MOJ
eISSN: 2374-6920


Research Article Volume 1 Issue 4
Department of Microbiology and Biotechnology, Bangalore University, India
Correspondence: Savitha J, Department of Microbiology and Biotechnology, Bangalore University, Bangalore-560056, Karnataka, India, Tel 8022961461
Received: August 26, 2014 | Published: September 22, 2014
Citation: Bhargavi SD, Praveen VK, Savitha J. Bioinformatic comparative analysis of lovastatin gene cluster in endophytic fungi and a soil fungus, Aspergillus terreus. MOJ Proteomics Bioinform. 2014;1(4):114?117. DOI: 10.15406/mojpb.2014.01.00026
Genes responsible for lovastatin production in certain fungi are often clustered (64kb DNA). In the present study, we report the comparative analysis of the genome of sixty one endophytic fungi and a soil fungus for the presence of lovastatin gene sequences. Nucleotide sequences were obtained from NCBI and aligned with lovastatin gene cluster sequence (AF141924.1& AF141925.1). DNA sequences that are identical to lovastatin gene were identified in Aspergillus terreus, (AH007774.1), a soil isolate, whereas all the other sixty one endophytic fungi including a species of Aspergillus terreus showed very limited or no homology with the lovastatin gene cluster.
Keywords: lovastatin, gene cluster, alignment, endophytic fungi, soil fungus, aspergillus terreus
Fungi belonging to different genera produce lovastatin, a secondary metabolite that competitively inhibits the enzyme Hydroxyl Methyl Glutaryl Coenzyme A (HMG CoA) reductase, which is involved in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Lovastatin is an effective drug for treatment of hyperlipidemia, a condition in which there is a considerable elevated level of lipids in blood.1 Owing to its biomedical importance, research on lovastatin and lovastatin producing microorganisms has intensified in recent years. Specifically, terrestrial filamentous fungi and aquatic filamentous fungi have been explored extensively but reports on fungi inhabiting unusual environment are meagre.
Genes responsible for secondary metabolism in fungi are often linked or clustered. In recent years, there has been an exponential increase in the number of reports on the whole genome sequence of fungi in general, and pharmaceutically important fungi, in particular. Comparison of these sequences with the gene sequence of interest has proved to be an excellent resource and promising approach for recombinant DNA technology.2
Studies on structural analysis of the lovastatin gene in Aspergillus terreus revealed that there were 18 open reading frames (ORF) within the cloned 64kb DNA; 13 of which had been functionally determined by basic local alignment search tool (BLAST). The gene cluster consists of the lovastatin nonaketide synthase gene (lovB), lovastatin diketide synthase gene (lovF), enoyl reductase gene (lovC), transesterase gene (lovD), HMG-CoA reductase gene (ORF8), regulatory genes (lovEandORF13) which encodes a GAL4-like transcriptional factor and cytochrome P450 monooxygenase gene.3
In our previous study, we screened endophytic fungi isolated from medicinal plants as well as terrestrial fungi isolated from soil for their ability to produce lovastatin using wheat bran as substrate. The isolate that produced copious amounts of lovastatin was identified as Aspergillus terreus (KM017963). None of the 54 endophytic fungi isolated from medicinal plants produced any detectable levels of lovastatin.4 This present study was initiated to determine if the lack of lovastatin production by endophytic fungi is due to absence of genetic elements associated with lovastatin biosynthesis or due to other physiological factors.
A total of sixty two filamentous fungi including two strains of Aspergillus terreus were considered for the study. Sixty one out of sixty two isolates were endophytic fungi and one was a soil isolate (Aspergillus terreus). Whole genome nucleotide sequences of all the fungi and lovastatin gene cluster sequence (AF141924.1 & AF141925.1) used in the present study were obtained from NCBI genbank database in the FASTA format. Both AF141924.1& AF141925.1 represents the gene cluster of lovastatin. Pair wise alignment tool of European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL-EBI) was used to compare lovastatin gene cluster sequence with the whole genome sequences obtained from genbank database. Each Nucleotide sequence from genbank is used as a query sequence for pair wise alignment.5
Pair wise alignment starts between query sequence (lovastatin gene cluster) and the hit sequence (whole genome nucleotide sequences of different fungi), identifies regions of local similarity between the 2 sequences and thus calculates the statistical significance of matches. This offers a convenient approach to calculate the percentage identity.6
A pair wise score is calculated for every pair of sequences that are aligned. Percent identity is calculated by multiplying the number of matches in the pair by 100 and dividing by the length of the aligned region, including gaps. Score is calculated by dynamic programming (slow but accurate) or by the method of Wilbur and Lipman (extremely fast but approximate).7,8 Percent match was calculated using the formula:
Percent Identity=(Matchesx100)/Length of aligned region (with gaps)
The analysis of the whole genome sequence of fungi has proven useful and provided many new insights into secondary metabolism.9,10 We have previously demonstrated that none of the 54 endophytic fungi isolated from medicinal plants produced any detectable levels of lovastatin even after 10 days of incubation.4 It was of interest that an endophytic strain of Aspergillus terreus did not produce lovastatin while a soil isolate of the same fungus produced significant levels of Lovastatin under identical growth conditions. Therefore, an attempt was made to analyze and compare the genetic makeup of these two isolates of Aspergillus terreus and other endophytic fungi in relevance to lovastatin production using bioinformatics tool.
The data set consisted of 62 filamentous fungal whole genome sequences. Sixty one were endophytes including a strain of Aspergillus terreus (NT165934.1), and a soil isolate of Aspergillus terreus (AH007774.1) which were matched with the available lovastatin gene cluster (AF141924.1 & AF141925.1). All endophytic fungi utilized in this study showed much less homology to lovastatin DNA sequences including an endophytic fungi strain of Aspergillus terreus (Figure 1). On the other hand, the soil isolate Aspergillus terreus (AH007774.1) showed perfect homology to lovastatin DNA sequences with 100% identity with lovastatin gene cluster sequence (55328/55328) (Table 1, Figure 1). These results are in perfect agreement with our previously published results4 on the lack of lovastatin production by endophytic fungi and suggest that, the lack of lovastatin production may be due to the absence of lovastatin encoding DNA sequences.
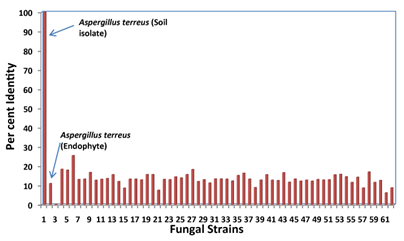
Figure 1 Percent identity for pairwise alignment of different fungi with lovastatin gene cluster DNA sequences.
Sl. no |
Fungal organism |
NCBI accession number |
Percent identity |
1 |
Aspergillus terreus (soil fungus) |
AH007774.1 |
100 |
Endophytic fungi |
|||
2 |
Aspergillus terreus NIH2624 |
NT_165934.1 |
11.02 |
3 |
Colletotrichum gloeosporioides Nara gc5 |
KB020205.1 |
17.74 |
4 |
Colletotrichum fioriniae PJ7 |
NW_006889833.1 |
18.44 |
5 |
Colletotrichum higginsianum IMI 349063 |
CACQ02000033.1 |
17.98 |
6 |
Cucmissativus |
KB722789.1 |
25.56 |
7 |
Glomerella graminicola M1.001 |
GG697332.1 |
13.14 |
8 |
Glomerella graminicola M1.001 |
GG697331.1 |
13.31 |
9 |
Glomerella graminicola M1.001 |
CM001021.1 |
16.81 |
10 |
Ascocoryne sarcoides NRRL 50072 |
KB205939.1 |
12.71 |
11 |
Ascocoryne sarcoides NRRL 50072 |
KB205940.1 |
13.25 |
12 |
Ascocoryne sarcoides NRRL 50072 |
KB205941.1 |
13.64 |
13 |
Leptosphaeria maculans |
NW_003533878.1 |
15.64 |
14 |
Pestalotiopsis fici W106-1 |
KI912109.1 |
12.09 |
15 |
Pestalotiopsis fici W106-1 |
KI912110.1 |
8.63 |
16 |
Diaporthe longicolla MSPL 10-6 |
KI547258.1 |
13.3 |
17 |
Diaporthe longicolla MSPL 10-6 |
KI547259.1 |
13.3 |
18 |
Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordeiDH14 |
HF938678.1 |
12.9 |
19 |
Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordeiDH14 |
HF942516.1 |
15.7 |
20 |
Puccinia striiformis f. sp. triticiCY32 |
KI515781.1 |
15.7 |
21 |
Puccinia striiformis f. sp. triticiCY32 |
KI515782.1 |
7.55 |
22 |
Puccinia striiformis f. sp. triticiCY32 |
KI515783.1 |
13.2 |
23 |
Magnaporthe oryzae |
NW_003803360.1 |
13.06 |
24 |
Rhizoctonia solani AG-3 Rhs1AP strainAG-3 |
JATN01000001.1 |
14.49 |
26 |
Rhizophagus irregularis DAOM 181602 strain DAOM 197198 |
KI274019.1 |
13.92 |
27 |
Rhizophagus irregularis DAOM 181602 |
KI274025.1 |
15.67 |
28 |
Verticillium dahliaeJR2 |
CM001863.1 |
18.33 |
29 |
Ashbya gossypii ATCC 10895 |
NC_005785.6 |
12.09 |
30 |
Verticillium dahliae JR2 |
CM001864.1 |
13.04 |
31 |
Ustilago maydis 521 |
NW_101240.1 |
11.3 |
32 |
Phanerochaete chrysosporium RP-78 |
DQ097842.1 |
13.4 |
33 |
Sporisorium reilianum SRZ2 |
FQ311472.1 |
13.4 |
34 |
Nectria haematococca MPVI |
GG698896.1 |
13.33 |
35 |
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum |
NW_001820835.1 |
12.34 |
36 |
Podospora anserina |
NW_001939194.1 |
42.98 |
37 |
Myceliophthora thermophila ATCC 42464 |
CP003008.1 |
16.4 |
38 |
Claviceps purpurea 20.1 |
CAGA01000035.1 |
13.3 |
39 |
Cochliobolus sativus ND90Pr |
NW_006912048.1 |
8.92 |
40 |
Claviceps purpurea |
CAGA01000001.1 |
12.82 |
41 |
Microbotryum violaceum p1A1 |
GL541643.1 |
15.62 |
42 |
Alternaria brassicicola strain Abra43 |
AY700092.1 |
12.799 |
43 |
Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici |
GL385395.1 |
12.61 |
44 |
Alternaria brassicicola brassinin |
KC814178.1 |
16.67 |
45 |
Trichoderma atroviride IMI 206040 |
ABDG02000003.1 |
11.7 |
46 |
Botryotinia fuckeliana B05.10 |
JH78064.1 |
13.36 |
47 |
Marssonina brunnea |
JH921428.1 |
12.26 |
48 |
Botryotinia fuckeliana BcDW1 |
KB707673.1 |
12.79 |
49 |
Oidiodendron maius |
EU386164.1 |
12.26 |
50 |
Bipolaris zeicola |
KI964537.1 |
13.12 |
51 |
Fusarium asiaticum strain SCK04 |
KF765494.1 |
12.87 |
52 |
Marssonina brunnea |
NW_006763052.1 |
13.02 |
53 |
Melampsora larici-populina |
GL883090.1 |
15.54 |
54 |
Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici |
DS178262.1 |
15.83 |
55 |
Penicillium digitatum |
JH993674.1 |
14.6 |
56 |
Blumeria graminis |
HF943549.1 |
11.61 |
57 |
Mycosphaerella graminicola |
CM001196.1 |
14.3 |
58 |
Cochliobolus heterostrophus |
KB445584.1 |
8.76 |
59 |
Dothistroma septosporum NZE10 |
KB446544.1 |
16.99 |
60 |
Serpula lacrymans |
GL945474.1 |
11.64 |
61 |
Heterobasidion irregulare |
KI925456.1 |
12.66 |
62 |
Pyrenophora teres |
GL537212.1 |
6.21 |
Table 1 List of fungi exhibiting their percent identity with lovastatin gene cluster DNA sequences
The presence of lovastatin gene cluster in lovastatin producing Aspergillus terreus (soil in origin) is well documented.11,12 However, an endophytic strain of the same organism does not possess DNA sequences homologous to lovastatin genes. Considering the endophytic relationship with host plant systems, it may be an advantage for a fungal strain not to produce secondary metabolites that may interfere with plant growth promoting characteristics.13 Thus, there probably was no need for retaining/acquiring lovastatin biosynthetic pathway genes by these endophytic fungi isolated from medicinal plants. This is the first report on comparative analysis of genomic DNA sequence of Aspergillus terreus that is both endophytic and non-endophytic in nature. The lovastatin gene cluster includes 18 genes that are involved in lovastatin biosynthetic pathway and, of which LovE and LovF encode for transcriptional regulatory factor and diketide synthase (DKS), respectively.3,14 Further studies with the endophytic fungi at the molecular level will categorically confirm our previous biochemical4 and the present bioinformatic study.
The results of this present analysis provide physical evidence that the apparent inability of endophytic fungi to produce lovastatin secondary metabolite13 is due solely to the lack of DNA sequences that are identical or homologous to lovastatin gene present in lovastatin producing organism. The lack of production of lovastatin by endophytic fungi is apparently not due to suboptimal physiological conditions or altered regulation of lovastatin biosynthetic pathway enzymes. Owing to the symbiotic association with plant system, the lack of lovastatin homologues in endophytic fungi is of considerable ecological importance and further confirms our hypothesis that endophytic fungi from medicinal plants appear not to produce lovastatin.
The authors would like to thank the financial support provided by the Department of Science & Technology (DST), Govt. of India, vide grant number -DST/SO/FNo.SERB.SR/SO/PS/046/2011.
The author declares no conflict of interest.

©2014 Bhargavi, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.