- Many bacteria, in particular, have unpredictable susceptibilities to antimicrobial agents, and their susceptibilities can be measured in vitro to help guide the selection of the most appropriate antimicrobial agent.
Susceptibility to antibiotics
- The term susceptible means that the microorganism is inhibited by a concentration of the antimicrobial agent.
- The term resistant indicates that the microorganism is resistant to a concentrations of the antimicrobial agent.
Minimum inhibitory concentration [MIC]
- The lowest concentration of antimicrobial agents that will inhibit the visible growth of a microorganism. Widely used in the comparative testing of new agents.
Dilution methods (agar dilution or broth dilution)
- Used to determine the [MICs] and are the reference methods for antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
Agar dilution test
- Is the standard method for determining levels of microbial resistance to an antimicrobial agent.
- Serial dilutions of the test agent are made in a agar microbial growth medium which is inoculated with a few amount of microorganisms and incubated for a prescribed time.
- The lowest concentration (highest dilution) of test agent preventing the appearance of growth is considered to be the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC).
- Different enrichment and selective medium.
- Culture.
- Subculture.
- MIC test.
MIC medium
- Clear choice for a reference medium remains to be determined,
- Nutrient agar/broth: used for the cultivation of a wide variety of microorganisms.
- Brain-Heart Infusion agar
- Mueller-Hinton ll agar
- Media for Bacterial identification
- EMB agar.
- MacConkey agar.
- Triple Sugar Iron agar.
- Nutrient agar/broth.
Antimicrobial agents tested (Figure 1–Figure 4)
- Lincomycin.
- Cefaclor.
- Ampicillin.
- Gentamicin.
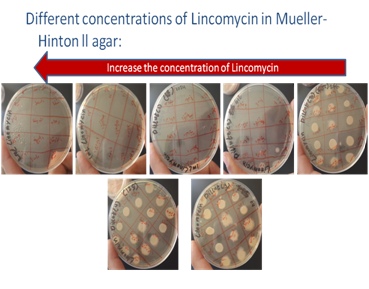
Figure 1 Increase the concentration of Lincomycin.
Antimicrobial agents Tested
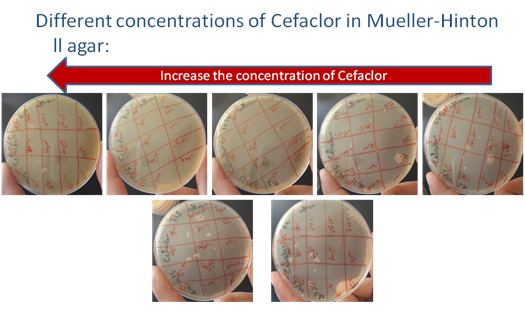
Figure 2 Increase the concentration of Cefaclor in Muller-Hinton II agar.
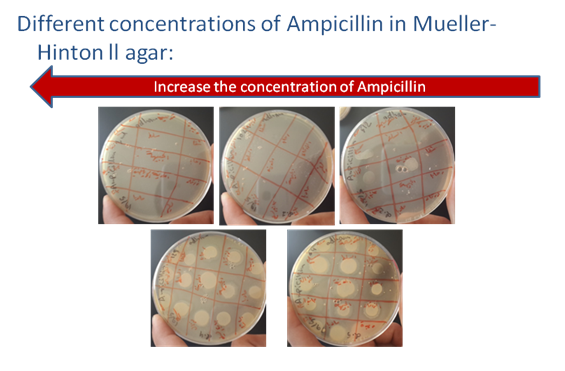
Figure 3 Increase the concentration of Ampicillin in Muller-Hinton II agar.

Figure 4 Increase the concentration of Gentamycin Muller-Hinton II agar.
Identification: matching characteristics of an unknown to lists of known organisms.
- Several culture and subculture for the bacterial samples done to reduce the number of bacterial colonies that have been isolated.
- Three different types of media used for identification, (EMB agar, Triple Sugar Iron agar, and MacConkey agar).
- For each sample, the three different types of media showed the same result (same species, which is identified by the morphology).
The author declares no conflict of interest.

© . This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the,
which
permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.


