 and 200 mg/kg |
SBP↓ |
|
rat aorta rings |
in vitro |
vasorelaxant activity↑ |
||
|
Methanolic extract of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) |
cerebral ischemia rats |
in vivo |
100, 300 mg/kg |
SOD↑, CAT↑, GSH↑, glutathione reductase↑, lipid peroxidation↓, oxidative stress↓, neuronal damage↓ |
|
Black chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) extract |
bovine coronary artery endothelial cells |
in vitro |
0.1 g/mL |
NO↑, eNOS phosphorylation↑ |
|
Saskatoon berry powder |
leptin receptor-deficient diabetic mice |
in vivo |
5% (w/w) |
monocyte adhesion to aorta↓, inflammatory, fibrinolytic or stress regulators in aorta or heart apex↓ |
|
Saskatoon berry powder |
leptin receptor-deficient diabetic mice |
in vivo |
5% (w/w) |
endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS)↓, unfolded protein response (UPR)↓ |
|
glycated LDLtreated HUVECs |
in vitro |
|||
|
19 fruits widely consumed in central Chile |
NA |
in vitro |
1 mg/mL |
anticoagulant activities: grape, raspberry fibrinolytic activity: raspberry |
|
Peach (Prunus persica) pulp ethylacetate extract |
cultured vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) |
in vitro |
50, 100, or 200µg/mL |
Angiotensin II (Ang II) induced intracellular Ca2+ elevation↓, generation of ROS↓ |
|
Methanolic extract of Lingonberry (Vaccinium vitisidaea L.) |
H9c2 rat myoblasts simulated IR |
in vitro |
5 and 10µM |
apoptosis↓, markers of nuclei condensation, caspase-3 activation, and MAPK signaling↓ |
|
Blueberry anthocyanin fraction (BBA), blackberry anthocyanin fraction (BKA), and blackcurrant anthocyanin fraction (BCA) |
RAW 264.7 macrophages treated by LPS bone marrowderived macrophages from Nrf2+/+ mice treated by LPS |
in vitro |
0–20μg/mL |
IL-1 β mRNA levels↓, NF-κB p65 translocation to the nucleus↓ cellular ROS levels↓, IL-1β mRNA levels↓ |
|
Pomegranate juice, together with date fruit and date seeds extract |
apoE−/− mice |
in vivo |
0.5µM gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/day |
TC↓, TG↓, PON1 activity↑, mouse peritoneal macrophage (MPM) oxidative stress↓, MPM cholesterol content↓, and MPM LDL uptake↓, aortas lipid peroxide content↓, aortas PON lactonase activity↑ |
Table 4 The cardioprotective abilities of fruits51
A few herbs and supplements may help in battling atherosclerosis, the hidden reason for most heart illness. Truth be told, certain herbs can impact pulse, triglycerides, cholesterol levels and irritation, which are all hazard factors for heart malady. They're likewise high in dietary nitrates, which have been appeared to lessen pulse, decline blood vessel firmness and enhance the capacity of cells covering the veins.53
Carotenoids
Carotenoids are a class of normal, fat-dissolvable shades found chiefly in plants. They have potential cancer prevention agent organic properties in view of their compound structure and collaboration with natural films. Carotenoids are generally across the board in the vegetable kingdom and are found in high focuses in algae and microorganisms. People and different animals can't orchestrate them, so they are important in their eating routine.61 The scope of uses of microalgae as wellspring of carotenoids isn't constrained to astaxanthin-based items yet in addition to the production of supplements with naturally dynamic carotenoids like β-carotene, lutein and zeaxanthin with huge commitments to human wellbeing that enter in the sustenance and supplement advertise, which is relied upon to achieve 220 $ billion all around in 2022.
Astaxanthin: Astaxanthin (3,3′-dihydroxy-β,β′-carotene-4,4′-dione), a red carotenoid shade delegated a xanthophyll, is known to have an amazing cell reinforcement capacity. The most astounding known dimension of astaxanthin in nature is in the chlorophyte alga Haematococcus pluvialis.62 Astaxanthin utilized in healthful supplements is typically a blend of configurational isomers created by Haematococcus pluvialis, a unicellular microalgae. Astaxanthin controlled orally for five-weeks in stroke inclined SHR additionally brought about a huge BP decrease. Oral astaxanthin likewise improved nitric oxide prompted vascular unwinding in the rodent aortas.63 Astaxanthin limits work out prompted skeletal and cardiac muscle harm in mice.64 Astaxanthin impacts on pulse in unexpectedly hypertensive rodents (SHR), normotensive Wistar Kyoto rodents (NWKR) and stroke inclined immediately hypertensive rodents (SPSHR) were accounted for. Human umbilical vien endothelial cells and platelets treated with the astaxanthin demonstrated expanded nitric oxide levels and lessening in peroxynitrite levels (Figure 4).65
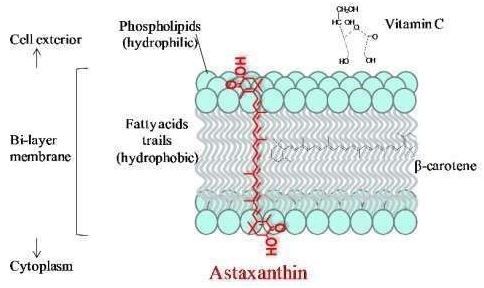
Figure 4 Transmembrane orientation of astaxanthin.
The polar end groups overlap the polar boundary zones of the membrane, while the nonpolar middle fits the membrane’s nonpolar interior. The dashed r ed line speculatively indicates “lightning-rod” conduction of electrons along the astaxanthin molecule, possibly to vitamin C or other antioxidants located outside the membrane.
Fucoxanthin: Fucoxanthin is an orange carotenoid present in consumable darker ocean growth, for example, Undaria pinnatifida (Wakame), Hijikia fusiformis (Hijiki), Laminaria japonica (Ma-Kombu), and Sargassum fulvellum.61 Fucoxanthin, a carotenoid compound, is found in the chloroplasts of darker ocean growth. This phytochemical has very calming and cell reinforcement properties.66 Fucoidan and fucoxanthin in mix can possibly lessen cardiac hypertrophy, cardiac fibrosis, ROS level, and abbreviated QT interim in maturing mice subjects. There were additionally critical enhancements in cardiac morphology and solid capacity after the maturing mice were bolstered with fucoidan alone or fucoidan supplemented with fucoxanthin.67 In addition, fucoxanthin additionally indicated antiobesity, antidiabetes, mitigating, anticancer, and hepatoprotective exercises just as cerebrovascular defensive impacts. Fucoxanthin can enhance the lipid profile and keep the harm in cardiovascular system by advancing the extent of DHA in the liver.68 Laminaria japonica and Undaria pinnatifida are among the most well known nourishment elements of Japanese food. Fucoxanthin, and its metabolite fucoxanthinol, lessens inflammatory changes in the connection among adipocytes and macrophages. These outcomes recommend that Fucoxanthin contained in eatable algae is helpful as a sustenance element for controlling corpulence related insulin opposition and for anticipating metabolic disorder (Figure 5) (Figure 6).69

Figure 5 Laminaria japonica (Ma-Kombu).
Laminaria japonica has frequently been used as a food supplement and drug in traditional oriental medicine. Among the major active constituents responsible for the bioactivities of L. japonica, fucoxanthin (FX) has been considered as a potential antioxidant. A low molecular weight fucoidan (DFPS), obtained from the brown seaweed Laminaria japonica, was separated into three fractions by anion-exchange column chromatography. Available data presented the content of sulfate group, the molar ratio of sulfate/fucose and sulfate/total sugar, and the molecular weight played an important role on antioxidant and anticoagulant activity.

Figure 6 Undaria pinnatifida (Wakame).
Brown algae and its carotenoids have been shown to have a positive influence on obesity and its comorbidities. Additionally, the treatments, ameliorated adipose tissue accumulation, insulin resistance, blood pressure, cholesterol and triglycerides concentration in serum, and reduced lipogenesis and inflammation by downregulating acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) gene expression, increasing serum concentration and expression of adiponectin as well as downregulating IL-6 expression.
Lycopene: Lycopene is the shade in charge of the red shading in a few leafy foods, which can be found in high focus in tomato items, red grapefruits, and watermelons. It is an unsaturated carotenoid, bringing about effective cell reinforcement, and utilization can anticipate both maturing and CVD.61 Generally speaking dietary lycopene admission and high-serum grouping of lycopene, altogether diminished the danger of major cardiovascular occasions.70 Lutein and lycopene supplementation fundamentally expanded the serum convergence of lutein and lycopene with a lessening in carotid vein CAIMT.71 Advantages of lycopene ought to be particularly considered in patients with high cardiovascular hazard, statin prejudice, marginal hypertension, headache medicine opposition, hyperactive platelets, vascular inflammatory infections, metabolic disorder and coronary heart malady, and its incorporation in blend treatments for the referenced issue, ought to be drawn nearer.72 Cholesterol decrease, hindrance of oxidation forms, balance of inflammatory markers, upgraded intercellular correspondence, restraint of tumourigenesis and enlistment of apoptosis, digestion to retinoids and antiangiogenic impacts was accounted for in another investigation.73 Nonetheless, the conceivable opposite affiliations noted for more elevated amounts of tomato-based items, especially tomato sauce and pizza, with CVD propose that dietary lycopene or different phytochemicals expended as oil-based tomato items give cardiovascular advantages (Figure 7).74
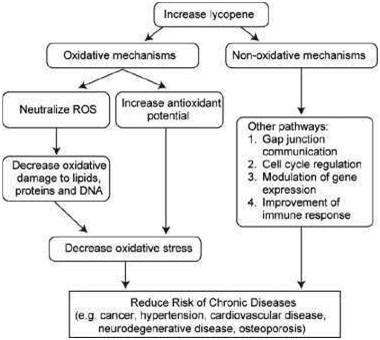
Figure 7 General mechanisms of action of lycopene.
The proposed mechanisms of action of lycopene (oxidative and nonoxidative) that decreases the risk of oxidative stress-mediated diseases. Lycopene most likely acts via the oxidative mechanism of action to prevent oxidative stress. Lycopene treatment has been shown to cause a 37% suppression of cellular cholesterol synthesis in J-774A.1 macrophage cell line, and augment the activity of macrophage LDL receptors. Oxidized LDLs are highly atherogenic as they stimulate cholesterol accumulation and foam cell formation, initiating the fatty streaks of atherosclerosis. LDL susceptibility to oxidative modifications is decrease by an acyl analog of platelet-activating (PAF), acyl-PAF, which experts its beneficial role during the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis. Purified lycopene in association with α - tocopherol or tomato lipophilic extracts has been shown to enhance acyl-PAF biosynthesis in endothelial cells during oxidative stress. ROS: reactive oxygen species.
Lutein: It is a pigment (xanthophyll) and a dietary oxygenated carotenoid comprising of 40-carbon hydroxylated compounds found in the human retina in high fixation. It is an isomer of the carotenoid zeaxanthin, with indistinguishable compound equations.61 it can simply be gotten from yellow corn, egg yolk, squeezed orange, honeydew melon, and different organic products, however particularly happening in dim green vegetables, for example, turnip greens, kale, parsley, spinach, and broccoli.75 Lutein applies powerful cell reinforcement and calming impacts in aortic tissue that may secure against advancement of atherosclerosis in guinea pigs.76 utilization of lutein expands plasma lutein fixations, and that this expansion is related with increments in movement and decreases in time spent occupied with inactive exercises.77 Lutein may go about as a chemo-preventive specialist against atherosclerosis, including oxidative pressure and lipid digestion upgrades. Diminished mRNA and protein articulation dimensions of hepatic peroxisome proliferator-enacted receptor-α, carnitine palmitoyl-transferase 1A, acyl CoA oxidase 1, low thickness lipoprotein receptors and forager receptor class B type I saw in mice with atherosclerosis were extraordinarily upgraded after treatment with lutein.78
Zeaxanthin: Like lutein, zeaxanthin is an oxygenated non-ace nutrient A carotenoid that comprises of a 40-carbon hydroxylated compound and they both are found from same dietary sources.79 Higher dietary and serum carotenoid levels are related with lower carotid intima-media thickness in moderately aged and older individuals.80 More elevated amounts of plasma oxygenated carotenoids (lutein, zeaxanthin, betacryptoxanthin) and alpha-carotene might be defensive against early atherosclerosis.81 Specialists found a connection between the dimension of lutein and zeaxanthin in the fat tissue and diet and the hazard for heart assault.82
β-cryptoxanthin: β-cryptoxanthin is a xanthophylls and one of the lesser-known carotenoids, whose best sustenance sources are oranges, peach, tangerines, red peppers and tropical organic products, for example, papaya and pumpkin. It likewise has ace nutrient an action and appears to have defensive wellbeing activity. The centralizations of β-cryptoxanthin in most mammalian tissues commonly are low contrasted and those of other dietary cancer prevention agents, for example, nutrients E and C.83 Intense β-cryptoxanthin treatment shows more prominent cardioprotective viability against I/R damage than astaxanthin and nutrient E by diminishing infarct sizes and lessening apoptosis, oxidative pressure, and mitochondrial brokenness in mice.84 Serum β-cryptoxanthin and lutein in addition to zeaxanthin were conversely identified with the degree of atherosclerosis.85 β-cryptoxanthin has hostile to corpulence and antioxidative impacts in C. elegans, it is enticing to conjecture that β-cryptoxanthin may have a defensive impact against advancement of the metabolic disorder. The metabolic disorder is a mind boggling jumble bunching stoutness, diabetes mellitus, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular maladies. β-cryptoxanthin fixations in serum are contrarily identified with files of oxidative DNA harm and lipid peroxidation.86 A converse relationship of baPWV with β-carotene and β-cryptoxanthin was watched freely of the glycemic state.87
Beta-carotene: Beta-carotene is a standout amongst the most generally examined carotenoids for the two its genius nutrient A movement and its wealth in foods grown from the ground, for example, carrot, orange, kale, spinach, turnip greens, apricot, and tomato.61 Low serum carotenoid levels may reflect either expanded lipoprotein thickness or the nearness of irritation, the two factors developing as imperative novel hazard factors for coronary heart infection.88 Notwithstanding its capacity to influence hazard and pathogenesis of cancer, beta-carotene has been considered for use in the executives of heart ailment dependent on its free radical searching limits, with the preventative note that it might likewise go about as a tissue-harming prooxidant-contingent upon the physiologic environment.89,90 Clear cardioprotective impact of beta-carotene at one chose measurements and moderation or end of that security at a higher portion is theoretical dependent on the results.91 One-month tobacco-smoke introduction instigates practical and morphological cardiac adjustments and BC supplementation weakens this ventricular redesigning process.92 More data is expected to determine the relationship between the admission of single supplements, for example, carotenoids, and the danger of CVD. As of now, the utilization of carotenoids in pharmaceutical structures for the treatment or aversion of heart infections can't be prescribed.93
Homocysteine level maintenance
Homocysteine levels increment in the body when the digestion to cysteine of methionine to cysteine is impeded. This might be because of dietary inadequacies in nutrient B6, nutrient B12, and folic acid.94 Lifted homocysteine level has been appeared to be related with the advancement of atherosclerotic heart illness, stroke, and myocardial ischemia. An ascent in serum creatinine likewise prompts an ascent in fasting all out homocysteine. The real course of homocysteine freedom from plasma is the kidney, and the ascent is because of inadequate digestion of homocysteine by the kidney.95 A 25% decrease in homocysteine levels was related with a 11% lower ischemic heart ailment chance and a 19% lower stroke chance.96 Trimethylglycine, Folate, Vitamin B12, Vitamin B6, Taurine, Creatine, Choline, NAcetylCysteine, Omega-3 Fatty Acids hold homocysteine levels under tight restraints (Figure 8).97,98
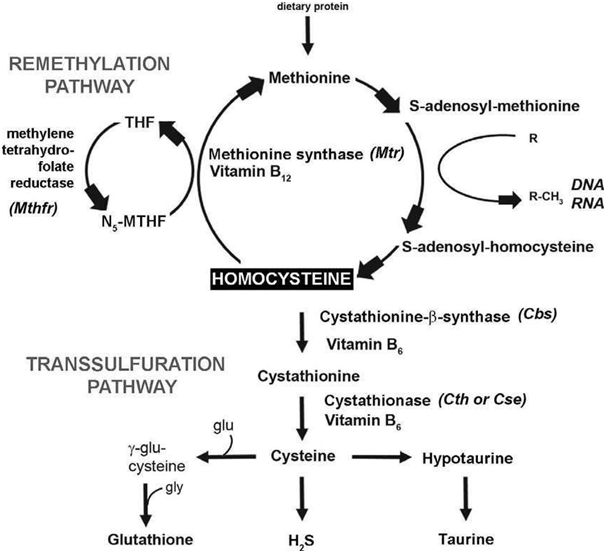
Figure 8 Pathways for the metabolism of homocysteine
Normal trans-sulfuration requires cystathionine β synthase with vitamin B6 as cofactor. Re-methylation requires 5, 10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase and methionine synthase. The latter requires folate as co-substrate and vitamin B12 (cobalamin) as cofactor. An alternative remethylation pathway also exists using the cobalamin independent betaine–homocysteine methyltransferase. For some years, attention focused on the role of heterozygosity for homocystinuria6 as a possible cause of the high homocysteine concentrations that is seen in up to 30–40% of patients with coronary artery disease.
Flavonoids
An extensive assemblage of proof backings that the dietary admission of polyphenols-especially of flavonoids and the particular class of flavonoids named flavanols-may almost certainly apply some gainful vascular impacts and lessen the hazard for cardiovascular horribleness and mortality.99 Various flavonoids of dietary criticalness have been appeared to give valuable effect on parameters related with atherosclerosis, including lipoprotein oxidation, blood platelet conglomeration and cardiovascular reactivity.100 In an investigation of around 5,000 subjects, the admission of dietary flavonoids and tea was contrarily connected with myocardial dead tissue.101 Flavonoids' defensive impacts against ischemic heart illness depends on a few clinical examinations that decidedly connect flavonoid admission to a decreased occurrence of the infection. Expending flavonoids like catechin, which is available in plant seeds and teas, brought about a 20% decrease in the frequency of the sickness102 (Further subtleties of flavonoids in CVD avoidance is talked about in later area) (Figure 9).
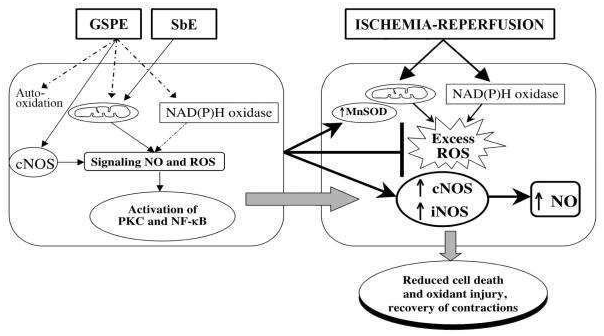
Figure 9 Potential mechanisms of Scutellaria baicalensis extract (SbE) and grape seed proanthocyanidin extract (GSPE) in delayed preconditioning in cardiomyocytes.
NO, nitric oxide; ROS, reactive oxygen species; PKC, protein kinase C; MnSOD, manganese superoxide dismutase; cNOS, constitutive nitric oxide synthase; iNOSinducible NOS. With respect to NO, flavonoids in SbE such as wogonin and baicalein, suppress its release by inhibiting NOS/guanylate cyclase. In normal tissue GSPE stimulates NO release via a purinergic pathway. GSPE has shown a reduced NO release, although only in models of inflammation, which could be an indirect effect of suppression of iNOS upregulating cytokines. Data suggest that cardiomyocytes show a non-toxic ROS response to SbE treatment but NO release with GSPE treatment during the induction phase. It appears that the two extracts may induce two distinct preconditioning mechanisms.
Magnesium and iron
The role of copper, iron, and other metal components in ischemic heart damage has been settled.103 Vegetables (lentils, beans and peas) pumpkin, sesame, hemp and flaxseeds, cashews, pine nuts and different nuts, tomato, potatoes, mushrooms, palm, prune, olives, mulberries, entire, grains (amaranth, oats), coconut milk, dull chocolate, dried thyme are rich wellspring of iron.104,105 Brazil nuts, almonds, pecans, cashews, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, flaxseeds, sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, quinoa seeds, cumin seeds, peach apricots, avocado, banana, blackberries, spinach, okra, broccoli, beetroot, swiss chard, green chime peppers, artichokes, buckwheat are rich wellsprings of magnesium.106 Iron is a segment of hemoglobin and subsequently assumes a key job in tissue oxygenation. It is additionally a segment of myoglobin, which is an oxygen restricting protein found in skeletal muscle and myocytes, permitting oxygen discharge in hypoxic conditions.107 The commonness of iron insufficiency in heart disappointment patients has been accounted for as being up to 50 %, even in patients without sickliness. In this way, IV iron ought to be considered in symptomatic HF patients with ID.108 Examination of the long haul security of the different intravenous iron supplementation techniques may in any case be justified (Table 5).109
|
Study type |
Clinical setting |
No. of Subjects |
Outcome |
Conclusion |
|
Meta-analysis of prospective studies |
General population |
>1,000,000 |
CVD (coronary heart disease, ischemic heart disease, stroke) and allcause mortality |
Increasing dietary Mg is associated with a reduced risk of stroke and heart failure, but not with total CVD, and all-cause mortality. |
|
Observational |
Elderly |
1400 |
All-cause and causespecific mortality |
Low plasma Mg levels increase allcause mortality. |
|
Meta-analysis of prospective studies |
General population |
532,979 |
CVD |
Inverse association between dietary Mg intake and CVD risk. |
|
Meta-analysis of prospective studies |
General population |
313,041 |
Incidence of CVD, including IHD |
Plasma and dietary Mg are inversely associated with CVD risk. |
|
Prospective |
Individuals at high risk of CVD |
7216 |
CVD and all-cause mortality |
Mg intake is associated with a lower mortality risk in this population, but not with CV events. |
|
Prospective |
Women free of disease |
86,323 |
CHD |
Dietary Mg intake was inversely associated with fatal CHD. |
Table 5 Summary of studies evaluating the effect of magnesium on cardiovascular-related outcomes in the general population104
Early secondary counteractive action preliminaries of fish and omega-3 polyunsaturated unsaturated fat (PUFA) cases announced useful impacts on CVD results, including all-cause mortality and sudden cardiac passing.110 Other than numerous medical advantages, incomprehensibly; extraordinary exercise can result in oxidative harm to cell constituents. Very still, muscle gets roughly 20% of the absolute blood stream, be that as it may, amid exercise, this can increment to over 80%. N-3 PUFAs appear to be among the most valuable supplements for an immense scope of the populace (untimely babies, old with sarcopenia, competitors, and patients with metabolic and inflammatory maladies). N–3 PUFAs can possibly be an ergogenic help that improves preparing and sport execution requiring little to no effort and little hazard.111 Omega3 unsaturated fats like EPA just at a pharmacologic portion diminish fasting TG and meddle with components of atherosclerosis that outcomes in decreased cardiovascular occasions. Extra robotic preliminaries will give further bits of knowledge into their job in decreasing cardiovascular hazard in subjects with all around oversaw LDL-C yet lifted TG levels (Figure 10).112
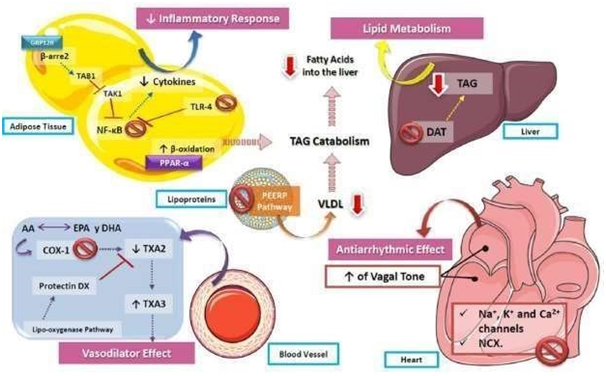
Figure 10 Role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in cardiovascular function
The actions of n3-PUFAs are diverse, including the decrease of the inflammatory response via NF-kB inhibition, as well as an increase of β-oxidation, causing the catabolism of triaclyglycerides and contributing to the decrease of lipids stored both in the liver and vessel walls. In addition, by increasing the production of TXA3 in vessel walls, PUFAs decrease vascular resistance, reducing blood pressure. On the other hand, one of the most described effects of n3-PUFAs is their action on cardiac arrhythmia, by inhibiting voltage-gated ion channels and exchangers, as well as increasing the vagal tone of the atria and ventricles, which leads to a lower heart rate. PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acids; TXA2, thromboxane A2; TXA3, thromboxane A3, COX-1: cyclooxygenase 1; DAT, 1,2 diglyceride acyltransferase; TAG, triacylglycerides; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa B; TLR-4, toll-like receptor 4; VLDL, very low-density lipoproteins.
Co-enzyme 10 (Q10)
CoQ10 isn't FDA-endorsed to treat any restorative condition in spite of the fact that it is generally accessible over-the-counter as a dietary supplement and prescribed by primary consideration doctors and pros alike.113 Q10 can build the creation of key cell reinforcements, for example, superoxide dismutase, a chemical fit for lessening vascular oxidative worry in hypertensive patients. Q10 diminishes dimensions of lipid peroxidation through the decrease of ace oxidative compounds. Q10 can upgrade blood stream and ensure veins by means of the safeguarding of nitric oxide.114 There's a solid job of CoQ10 in hypertension, ischemic heart malady, myocardial dead tissue, heart disappointment, viral myocarditis, cardiomyopathies, cardiac poisonous quality, dyslipidemia, corpulence, type 2 diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorder, cardiac methodology and revival.115 Q10 has the potential in hypertensive patients to bring down systolic circulatory strain by up to 17 mm Hg and diastolic pulse by up to 10 mm Hg without noteworthy reactions.116 Proof proposes that the CoQ10 supplement might be a valuable apparatus for overseeing patients with heart disappointment.117 In spite of positive discoveries, a bigger imminent preliminary is justified to help routine utilization of CoQ10 (Figure 11).118

Figure 11 Q10 treatment may intervene in the scheme where augmented ROS production contributes to postischemic injury and progression to heart failure.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) Increased myocardial levels of oxidative stress markers have been demonstrated in animal models of heart failure produced by coronary ligation , pressure overload and rapid cardiac pacing. ROS are key pathophysiological mediators in myocardial remodeling in heart failure. In human heart failure, there is also evidence of increased levels of oxidative stress markers such as malondialdehyde (MDA) in serum, and isoprostanes in urine. Further- more the levels of these markers correlate with the severity of heart failure.
In traditional medicinal systems, hypertension is analyzed by its evident side effects. The traditional mending additionally portrays different side effects, for example, serious migraine, weariness, chest torment; sporadic heart beat among others for a determination of cardiac illnesses.119 A recent report demonstrated that 25% of present day medication and 75% of new medicines against harmful ailments are acquired from normal plant assets.120
Allium sativum (Family: Alliaceae or Liliaceae)
The protective mechanisms of the beneficial effects of garlic in CVDs may be achieved by suppressing LDL oxidation, increasing HDL, as well as decreasing TC and TG.121 While garlic supplementation reduced BP significantly in hypertensive patients, it did not appreciably affect patients with normal BP (Figure 12).122
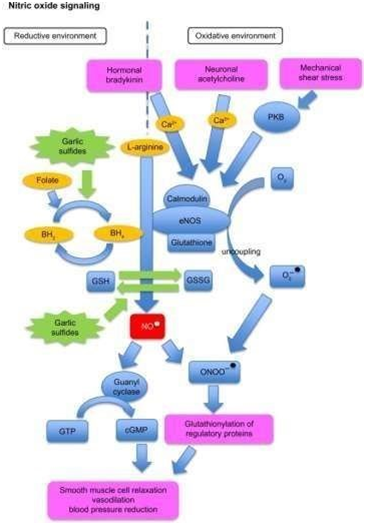
Figure 12 Effect of garlic on blood pressure via the NO pathway.
N.B. Blue rectangles illustrate metabolites, blue circles represent enzymes, orange circles are dietary cofactors, green star shapes are garlic and other organo sulfur containing nutrients, red rectangle represents NO, and purple rectangles denote direct and indirect influence of NO on vasodilation and blood pressure. NO pathway: in the presence of BH4, eNOS produces NO, which triggers pathways leading to smooth muscle cell relaxation and vasodilation. eNOS uncoupling leads to the formation of O2−. NO and O2− combine to form OONO−, which rapidly reacts with thiols and tyrosine residues of proteins, which in turn, leads to vasodilation and BP reduction independent of cGMP. Garlic and other dietary organosulfides may play a role in the regulation of the NO signaling pathway by creating a more reductive environment and therefore supporting NO production. Abbreviations: BH2, dihypdrobiopterin; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; Ca2+, calcium ion; cGMP, cyclicguanosyl-monophosphate; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; eNOS, endothelial-nitric-oxide-synthase; GSH, reduced free glutathione; GTP, guanosyl-tri-phosphate; NO, nitric oxide (radical); ONOO, peroxynitrite; O2, oxygen; O2−, superoxide anion radical; PKB, protein kinase-B.
Terminalia arjuna (Family: Combretaceae)
Bark of T. arjuna contains an extremely abnormal state of flavonoids, to be specific arjunolone, flavones, luteolin, baicaleiin, quercetin, kempferol, and pelargonidin assessed with other medicinal plants especially effect sly affecting cardiovascular sicknesses.123 T. arjuna is broadly utilized for treatment of cardiovascular sicknesses, including heart illnesses and related chest torment, hypertension and elevated cholesterol. Various clinical investigations have likewise detailed its helpful impacts in patients of interminable stable angina, endothelial brokenness, heart disappointment and even ischemic mitral spewing forth.124 Its bark decoction is being utilized in the Indian subcontinent for anginal agony, hypertension, congestive heart disappointment, and dyslipidemia, in view of the perceptions of antiquated doctors for quite a long time.125 No systematic survey has been directed for Terminalia arjuna in patients of ceaseless stable angina.126 It sustains and reinforces the heart muscle and advances cardiac working by directing pulse and cholesterol.127 T. arjuna essentially diminishes TC, LDL and TG levels and expands HDL and decreases atherosclerotic injury in aorta of hypercholesterolemic rabbits.128 The adequacy of T. arjuna stem bark as a cardioprotective and intense cancer prevention agent has been adequately shown in various trial and clinical investigations. Be that as it may, persistent research advance on T. arjuna stem bark is especially required in the respect of careful sub-atomic system, tranquilize organization, medicate sedate associations, and toxicological investigations (Figure 13).129
Allium cepa (Onion)
Onion strip extract supplementation for about fourteen days is advantageous as it diminishes the likelihood of creating key hazard factors for cardiovascular ailment by modifying the lipid profiles in sound young ladies.130 Garlic oil and onion oil have hostile to stoutness properties that can neutralize the impacts of a HFD on body weight, fat tissue weight, and serum lipid profiles.131 HPLC investigation of onion strip separate uncovered that it contains quercetin, one of the real flavonoids, which has hostile to platelet impact (a powerful inhibitor of collagen-invigorated platelet conglomeration in vitro), along these lines, it very well may be a promising and safe methodology for against cardiovascular sicknesses.132 Hyperglycemia has been recognized as a noteworthy hazard factor for cardiovascular intricacies connected to T2DM, and in this way known as a compelling restorative focus in the treatment of T2DM. Warmth handled onion concentrate can be a critical wellspring of arginyl-fructose, a noteworthy bioactive Amadori improvement compounds in warmth prepared onion, and phenolic compounds that apply postprandial blood glucose-bringing down and cancer prevention agent impacts, separately.133 Organization of garlic in addition to lemon juice brought about an enhancement in lipid levels, fibrinogen and circulatory strain of patients with hyperlipidemia.134 Onion globules (Allium cepa L.) are among the most extravagant wellsprings of dietary flavonoids and add to a substantial degree to the general admission of flavonoids (Figure 14).135‒137
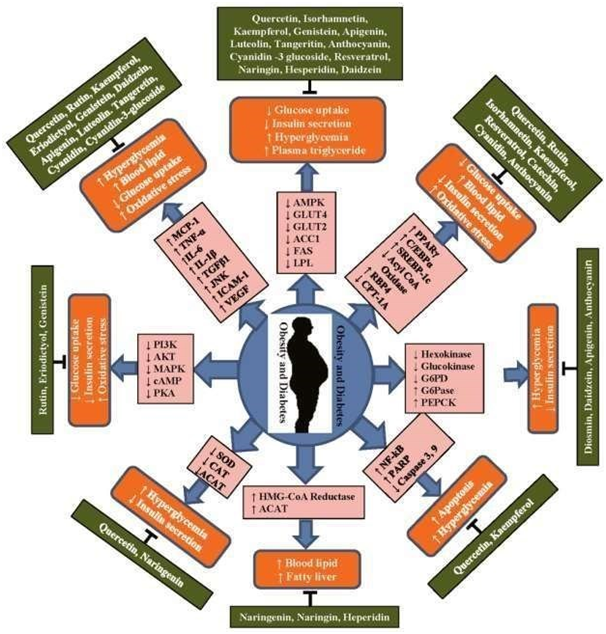
Figure 14 Schematic presentation of molecular functions of different flavonoids with anti-obesity and antidiabetic effects.
Flavonoids showed anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects by activating or inhibiting different cytokines, enzymes, and metabolites to prevent inflammation, oxidative stress, and metabolism to protect against obesity and diabetes. MCP-1, monocyte-chemo-attractant protein-1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-1β, interleukin 1 beta; FFA, free fatty acid, IRS1, insulin receptor substrate 1; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT, serine/threonine kinase; FA, fatty acid; IGT, impaired glucose tolerance; PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase; BCl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bak, Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer; Caspase 3, cysteine-dependent aspartate-directed proteases 3; PPAR γ, peroxisomal proliferatoractivated receptor gamma; SREBP1c, sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c; LPL, lipo protein lipase; AMPK, 5′ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; GLUT4, glucose transporter 4; G6PDH, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme; ACAT, acyl CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase; G6pase, glucose6-phosphatase; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA, protein kinase A.
Amla (Emblica officinalis)
Amla delivered critical hypolipidemic impact alongside a decrease in circulatory strain. Expansion of Amla to the as of now accessible hypolipidemic treatment would offer huge insurance against atherosclerosis and coronary conduit infection, with decrease in the portion and antagonistic impacts of the hypolipidemic operators.138 It has useful job on dyslipidemia and cardiac autonomic capacities in rodents treated with high fat eating regimen.139 A strong hindrance of collagen prompted platelet collection because of oral supplementation of an institutionalized concentrate of Phyllanthus emblica. Furthermore, the concentrate fundamentally repressed hypercholesterolemia and hs-CRP in overweight/Class-1 large grown-ups from the US populace.140 In a recent report, Amla remove has appeared potential in decreasing TC and TG levels just as lipid proportions, AIP and apoB/apo An I in dyslipidemic people (apo B, apo An I is a noteworthy apolipoprotein of HDL particles which enables the inversion to transport of cholesterol from fringe tissue to liver, in this manner lessening the danger of creating inflammatory reaction and development of plaques) and in this manner has degree to regard general just as diabetic dyslipidemia. A solitary specialist to lessen cholesterol just as TG is uncommon. Cholesterol decrease is accomplished without corresponding decrease of Co Q10, as opposed to what is seen with statins (Figure 15).141,142
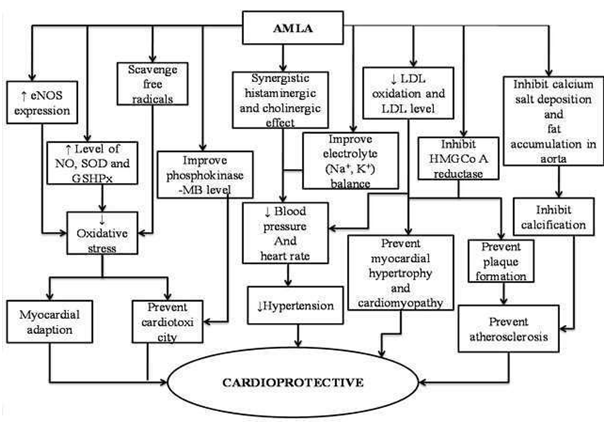
Figure 15 Mechanism of Amla as cardioprotective agent
(1) Reduction in hypertension and oxidative stress by increasing the expression of eNOS, by ameliorating the levels of nitric oxide (NO), SOD, GSHPx and electrolytes like Na+ and K+. (2) Aqueous extract of amla lowers the mean arterial blood pressure, heart rate and respiratory rate by showing synergistic histaminergic and cholinergic effect. (3) Cardioprotective potential in isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity through ameliorating the levels of antioxidant enzymes and creatinine phosphokinase-MB and LDH by its antioxidant free radical scavenging activity. (4) Amla fruit juice at dose of 1 ml/kg p.o for 8 weeks in diabetesinduced MI showed preventive action in myocardial hypertrophy, cardiomyopathy and hypertension by increasing heart rate, lowering blood pressure through its antioxidant potential and by maintaining the lipid profile and enzyme levels. (5) Methanolic extract and fruit powder of amla has been known to attenuate the induction and progression of atherosclerosis by preventing the formation of plaque in blood vessels and aorta via inhibiting HMG CoA reductase and LDL oxidation; and by reducing LDL cholesterol levels and subsequently increasing HDL levels.
Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha)
Ashwagandha root extricate upgrades the Cardiorespiratory perseverance and enhances QOL in sound athletic grown-ups.143 Ashwagandha is appeared in the writing to be an anxiolytic, upper, and antistress adaptogen. Various examinations have affirmed the antistress impact of ashwagandha.144-147 It additionally seems to apply a positive effect on the endocrine, cardiopulmonary, and focal sensory systems.148 avoided increment in adrenal weight and diminishing in ascorbic acid and Cortisol substance of adrenals amid stress. It seems to incite a condition of non-explicitly expanded obstruction (SNIR) amid stress (Figure 16) (Figure 17).149
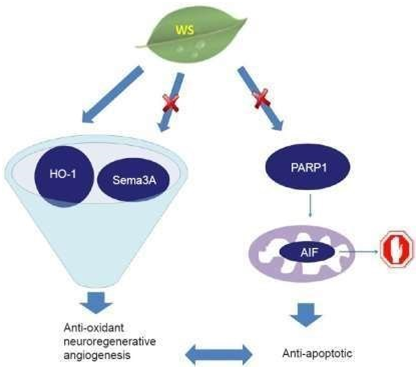
Figure 17 Probable mechanisms of action of an aqueous extract of Withania somnifera (WS) in ischemic stroke.
WS mediated attenuation of the expression of Semaphorin 3A (Sema3A) could promote neuronal regeneration. Moreover, HO-1 mediated vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induction and the antagonistic effects of Sema3A and VEGF could have the combined result of higher VEGF levels and a resulting pro-angiogenic effect. WS was also found to reduce levels of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1), which prevents translocation of antiapoptotic factor (AIF) from the mitochondria to the nucleus. The PARP1-AIF pathway is a prime mediator of caspase independent apoptosis, which is prevented by WS in this model of stroke.
Nardostachys jatamansi (Valerianaceae)
Possesses significant anti-stress activity, which might be because of its cancer prevention agent action.150 In vitro cell reinforcement action of hydromethanolic extricates (70%) of N. jatamansi was considered by estimating the free radical searching movement. Rakatchap Har (Each 500 mg top contains Sarpgandha 150mg, Shankhpushpi 75mg, Jatamansi 75mg, Jahar Mohra Khatai Pishti 75mg, Moti Pishti 75mg, Ras Sindoor 50mg) alongside way of life alteration and psychotherapy is a sheltered and useful solution for the treatment of all evaluations of hypertension in all age bunches with no constraint to its utilization.151 Brahmyadi Churna (Brahmi, Shankhapushpi, Jatamansi, Jyotishmati, Vacha, Ashwagandha Churna 1 section each) caused stamped decrease in the dimensions of all out BP. Manifestations, for example, migraine, sleep deprivation, and energy indicated stamped enhancement while very little decrease was seen in different side effects, for example, chest agony, exhaustion, and palpitation. SBP diminished impressively than DBP reduction in BP was watched notably with P<0.000.152 The fluid concentrates additionally shown defensive impacts against 2K1C-instigated cardiac hypertrophy in a rodent demonstrate (Figure 18).153
Triphala (combination drug)
An all-around perceived, polyherbal Ayurvedic medicine comprising of products of the plant species Emblica officinalis (Amalaki), Terminalia bellerica (Bibhitaki), and Terminalia chebula (Haritaki) in equivalent extent 1:1:1.154 Conceivably successful for a few clinical uses, for example, craving incitement, decrease of hyperacidity, cancer prevention agent, mitigating, immunomodulating, antibacterial, antimutagenic, adaptogenic, hypoglycemic, antineoplastic, chemoprotective, and radioprotective impacts, and avoidance of dental caries.155 Laghu shankha prakshalana kriya (LSP), a yogic bowel purifying strategy, coordinated methodology of yoga treatment (IAYT) is a protected and valuable system for patients with essential hypertension. LSP with triphala is progressively helpful.156 Assumes an essential job in pulse control and parities cholesterol.157,158 Triphala and its constituents can counter the impacts of an environment (ie, high dietary admission of fats) and have the potential for use as antiobesity operators with alluring lipid-profile balancing properties.159 Terminalia bellerica may impact cholesterol level for example increment the dimension of HDL and abatement LDL, and at the same time be valuable in the treatment of coronary supply route malady.160 β-sitosterol, which is the principle constituent of T. chebula, is an organic compound having a place with the group of phytosterols, whose synthetic structure takes after cholesterol. β-sitosterol and phytosterols may influence lipid digestion by restraining the retention of cholesterol from the digestive tract. β-sitosterol has likewise been concentrated for its potential in bringing down large amounts of blood-cholesterol.161 Triphala detailing was related with hypolipidemic impacts on the tentatively actuated hypercholesteremic rodents.162 Triphala tablets help enhances the course and is a successful equation for hypercholesterolemia (Figure 19‒21).163
Boerhavia diffusa (Nyctaginaceae)
Punarnava, a notable cardiotonic eatable medicinal plant against apoptosis in Angiotensin II (Ang II)- invigorated hypertrophic cardiac cells (H9c2), powerful in lessening apoptosis in cardiac cells, which is a noteworthy supporter of sudden cardiac demise notwithstanding its nutraceutical properties.164 Different dynamic compounds in B. diffusa incorporate punarnavine, ursolic acid, punarnavoside, liriodendrin, eupalitin, eupalitin-3-O-â-D-galactopyranoside, rotenoids like boeravinones A, B, C, D, E, F and G, quercetin, kaempferol, and so forth.165,166 Among these, quercetin shows cell reinforcement, antihypertrophic and antihypertensive potential in vitro and in vivo test models.167,168 Ursolic acid is accounted for to have cardioprotective potential through initiating uncoupling of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and lessening mitochondrial H2O2 generation.169 Kaempferol is additionally answered to have cardioprotective potential and boeravinone G is another cancer prevention agent and genoprotective compound in B. diffusa.170,171 Liriodendrin segregated from B.diffusa is accounted for to have Ca2+ divert hostile properties in heart.172 Nearness of these dynamic constituents may be in charge of its defensive action against Ang II instigated hypertrophy. Cell organelles are likewise the objectives of Arsenic trioxide (ATO)- initiated cardiotoxicity notwithstanding other detailed targets like particle channels, and ethanolic concentrate of Boerhavia diffusa can possibly ensure the cardiotoxicity incited by ATO (Figure 22).173
Cruciferous vegetables
This incorporate broccoli, Brussel grows cabbage, cauliflower, kale, radish, rutabaga, turnip and even arugula. cruciferous vegetables contain isothiocyanates, which can create the redox-controlled cardioprotective protein, thioredoxin, it was contemplated that utilization of broccoli could be advantageous to the heart. Sulforaphane is by a wide margin the most generally concentrated and best described isothiocyanates.174,175 Research is demonstrating that sulforaphane assists with irritation of the blood vessel dividers, restrains corpulence, diminishes hypertension, and different conditions that are a piece of or lead to CVD.176 Oxidative pressure brought about by diminished generation of nitric oxide as well as expanded creation of ROS (principally superoxide) may advance endothelial brokenness. Accordingly, expanded oxidative pressure speaks to one conceivable driver of the expanded predominance of hypertension. An eating routine containing broccoli grows high in Grn (Grn+) diminished oxidative pressure and related issues in male immediately hypertensive stroke-inclined rodents (SHRsp).177 As one of Grn key metabolites, SFN was additionally found to enhance pulse. Weight is related with metabolic turmoil, which is another hazard factor for atherosclerosis and CVD. Choi et al. examined whether SFN counteracted high-fat eating regimen (HFD-) instigated corpulence in C57BL/6N mice. SFN may actuate hostile to corpulence impacts by restraining adipogenesis.178 75% of the sulforaphane will be retained into the circulation system after gobbled and taken up by cells. Once inside sulforaphane can harm essential intracellular structures like mitochondria and compounds. This drains glutathione (most powerful human cancer prevention agent) leaving cells defenseless against further oxidative harm. Sulforaphane can even disturb epithelial hindrances giving one more plant concoction that can add to "flawed gut (Figure 23)."179
Nigella sativa (Ranunculaceae)
It has been utilized in traditional medicine and a few investigations have been performed in the most recent decades to uncover the impacts of it on various therapeutic issue, for example, diabetes, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and stoutness.180 N. sativa oil at a portion of 2.5mg/kg constricts the Nω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME)-instigated increment in BP and was related with a decrease in cardiac redox status and angiotensin-changing over catalyst movement and an expansion in heme oxygenase (HO-1) action. N. sativa oil additionally anticipated plasma NO misfortune. Remarkably, the BP-bringing impact was similar down to that of nicardipine in hypertensive rodents.181 N. sativa and its segment thymoquinone have the helpful impact on hypertension most likely because of weakening cardiovascular impacts of angiotensin II.182 Thymoquinone (the fundamental constituent Nigella sativa) supplementation lessens cyclophosphamide-actuated cardiotoxicity, at any rate partially, by its capacity to diminish oxidative and nitrosative pressure and to save the movement of cancer prevention agent catalysts just as its capacity to enhance the mitochondrial capacity and vitality creation.183 A comparative report was found with cyclosporine An and Doxorubicin. N. sativa oil diminished the resulting cyclosporine damage in rodent heart, exhibited by standardized cardiac histopathology, decline in lipid peroxidation, and enhancement in cancer prevention agent catalyst status and cell protein oxidation.184 Thymoquinone as a possibly particular cytoprotective operator, which may enhance cardiotoxicity without diminishing DOX antitumor movement (Figure 24).185
Zingiber officinale (Zingiberaceae)
The pharmacological exercises of ginger were mostly ascribed to its dynamic phyto compounds 6-gingerol, 6-shogaol, zingerone adjacent to different phenolics and flavonoids. 6-gingerol was accounted for as the most plentiful bioactive compound in ginger with different pharmacological impacts including cell reinforcement, pain relieving, mitigating and antipyretic properties. Likewise, different investigations demonstrated that 6-shogaol with most reduced fixation in ginger speak to all the more naturally actives contrasted with 6-gingerol. As per creature ponders ginger can possibly offer a characteristic elective dietary supplementation to traditional enemy of hypertensive operators, yet increasingly human preliminaries of ginger on hypertensive patients utilizing diverse measurements of an institutionalized concentrate are required.186 The antihyperlipidemic impact of ginger was bolstered by creature examines, gingerol forestalls HFD-incited hyperlipidemia by regulating the outflow of compounds critical to cholesterol digestion.187 Also, the bringing down impact of ginger on serum cholesterol might be because of the inhibitory impact of cholesterol biosynthesis and the change of cholesterol into bile acids by raising the movement of hepatic cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. Moreover, niacin, a supplement in ginger, might be a potential dynamic fixing in bringing down serum triglyceride level, expanding leeway of VLDL, improving hepatic take-up of LDL-c, and hindering cholesterol combination.188 Late investigation appears, 6-gingerol could diminish cell all out cholesterol and free cholesterol levels by means of up-direction of LDLR through initiation of SREBP2 just as up-control of cholesterol efflux-related qualities LXRα and ABCA1 (part 1 of human transporter subfamily ABCA).189 Day by day organization of 1g ginger diminishes serum triglyceride fixation, which is a hazard factor for cardiovascular illness, in peritoneal dialysis patients (Figure 25).190,191
The pharmacological activities of herbs or herbal segregates appear to positively regulate a few parameters ensnared in the pathogenesis of pulse, including however not restricted to ROS creation, VSMC phenotype, endothelial capacity, platelet initiation, star inflammatory flagging, and quality articulation. With such an expansive range of activities, one may anticipate that herbal cures will get considerably more consideration in the coming years, maybe emphasizing the requirement for further experimentations and clinical preliminaries. To be sure, the absence of adequate clinical preliminaries establishes a noteworthy impediment on the ir use right now. Of equivalent significance, it might be prudent that patients be fittingly taught, especially in connection to herbs whose utilization has been viewed as safe for a huge number of years (dark cumin, Chinese sage, coriander, garlic, ginger, ginseng, and tea), and has been bolstered by sound logical proof, for example, one dependent on clinical preliminaries with substantial populace gatherings. The recharged enthusiasm for the scan for new medications from characteristic sources, particularly from plant sources, has increased worldwide consideration amid the most recent two decades. The tropical downpour woods have turned into an essential purpose of this movement, principally because of the rich biodiversity they harbor, which guarantees a high decent variety of chemicals with the potential novel structures. Be that as it may, of this rich biodiversity, just a little segment has been concentrated for its medicinal potential. The proof exhibited is emphatically characteristic of the idea that herbs and plants are ending up some portion of proof based medicine in the avoidance and additionally treatment of CVD.
None.
Author declares that there is no conflicts of interest.

©2019 Mohiuddin. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.