eISSN: 2377-4304


Case Report Volume 6 Issue 5
1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Lincoln Medical and Mental Health Center, USA
2St. George's University, West Indies
3Department of Urology, Lincoln Medical and Mental Health Center, USA
4Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Houston Methodist St. John Hospital, USA
Correspondence: Dilfuza Nuritdinova, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Lincoln Medical and Mental Health Center, 234 East 149th Street, Bronx, New York, 10451, USA
Received: November 14, 2016 | Published: April 17, 2017
Citation: Rezai S, LoBue S, Bahl N, et al. A True Paraurethral Leiomyoma, A Case Report and Review of Literature. Obstet Gynecol Int J. 2017;6(5):114-117. DOI: 10.15406/ogij.2017.06.00218
Leiomyoma is a benign mass of smooth muscle cells that most frequently occurs in the gastrointestinal and genitourinary system. However, leiomyomas arising from the female urethra, especially paraurethral, are exceedingly rare. We present a case of a true paraurethral leiomyoma. The initial presenting complaints were dyspareunia, increased urinary frequency, and a 1.8 cm lesion in the anterolateral wall of the vagina that was suspicions of a Gartner's duct cyst. However, the patient was lost to follow-up for 5 years. On return, the patient continued to complain of dyspareunia, urinary frequency, suprapubic pain, and dysuria. The patient was treated for multiple instances of urinary tract infections (UTIs) without symptomatic improvement. A pelvic MRI demonstrated a 3.8 x 4.1 x 4.7 cm mass within the left anterior aspect of the lower cervix/vagina. Cystoscopy was notable for an unremarkable urethra with an anterior vaginal wall mass extrinsically pushing the bladder trigone without penetration into the bladder mucosa or communication with the ureter or vagina. A biopsy from the paraurethral mass revealed well-delineated cells with low mitotic figures encompassed in a fibrous capsule non-adherent to adjacent structures. The mass was subsequently excised through the anterior vaginal wall with no complications and complete resolution of symptoms.
Keywords: Benign urethral tumors, Female urethral leiomyoma, Fibroid, Leiomyoma, Paraurethral leiomyoma, Paraurethral mass, True paraurethral leiomyoma, Urethral fibroid, Urethral leiomyoma
A Leiomyoma is a benign mass of smooth muscle cells. The most frequent sites for these lesions are the gastrointestinal tract and the genitourinary system. Locations of leiomyoma in the genitourinary tract have been documented in the uterus, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder wall, and urethra in women.1 However, leiomyomas arising from the female urethra, especially paraurethral, are exceedingly rare.2 Of the reported urethral tumors, only a few have been reported as true paraurethral tumors.2-4 A true paraurethral tumor is defined as a mesenchymal neoplasm growing in the paraurethral space without any communication with the urethra, bladder, or vagina.4-6 We present a case of a paraurethral leiomyoma confirmed by cystoscopy and biopsy in a young female.
A 29-year-old non-pregnant, G5P2032 woman was seen in the gynecology clinic for a chief complaint of a vaginal mass, dyspareunia, and increased urinary frequency for the past year. The patient denied any abdominal pain, menorrhagia, or post-coital bleeding. On physical examination, the abdomen was soft and non-tender without organomegaly or masses. The uterus was normal size and anteverted with the adnexa free of masses and tenderness. On examination of the vagina a 2 cm round, mobile, and firm lesion was appreciated in the left anterolateral wall of the upper 2/3 of the vagina.
A pelvic ultrasound and abdominal/pelvis computed tomography (CT) scan imaging identified a 1.8 cm lesion in the anterolateral wall of the vagina consistent with a Gartner's duct cyst. The patient did not present for care for 5 years at which time, she continued to complain of dyspareunia, urinary frequency, suprapubic pain, and dysuria. She was treated for multiple instances of urinary tract infections (UTIs) without symptomatic improvement, despite the last urine culture being negative. A pelvic ultrasound and pelvic MRI were obtained. Real-time sonography demonstrated the mass illustrated in Figure 1. The uterus was anteverted measuring 7.8 x 5.0 x 4.4 cm in the sagittal, anteroposterior, and transverse dimensions. The endometrial stripe measured 0.70 cm in a 2-layer thickness, with its empty cavity. Follow up pelvic MRI (Figure 2 & 3) demonstrated a mass within the left anterior aspect of the lower cervix/vagina that by CT scan had enlarged since imaging preformed s5 years earlier. The radiologist impression was that of a mass with a differential diagnosis that included fibroid, fibroepithelial polyp, or an adenomyoma. Additionally, the MRI identified a small subserosal myoma in the uterine fundus.
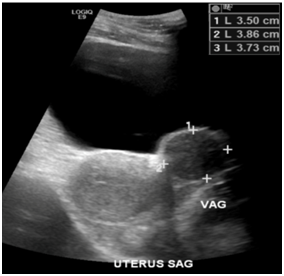
Figure 1 Real-Time transabdominal sonography of the pelvis. A small ovoid hypoechoic nodular lesion was evident within the upper left lateral periphery of the uterine cervix wall, which appeared to have further enlarged from the previous study almost six years prior. The mass now measures 3.50 x 3.86 x 3.73 cm in size.

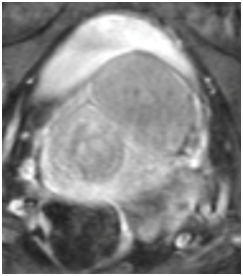
Figure 2 Pelvic T2 weighted MRI, Axial View, demonstrating a 3.8 x 4.1 x 4.7 cm hypointense mass within the left anterior aspect of the lower cervix/vagina.
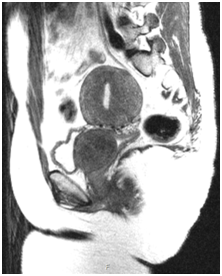
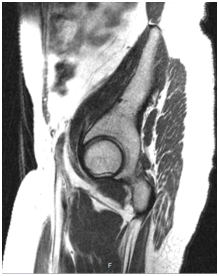
Figure 3 Pelvic MRI, Saggital View, Positive FFS, Series 2: Image 23 (Left Picture), Image 36 (Right Picture): showing Large solid-appearing lower cervical/vaginal mass.
Follow up appointment with gynecology recommended consultation with urology and cystoscopy due to the lesion’s close proximity to the urethra. The cystoscopy findings consisted of an unremarkable urethra with an anterior vaginal wall mass protruding into the bladder trigone without penetration into the bladder mucosa.
A biopsy was taken of the paraurethral mass during cystoscopy that revealed a leiomyoma. The patient was informed of the pathology results and options for treatment of the paraurethral leiomyoma. Surgical excision of the mass was agreed upon and consultation with urology for possible bilateral ureteral stent placement was scheduled.
Preoperative cystoscopy revealed a mass near the bladder trigone not invading the mucosa, but extrinsically pushing the trigone up. The right ureteral orifice was undisturbed by the mass. However, the left ureteral orifice had become partially compressed by the paraurethral mass with efflux visualized and not fully obstructed. Therefore, a stent was placed in the left ureteral orifice.
Transvaginal excision was undertaken (Figure 4-6) and there were no intraoperative complications. The excised specimen (Figure 6) was noted to be 6 cm (length) x 4 cm (width) x 3. 5 cm (height) in size and was sent to pathology for final determination. Gross pathology was described as a nodular mass weighing 46 grams with a firm cut surface of firm, whitish/tan whorled tissue. Final pathology was reported as leiomyoma.
One-week post operatively the left ureteral stent was removed by urology without complication. Additionally, three weeks postoperatively at a follow up gynecology appointment, the patient denied any urinary tract complaints, vaginal bleeding, or dyspareunia. On vaginal speculum examination, the wound was clean, healing well, and absent of induration or discharge. The cervix was clean and without discharge. On manual exam, no vaginal or adnexal masses were palpated and no tenderness was noted.
The distinction between vaginal, urethral, and paraurethral leiomyoma is often very difficult due to their close anatomic positioning. From anterior to posterior, there are four layers separating the exterior vaginal wall from the paraurethral space including epithelium, submucosa, fibromuscular banding containing smooth muscle, and periurethral fascia.7 Among women, urethral leiomyomas occur most commonly on the posterior urethral wall. However, vaginal wall leiomyomas most commonly occur on the anterior vaginal wall.8 Thus, paraurethral leiomyomas tend to occur between these areas in the vesicovaginal septum or paraurethral space. It is hypothesized that the extreme rarity of paraurethral leiomyoma is due to a drastic reduction of tissue found in the vesicovaginal septum or paraurethral space.9
Differentiating the anatomical location of the leiomyoma by the clinical presentation is also not reliable. Signs and symptoms of vaginal, urethral, and paraurethral leiomyoma may present very similarly. Common complaints of all three include urinary tract infection, a mass, dyspareunia, urinary retention, hematuria, dysuria, dyspareunia, and obstructive voiding symptoms.6,10-15 Patients also may be completely asymptomatic. Overall, the median age for these types of neoplasms ranges from 40 to 44.16-17
Our patient presented with complaints much earlier than those of the median. At 29 years of age, the patient presented with a vaginal mass, dyspareunia, and increased urinary frequency. A 2cm round, mobile, and firm lesion was found in the left anterolateral wall of the upper 2/3 of the vagina during the physical exam. A Gartner's duct cyst was initially suspected. However, the patient was lost to follow-up for 5 years. On return, the patient continued to have dyspareunia, urinary frequency, suprapubic pain, and dysuria. The mass in this woman was thought initially to be related to an infectious process or a urinary tract infection. She was treated for multiple instances of urinary tract infections (UTIs) without symptomatic improvement. A pelvic MRI demonstrated a 3.8 x 4.1 x 4.7 cm mass within the left anterior aspect of the lower cervix/vagina. Common differentials for a mass in this area include Bartholin gland cyst, Gartner's duct cyst, urethral carcinoma, urethral caruncle, urethral diverticulum, urethral mucosal prolapse, vaginal wall cysts, endometriosis, skene duct abscess, fibroid, fibroepithelial polyp, or an adenomyoma.9,17
Imaging in the form of ultrasound and MRI provided useful preoperative diagnostic information. High-frequency transvaginal ultrasound shows leiomyomas as solid tumors with a homogeneous internal echo structure.18 Ultrasound provides a quick and effective means of locating the mass in relationship to the urethra as wells as ruling out infiltration and diverticula.18 Multi-slice MRI is also very effective. It can be used preoperatively to determine the precise location of the mass with respect to the urethra as well as rule out other disorders. Neoplasms of muscular origin are portrayed as hypointense or isointense on T1-weighted images or hyperintense or isointense on T2-weighted images.18,19
In our case, cystoscopy noted an unremarkable urethra with an anterior vaginal wall mass extrinsically pushing the bladder trigone up without penetration into the bladder mucosa. A biopsy from the paraurethral mass revealed well-delimited cells with low mitotic figures encompassed in a fibrous capsule, not adhered to adjacent structures. A definitive diagnosis of paraurethral leiomyoma was made.
Although the pathogenesis of vaginal, urethral, and paraurethral leiomyomas is not certain, some reports have documented hormonal dependence to estrogen. One case report describes a fluctuation of the size of the mass during pregnancy. The mass enlarged in the antepartum and regressed in the postpartum.20,21 Another study found estrogenic receptors on immunohistochemistry staining.22 Our patient’s last live birth was ten years prior to presentation to our clinic, although she had 3 medical Voluntary Termination Of Pregnancy (VTOP), since her last live birth.
Surgical intervention is the standard of care for symptomatic patients.9,16 Additionally, the surgical technique will differ according to the site of the mass. A vaginal approach should be used for excision of leiomyomas in the anterior urethra, near or protruding through the meatus, and paraurethral leiomyomas. On the other hand, transurethral excision is used for urethral leiomyomas attached to the middle or posterior urethra.23,24 Resection in our patient was performed vaginally through the anterior vaginal wall. Also, a stent in the left ureteral orifice was placed due to the close proximity of the lesion.
A true paraurethral leiomyoma is often defined as a mesenchymal neoplasm growing in the paraurethral space or vesicovaginal septum with no communication with the urethra, bladder, or vagina. Our patient meets the criteria with a 3.8 x 4.1 x 4.7 cm mass which did not communicate with the urethra, bladder, or vagina. However, verifying the exact anatomic location of the mass remains difficult and must be inferred through histology.
According to Navarro et al.,25 paraurethral leiomyoma presented as benign neoplasms of mesenchymal origin contained in a fibrous capsule not adherent to adjacent structures,25 a histopathologic presentation identical to our case. The mass was also in very close proximity to the left ureter, partially obstructing the view on imaging as well as extrinsically applying pressure to the bladder trigone. Although the mass has a close proximity to the ureter, it is unlikely a urethral leiomyoma for several reasons. For one, urethral leiomyomas can frequently be seen protruding through the urethra.26 Secondly, surgical dissection is highly associated with damage to the urethral mucosa. A removed leiomyoma that results in no disruption to the urethral mucosa is unlikely urethral in origin.26 Lastly, urethral leiomyomas tend to be fixed in a position compared to paraurethral leiomyomas which are often mobile.26 Our patient had a mobile mass which was not protruding through the urethra. Also, no disruption or injury to the urethra occurred during excision of the mass. Thus, there is evidence that the patient presented with a true paraurethral leiomyoma. Nevertheless, the clinical and histologic courses of paraurethral leiomyomas are identical to vaginal and urethral leiomyomas. Strict classification holds more academic merit as there has been confusion regarding accurate classification in the literature.26,27
None.
None.

©2017 Rezai, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.