eISSN: 2377-4304


Objective: To describe a case of a small cell neuroendocrine tumour of the cervix.
Case report: a 46 year old lady was diagnosed with an infiltrative high grade small cell neuroendocrine adenocarcinoma which was infiltrating the uterus, after she presented with unprovoked vaginal bleeding. Surgery was done successfully, after which she was referred for chemotherapy.
Discussion: MR imaging was essential in staging the tumour. It is also important to appreciate the rarity of such a diagnosis and the intricacies of its management
Conclusion: A multidisciplinary approach in such cases is essential, as well as appropriate counselling of the patient.
Cervical malignancy is the fifth deadliest malignancy and the second most common worldwide killing 9 per 100,000 per year.1 Neuroendocrine tumours of the cervix account for a mere 2% of the total cervical malignancies,2 exhibiting features of endocrine and neural tissue. Usually they follow a rapid progression and poor prognosis.
A 46 year old patient with 2 previous normal vaginal deliveries presented with unprovoked vaginal bleeding. On examination an erythematous cervix was noted and the cervix was adherent to the posterior wall of the vagina. The patient was scheduled for an urgent colposcopy and hysteroscopy.
Hysteroscopy was attempted yet failed due to a highly stenosed and deformed cervical os. Colposcopic histology showed an extensive necrotic invasive small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma with extensive synaptophysin expression. MRI imaging illustrated a 4cm in diameter mass within the cervix (Figure 1) which extended partially to the lumen of the uterine body. There was no evidence of extension outside the uterine corpus or to the lower third of the vaginal wall. No pelvic lymphadenopathy was noted. The patient was scheduled for surgery and a radical hysterectomy with internal iliac node sampling was performed. This was done after discussion with the oncologists since unusual cell types are more likely to disseminate directly into surrounding tissues, as happened in this case as the cervix was adherent to the posterior wall of the vagina, and via lymphatic pathways, with the commonest route being via the internal iliac nodes. It can also spread haematogenously, which did not happen in this case.3–5
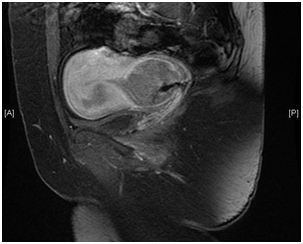
Figure 1 MR image showing the 4cm in diameter neuroendocrine small cell tumour on the cervix with uterine extension.
Histology showed an infiltrative high grade small cell neuroendocrine adenocarcinoma infiltrating the endocervix and isthmic zones of uterine body perforating the cervix, pT2Nx Figo stage 2. The patient was discharged from hospital in good health following surgery with subsequent oncology follow-up for chemotherapy.
Neuroendocrine tumors of the cervix are extremely rare and rapidly progressing accounting for only 2% of cervical carcinomas.2 They usually arise from the diffuse neuroendocrine cell system within the cervix. The site of origin and histologic subtype determine the prognosis. There are four types of neuroendocrine tumours: carcinoid and atypical carcinoid include the well differentiated subtypes whilst small cell and large cell tumours are the poorly differentiated groups. The latter having a poorer prognosis because of the poor differentiation. Most of such tumours express synaptophysin and chromogranin A by immunochemistry thus well and poorly differentiated tumours are grouped together due to such marker expression.2,6 This makes the degree of expression not correlate with the severity of the malignancy.
Small cell malignancy being the most common with 300 cases described is associated with human papilloma virus subtype 187 and is divided into hypercalcaemic and pulmonary type making it most sensitive to platinum compounds chemotherapy.8 Large cell neuroendocrine tumour accounts for only 78 reported cases in the medical literature.9 The aetiology is poorly understood in view of the low incidence; however, many believe that human papilloma virus and smoking may have a role. Unlike other forms of cervical cancer, this form does not have a pre-invasive lesion that can be detected by screening.7
Such tumours generally present like other forms of cervical carcinoma, including post-coital bleeding, increased vaginal discharge and dyspareunia. If more advanced it can also present with cachexia, weight loss, abdominal pain and symptoms of metastatic disease. If endocrinologically active, it can also lead to hypercalcaemia, Cushing syndrome and syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion.10,11
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a gold-standard imaging modality for such tumours. A tumour of 4cm or less is amenable to surgery followed by chemotherapy. A tumour of >4cm is amenable to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. A late stage or candidates not fit for surgery should have combination chemotherapy and chemo radiation following the Hoskins protocol.2
The prognosis varies from 80% 3year survival if grade 1-2 to 38% 3 year survival if grade 3-4.12,13 However, in cases where the tumour was <4cm there are usually no recurrences.14 Distant sites of recurrence especially lung and bone (28%) are described being more common than local spread (13%),15,16 especially if the tumour is mixed and larger than 4cm.
Counselling and adequate investigations are required for proper management of such rare form of cervical malignancy. A multidisciplinary approach is best advised to give good standards of care.
None.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.

© . This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.