MOJ
eISSN: 2574-9722


Research Article Volume 2 Issue 3
1School of Pharmacy, Suresh Gyan Vihar University, India
2Ayushraj Enterprises Pvt Ltd, India
Correspondence: Jitendra Mittal, Ayushraj Enterprises Pvt Ltd, Village Mansinghpura, Dehmi Begus Road, Ajmer Road Jaipur, India
Received: October 22, 2017 | Published: November 21, 2017
Citation: Jain M, Gilhotra R, Singh RP, et al. Curry leaf (Murraya Koenigii): a spice with medicinal property. MOJ Biol Med. 2017;2(3):236–256. DOI: 10.15406/mojbm.2017.02.00050
The all the traditional system of medicines are included in the account of AYUSH. The AYUSH department included the following system of medicines Ayurvedic, Yoga, Unani, Siddha and Homeopathy (AYUSH). These systems help us to eradicate or help in to overcome the problems related to the allopathic medicines such as side effect, drug resistance and adverse effect of the drug. Due to all these reasons the plant source for medicinal purpose are highly prefer. This review article describes the medicinal importance of the medicinal plant Murraya koenigii. The therapeutic value of Murraya koenigii extract for the various diseases with its other pharmacognostic features such as morphology, growth constraints, biochemical composition and biological activities. This review contains the description of Murraya koenigii with its pharmacological activities of isolated compounds and bioactivity of extract on different animal models in various laboratories. In addition to that, it highlights its potential to have a various type of pharmacological activity.
Keywords: medicinal plant, plant extract, phytochemistry, biological activity, research work
India is frequently known by enormous biodiversity of medicinal plants. Among them Murraya koenigii have a lots of bioactive principles due to which plant has been proven as the medicinally important plant but least or no attention received by the scientist. Murraya koenigii is proven as the natural medicinal plant.1 There are different forms of Murraya koenigii due to which they are found as the useful plant such as extract, essential oil, or directly used due to the presence of following active constituent bismahanine, murrayanine, murrayafoline-A, bi-koeniquinone-A, bismurrayaquinone, mukoenine-A, mukoenine-B, mukoenine-C, murrastifoline, Murrayazolinol, murrayacine, murrayazolidine, murrayazoline, mahanimbine, girinimbine, koenioline, xynthyletin, koenigine-Quinone A and koenigine-Quinone B for therapeutic purpose by folk people.2–5 Many medicines such as digitalis, vinblastine, aspirin and quinine has plant as a source of origin for example foxglove (Digitalis purpurea), willow bark (Salix spp.), quinine bark (Cinchona officinalis). For therapeutic or prophylactic purposes medicinal plant are used. For the therapeutic properties of medicinal plants presence of secondary metabolites plays a very important role such as alkaloids, flavonoids, terpinoids, vitamins, tannins etc., these all are the secondary metabolites of the plant as active constituent.6 These all secondary metabolites of plant physiologically affect the body at different stages of body development and make the body disease free. The plant Murraya koenigii belonging to the family Rutaceae is largely growing plant throughout the spring, summer and in rain fall season in every part of the tropical region up to the height of 1500 to 1655m from sea level.6,7 It is also known as Curry Leaf English, Mitha Neem in Hindi, and Karuveppilei in Tamilnadu and Surabhinimba in Sanskrit.8
Synonym in Indian Language
Curry Leaf (English), Karepaku (Andhra Pradesh), Narasingha (Assam); Barsanga, Kartaphulli (Bengal); Gorenimb (Gujrat); Mitha Neem (Himachal Pradesh); Kathnim, Mitha Neem, Kurry Patta (Hindi); Karibeva (Karnataka); Kariveppilei (Kerala); Gandhela, Gandla, Gani (Kumaon); Bhursanga (Orissa); Mahanimb (Sanskrit); Karivempu (Tamilnadu).
Synonym in other language
Burmese: Pindosine; Danish: Karrry bald; Dutch: Kerriebladeren; English: Curry leaves; French: Feuilles de cury; German: Curryblatter; Indonesian: Daun kari; Italian: Fogli de Cari; Spanish: Hoja.
Biological source
The species name commemorates the botanist Johann König. The genus Murray commemorates Swedish physician and botanist Johann Andreas Murray who died in 1791. Hence the botanical name of the curry leaves is Murraya koenigii.9
Taxonomic status
History
The history of curry leaves are seen in early 1st to 4th century AD. In Tamil and Kannada literature it was updated as word ‘kari’ with its uses. The word now popularly used for the Murraya koenigii is curry leaf which is originated from Tamil word Kari which means as ‘spiced sauce’.10 In the early literatures of Tamil and Kannada the use of Murraya koenigii is described as the flavouring agent for the vegetables.11 Today Murraya koenigii are grown as the cultivated crop in India, Sri Lanka, Southeast Asia, Australia, Pacific Islands and Africa as flavouring agent for the food.12
Distribution
Murraya koenigii originates from east and south part of India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, China and Hainan but widely cultivated in South-East Asia and some parts of the United States and Australia.13 It grows throughout India up to the height of 1500 to 1655m from sea level and in the Andaman Islands.14 It is also available in other part of Asian region like in moist forests of 500-1600m15 height in Guangdong, Shainan, S Yunnan (Xishuangbanna), Bhutan, Laos, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Vietnam. Together with South Indian immigrants, curry leaves reached Malaysia,16,17 South Africa and Reunion Island.3,4 Out of the 14 global species that belong to the genus Murraya, only two are known to be found in India, which is Murraya koenigii (Spreng) and Murraya paniculata (Jack).18,19 Can grow in full sun or light shade.Murraya koenigii is distributed from south and East Asia to Australia.20–22
Curry Leaf plant to have flowers and vibrant green leaves throughout the spring, summer and in rain fall. The leaves drop off during its’ resting period in the winter months. They like full sun, well-drained soil, which should be the dry side and they need fertilizer in the month of summer.23,24 The fruiting season was observed to continue from the end of June to the end of August, and the July is considered as the peak fruiting season. In India, harvesting of leaves started from 15 months after planting out and collection of leaves repeated in every 2 to 3 months.25 In cold countries such as in Southern California, South Texas and South Florida, outdoors growth needs protection from freezing. Seeds are fragile so handle with care.26
Tree
Murraya koenigii is semi deciduous, unarmed aromatic small spreading shrub or tree with strong woody stem but slender with the stem which is dark green to brownish in colour the tree is 4–8.7m (13–31 feet) tall, with a trunk up to 81cm27 diameter.28The diameter of main stem is about 16cm.28,29
Flower
The flowers of curry leaves is small, white fragrant and funnel- shaped, regular, pentamerous, stalked, complete, ebracteate, hypogynous, persistent, inferior, green, corolla, polypetalous, androecium, polyandrous, lanceolate, stigma, bright, sticky, style, short, ovary, inflorescence, a terminal cyme, the diameter of a flower is 1.12cm in the fully opened form, each cluster bear approximately 60 to 90 flowers at a time after flowering at once, 5-lobed calyx, with petals in having length 5 mm and the petals are 5 in number, with stamen in number 10 and in small in size approximate number 4 mm, dorsifixed, arranged into circles, with long superior gynoecium with size 5 to 6mm.20 Curry tree flowers have a sweet fragrance, bisexual with self-pollinated for produce black berries in small size with shiny appearance containing a large visible seed with the number 1.21
Leaf
Curry leaves are aromatic in nature having characteristic aroma, leaves of curry leaves are shiny and smooth with paler undersides.30 Leaves are pinnate, exstipulate, having reticulate venation and having ovate lanceolate with an oblique base,30 with 11-21 leaflets whose size description is each leaflet is 0.79–1.57inch long and 0.39–0.79 inch broad. Leaflets are short stalked, alternate, gland dotted and having 0.5-cm-long petiole The leaf margins are irregularly serrate.20,31 The yield of a bush in approximately found about 480 g in three to four pickings.32
The stem of Murraya koenigii is brown to dark green in colour, with dots on the bark like small node on it, when the bark was peeled off longitudinally under the exposing the white wood underneath; the girth of the main stem is 16cm up to 6 meters in height and 15 to 40cm in diameter.33
Fruit
Fruits of the Murraya koenigii occur in cluster form varies in 32 to 80 in number.34 The fruits are in the ovoid or subglobose and small in size in the spinach green colour seed in one or two number which are enclosing each other in thin pericarp.6 The fruits are 1 to 1.2cm in the diameter with length 1.4 to 1.6cm, purple black after ripening and they are edible and yields 0.76% of a yellow volatile oil.35 Curry leaf fruit is 11mm long and weigh about 445mg Fruits. The plant produces small white flowers which can self-pollinate. The weight of pulp is 880mg and the volume is 895 microliters.14,10 The seeds of the Murraya koenigii are poisonous in nature and should not be consumed for any purpose.6
Microscopy
The microscopically view of Murraya koenigii is as follow:
Leaves: The leaves have the obliquely ovate or fairly rhomboid with acuminate obtuse or acute apex. The petiole is about 20 to 30cm in length and the leaves have reticulate venation and dentate margin with an asymmetrical base.36 In the microscopic studies, it was elucidate that the stomata were distributed on adaxial surface and the adaxial surface does not have stomata and the type of stomata that was found is anomocytic. The transverse section of the leaves has a layer of epidermis which is composed of rectangular cell. The upper epidermis was covered with cuticle and in the midrib the epidermis has 1 to 4 layers of collenchymatous hypodermis with 2-5 layers of chlorenchyma cells.37 The ground tissue is oval to polygonal parenchyma cell with vascular bundle. Calcium oxalate found in sandy and prismatic crystals.38 The curry leaf shows the presence of unicellular trichomes with obliterated lumen, parenchymatous pith in petiole, long pericyclic fibre in the midrib, large cruciferous stomata and prismatic calcium oxalate crystals. Fresh leaves on steam distillation under pressure yield 20.6% of volatile oil and without pressure less than 2%.39,40 The fibres measure 2000μ in length.
Root: The root shows tetrarch to pentarchstele, phelloderm fibres are absent and concentric grains of parenchyma are present.41
Powder: Green in colour with no distinct odour or taste, unicellular, bent or curved trichomes, two layered palisade, portion of secretory canals, well developed pericyclic fibres and a few prismatic crystals of calcium oxalate are the important identifying characters.41
Murraya koenigii is very rich source of organic compounds with different chemical composition such as alkaloids, flavonoids carbohydrates, and sterol is present in the plant extract prepared in solvents such as petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, chloroform, ethanol and water.42,43,34,44,45 The major chemical constituents are explained For the confirmation of the phyto-constituents in the plant extract, various numbers of tests were performed:
The essential oil composition of Murraya koenigii was studied and then presence of D-Sabinene, D-α-Terpinol, di-α-phellendrene, D-α-pinene, caryophyllene and dipentene 47 and the property of Murraya koenigii oil is explained (Table 1).
Sl. No |
Property |
Value |
1 |
Specific Gravity (25°C) |
0.9748 |
2 |
Refractive Index (25°C) |
1.5021 |
3 |
Optical Rotation (25°C) |
+ 4.8 |
4 |
Saponification Value |
5.2 |
5 |
Saponification Value after Acetylation |
54.6 |
6 |
Moisture |
66.3% |
7 |
Protein |
6.1% |
8 |
Fat (Ether Extract) |
1.0% |
9 |
Carbohydrate |
18.7% |
10 |
Fibre |
6.4% |
11 |
Mineral Matter |
4.2% |
12 |
Calcium |
810 Mg/100 G |
13 |
Phosphorus |
600 Mg/100 G |
14 |
Iron Of Edible Portion |
3.1 Mg/100 G |
15 |
Carotene (As Vitamin A) |
12 600 Iµ/100 G |
16 |
Nicotinic Acid |
2.3 Mg/100 G |
17 |
Vitamin C |
4 Mg/100 G |
18 |
Thiamine And Riboflavin |
Absent |
Table 1 The Essential Oil Property of Murraya koenigii.
Leaves
The fresh leaves of Murraya koenigii contain 61.77- 66.2% of moisture, 2.1-12.5%of protein, 14.6-18.97% of total sugar, 9.7-13.06% of total ash, 1.35-1.82% of acid insoluble ash, 1.35-1.82% of alcohol soluble extractive and water extractive value ranges between 27.33-33.45%.48 The nutritional value is explained. Solvents used in preparation of the extract are ethyl acetate, ethanol, petroleum ether, water and chloroform and compounds such as alkaloids, flavonoids and sterols have been extracted. In leaves by acetone extract Koenigine, koenine, koenidine and (-) mahanine were isolated.39 Form the hexane mahanimbine, isomahanimbine, koenimbidine and murrayacine where isolated.49 Isomahanimbicine was isolated in the petroleum ether39 (Table 2).
S.No. |
Nutrients Value as Per 100 Gram |
Fresh Curry Leaf |
Dry Curry Leaf |
1 |
Protein |
6g |
12g |
2 |
Fat |
1g |
5.4g |
3 |
Carbohydrate |
18.7g |
64.31g |
4 |
Calcium |
830mg |
2040mg |
5 |
Iron |
0.93mg |
12mg |
6 |
Β-carotene |
0.0031mg |
0.0059mg |
Table 2 Nutrients Value of Murraya koenigii.
Seed of Murraya koenigii consist of furocoumarin lactone, carbazole alkaloids, glycolipids, Phospholipids and terpinene. It also contains 4.4% of total lipids in which 85.4 % are neutral lipids, 5.1 % are glycolipids and 9.5 % are phospho-lipids. 73.9% triacylglycerol, 10.2% free fatty acids and small amounts of diacylglycerols, monoacylglycerols and sterols which are present in neutral lipids. The seeds of Murraya koenigii contain terpinene these are as follow terpinene, terpinen-4-ol, linolol,50 ocimene, limblee, limbolee and simbolee.51-53 The fruit contain pulp which is having 64.9% of moisture, 16.8% of total soluble solids,48 9.76% of total sugar,54 9.58% of reducing sugar,55 0.17% of non-reducing sugar, 13.35% of vitamin C,56 2.162% of total ash, 1.97% of protein,57 0.082% of phosphorus, 0.811% of potassium (32,2), 0.166% of calcium, 0.216% of magnesium,58 0.007% of iron and 0.00057% of tannin.
Stem and bark
The chemical constituent of matured stem and bark of Murraya koenigii are carbazole alkaloids, coumarin galactoside, Carbazole carboxylic acid, glycolipids, Phospholipids etc.
Roots
The roots of Murraya koenigii include many types of bioactive compounds. The extraction of root was done in benzene and petroleum ether (Table 3).
Chemical Composition |
Structure |
Nature |
Extracted From |
Percentage
|
Reference |
|
α-Copaene |
 |
Sesquiterpenoid |
Leaves |
0.82 |
||
α-Pinene |
 |
Turpentine |
Leaves |
42.676 |
[19] |
|
α-Humulene |
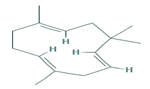 |
Sesquiterpene |
Leaves |
2.770 |
||
Aromadendrene |
 |
Sesquiterpene |
Leaves |
0.72-0.78 |
||
α-Selinene |
 |
Monoterpenoid |
Leaves. Stems |
6.10 |
||
β- Elemene |
 |
Sesquiterpene |
Leaves. Stem |
0.35-7.09 |
||
Bismurrayafoline E |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
0.76-1.23 |
||
Bispyrafoline |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
0.34-0.98 |
||
β-Myrcene |
 |
Olefinic Natural Organic Hydrocarbon |
Leaves, Stems |
1.103 |
||
Bornyl Acetate |
 |
Terpene |
Leaves, Stems, Roots |
1.165-1.68 |
||
Bicyclomahanimbicine |
 |
Terpenoid Alkaloids |
Leaves, Stems, |
1.43 |
||
β-Bisabolene |
 |
Sesquiterpene |
Leaves |
2.3 |
||
β-Pinene |
 |
Terpene |
Leaves |
8.347 |
||
β-Caryophyllene |
 |
Sesquiterpene |
Leaves, Seeds |
7.3-19.50 |
||
β-Costol |
 |
Alcohols |
Leaves |
0.9 |
||
β-Eduesmol |
 |
Alcohols |
Leaves |
9.61 |
||
β-Phellandrene |
 |
Cyclic Monoterpenes |
Leaves |
6.5 |
||
Bikoeniquinone |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Roots |
0.001109 |
||
Bicyclomahanimbine |
 |
Alkaloids |
Leaves, Stems, Roots |
0.324 |
||
Butanedioic Acid |
 |
Dicarboxylic Acid |
Leaves, Stems |
2.18 |
||
Butyl Myristate |
 |
Esters |
Leaves, Stems |
0.66 |
||
β-Selinene |
 |
Sesquiterpenes |
Leaves, Stems |
3.81 |
||
Bismahanine |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
0.0208 |
||
Bis-3-Hydroxy-3- Methyl Carbazole |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Roots |
0.00136 |
||
β-Terpineol |
 |
Alcohols |
Leaves |
2.52 |
||
β- Cadina |
 |
Oleoresin |
Leaves |
6 |
||
Carotene |
 |
Terpene |
Leaves |
0.898 |
||
Camphene |
 |
Bicyclic Monoterpene |
Leaves |
2.16 |
||
Cis-2-Cyclohexen-1-Ol |
 |
Monoterpenoid Alcohol |
Leaves |
0.54 |
||
Chrysanthenyl Acetate |
 |
Monoterpene |
Leaves, Stem |
0.39 |
||
Cycloheptane |
 |
Cycloalkane |
Leaves |
0.13 |
||
Citral |
 |
Monoterpenoidal Aldehyde |
Leaves, Stems |
0.76 |
||
3-Carene |
 |
Bicyclic Monoterpene |
Leaves, Stems |
0.543 |
||
Cadinene |
 |
Sesquiterpene |
Leaves |
5.2 |
||
Cyclomahanimbine |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Leaves |
1.233 |
||
Curryanine |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Stems |
1.003 |
||
Δ-Cadinene |
 |
Sesquiterpene |
Leaves |
2.30-5.20 |
||
Cis-Caryophyllene |
 |
Sesquiterpense |
Leaves |
11.74 |
||
CarvoMenthone |
 |
Ketone |
Leaves |
2.3 |
||
Cubenol |
 |
Sesquiterpenes |
Leaves, Stems |
0.57 |
||
4-Diene |
 |
Diolefin |
Leaves, Stems |
0.50 |
||
Dipentene |
 |
Monoterpene |
Leaves |
11.3-15.9 |
||
6,7-Dimethoxy 1-Hydroxy Carbazole |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloids |
Leaves, Stems, Roots |
0.0004 |
||
Dehydro Aromadendrene |
 |
Sesquiterpense |
Leaves, Stems, Roots |
2.75 |
||
Euchrestine |
 |
Protein |
Leaves |
0.09 |
||
Eustifoline-D |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Roots |
0.0005 |
||
Formlycarbozole |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Roots |
0.00072 |
||
Frnesol s |
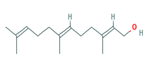 |
Alcohols |
Leaves |
1.56 |
||
Girinimbine |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems, Roots, Fruits, Seeds |
0.015-0.1622 |
||
Glycozoline |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloids |
Stems |
0.034 |
||
Gurjunene |
 |
Carbotricyclic Sesquiterpene |
Leaves |
0.002 |
||
Girinimbilol |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems, Roots |
0.15 |
||
Heraclenin |
 |
Coumarin |
Leaves |
0.454 |
||
1-Hydroxy-3-Methyl Carbazole |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Stems |
0.0022 |
||
Isomahanine |
 |
Pyranocarbazole Alkaloids |
Leaves |
1.23 |
||
Isomurrayazoline |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
2.34 |
||
Isomurrayazolinine |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
3.22 |
||
Iso Caryophyllene |
 |
Sesquiterpense |
Leaves, Stems |
6.72 |
||
Isogirinimbine |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloids |
Leaves, Stems |
2.004 |
||
Imperatorin |
 |
Furocoumarin |
Leaves |
3.433 |
||
Iso Menthone |
 |
Ketone |
Leaves, Stems, Roots |
0.6 |
||
Isomahanimbine (+) |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Fruit |
1.9903 |
||
Juniper Camphor |
 |
Terpenoid |
Leaves |
1.57 |
||
Junipene |
 |
Sesquiterpense |
Leaves |
4.90 |
||
Koenimbine |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Fruits |
02.33 |
||
Koenoline |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Seeds |
20.34 |
||
Kurryam |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves |
7.89 |
||
Koenimbidine |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
13.5 |
||
Koenigicine |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
3.89 |
||
Koenigine |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Leaves |
3.893 |
||
Koenine |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Leaves |
2.44 |
||
Linalool |
 |
Terpene Alcohol |
Leaves, Stems, Roots |
0.56 |
||
Lutein |
 |
Xanthophyll |
Leaves |
0.25-0.59 |
||
Linalyl Acetate |
 |
Acetate Ester |
Leaves, Stems |
0.93 |
||
Limonene |
 |
Cyclic Terpene |
Leaves, Stems |
5.374 |
||
Lavandulyl Acetate |
 |
Acetate Ester |
Leaves, Stems |
1.67 |
||
Mahanimbinine |
 |
Terpenoid Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
5.5464 |
||
Murrayamine-J |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
2.45-2.90 |
||
Marmesin-1'-O-Beta-D Galactopyranoside |
 |
Coumarin Galactoside |
Stems |
1.114 |
||
Murrayamine-M |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
1.34-1.99 |
||
Murrayamine-G |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
1.32-2.09 |
||
Murrayazolidine |
 |
Pentacyclic Carbazole Alkaloid. |
Leaves, Stems |
0.43-1.89 |
||
Murrayacine |
 |
Pyrano-Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
1.00-1.90 |
||
Murrayacinine |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
1.32-2.43 |
||
Mahanimboline |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
1.32-2.98 |
||
Mukoeic Acid |
 |
Carbazole Carboxylic Acid |
Leaves, Stems |
1.02-1.98 |
||
Mukonine |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems, Roots |
1.23-2.78 |
||
3-Methyl Carbazole |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloids |
Leaves, Stems, Roots |
0.23-2.34 |
||
Mahanimbicine |
 |
Alkaloids |
Leaves, Stems |
0.23-2.34 |
||
Mukonidine |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloids |
Leaves, Stems |
0.29-2.89 |
||
Murrayakoeninol |
 |
Alkaloids |
Leaves |
1.45-2.89 |
||
Mahanimbine |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Roots, Leaves |
0.0113 |
||
Mukoline |
 |
carbazole alkaloid |
Roots |
1.89-2.99 |
||
Murrayanol |
 |
Alkaloids |
Roots, Leaves, Stems |
0.23-2.87 |
||
Murrayazolinine |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Seeds |
0.89-1.29 |
||
Murrafoline-I |
 |
Biscarbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems, Seeds |
0.34-2.43 |
||
Mukonicine |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Fruits, Seeds, Leaves |
2.98-3.09 |
||
Murrayacinine |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
1.32-2.43 |
||
Mukoenine A |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Roots |
0.0015 |
||
2-Methoxy-3-Methyl |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Leaves, Stems |
0.0022 |
||
O-Methyl Murrayanine |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloids |
Roots, Leaves, Stems |
2.45-2.99 |
||
Mukolidine |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves |
0.23-1.98 |
||
Mukonal |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves |
0.54-2.09 |
||
Murrayazolinol |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Leaves |
1.78-2.099 |
||
Murrayazoline |
 |
Carbozole Alkaloid |
Leaves |
2.90-3.58 |
||
Mahanimbinol |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Stems, Leaves, Roots |
0.29-2.86 |
||
Mahanine |
 |
Indole Alkaloid |
Stems, Leaves, Roots |
0.00116 |
||
Murrayanine |
 |
Carbazole Alkaloid |
Stems, Leaves |
0.05-1.78 |
||
Menthol |
 |
Alcohols |
Leaves |
2.83 |
||
Nicotinic Acid |
 |
Carboxylic Acid |
Stems, Leaves, Roots |
2.3 |
||
2-Naphthalenemethanol |
 |
Naphthalenes |
Stems, Leaves |
0.66 |
||
Steary Alcohol |
 |
Alcohols |
Stems, Leaves, Roots |
1.01 |
||
Stearaldehyde |
 |
Aldehyde |
Stems |
1.53 |
||
Sabinene |
 |
Terpenes |
Stems, Leaves |
0.10 |
||
Tocopherol |
 |
Alcohol |
Leaves |
2.788 |
||
α-Terpinene |
 |
Terpenoids |
Leaves, Stems |
1.438 |
Table 3 Chemical Constituent of Murraya koenigii.
Many methods are available for the preparation of the extract in which some methods are as follow:59,60
Uses
Biological activity of Murraya koenigii are reported which included the following these activities are studied on the following the crude extracts which are as follow in the Murraya koenigii has been mentioned in the traditional medicinal system in Ayurveda different studies were performed on the Bark, root, leaves, fruit and fruit pulp of Murraya koenigii65 (Table 4).
S.No |
Uses |
Chemical Constituent Used |
Pharmacological Action On |
Animal Used |
Dose |
Reference |
1 |
Anti-Diabetic |
Koenimbidine, Murrayacine, Murrayazolinine. |
Decreases Oxidative Stress By Acting On Paraoxonase 1 Activity |
Rats |
75 Mg/Kg |
|
2 |
Anti-Trichomonal |
Girinimbine, Mahanimbilol |
Act Against Trichomonas Gallinae |
Rats |
1.08 To 1.20 Mg/ml |
|
3 |
For Oral Health |
Essential Oil |
By Stimulating The Salivation Process |
Rabbit And Rats |
25mg/Kg |
|
4 |
Vasodilation |
Mahanimbilol, Murrayazolinine. |
By Acting On Negative Chronotropic Effect |
Frog |
85mg/Kg |
|
5 |
Anti-Oxidation Activity |
Mahanimbine, Koenigine |
Increases The Gsh Content In The Liver And Reduction In Hepatic Malondialdehyde In Kidney |
Male Wistar Rat’s |
15mg/Kg |
|
6 |
Anti-Cancer Activity |
Mahanimbine, Girinimbine, Mahanine, Murrayafoline |
Increase The Death Of Cancerous Cell Proteasome Inhibitor |
Mice |
150mg/Kg |
|
7 |
Effect On Bronchial Disorders |
Girinimbine, Mahanine |
By Blocking 5-Lipooxygenase Activity |
Frog |
35mg/Kg |
|
8 |
Effect On Dental Caries |
Isomahanine, Murrayanol And Mahanine |
Inhibition Of Cavity Formation |
Rabbits |
50mg/Kg |
|
9 |
Anthelmintic Activity |
Mahanine, Koenimbidine |
Cause Paralysis |
Test Worm |
100 Mg/Ml |
|
10 |
Wound Healing Effect |
Mahanine, Mahanimbicine, Mahanimbine And Essential Oil |
Act Against Inflammatory Cells And The Collagen Deposition Was Reduces |
Male Albino Rat |
65mg/Kg |
|
11 |
Anti-Amnesic |
Koenimbidine, Mahanimbicine, |
Protect Against The Neurodegenerative Diseases |
Aged Mice |
100mg/Ml |
|
12 |
Protects The Eyes And Improves Eyesight |
Essential Oil, Vitamin A |
Eye Sight Improvement |
Gunia Pig |
5mg/Ml |
|
13 |
Radiation Protection Activity |
Mahanine, Murrayafoline |
Increases Glutathione, Its Enzymes Levels And Decrease The Chromosomal Damage |
Mice |
100 Mg/Kg |
|
14 |
Anti-Ulcer Activity |
Mahanimbine And Essential Oil |
Effect Against Lesion Index, Area And Percentage Of Lesion And On Ulcer |
Albino Rats |
85mg/Ml |
|
15 |
Anti-Microbial Activity |
Mahanimbine, Murrayanol And Mahanine, |
Inhibition Of Topoisomerase I And Ii |
Bacteria, Fungi |
3.13-100 Μg/Ml |
|
16 |
Anti-Diarrheal Activity |
Kurryam, Koenimbine Koenine |
Prostaglandin E2-Induced Enter Pooling And Reduction In Gastrointestinal Motility |
Albino Mouse, Wister Rats |
20ml/Kg |
|
17 |
Chemoprotective Activity |
Koenimbin |
Reduction In Induced Chromosomal Damage |
Swiss Albino Mice |
100 Mg/Kg |
|
18 |
Immunomodulatory Activity |
Mahanimbine, Mahanine, |
Increase In Phagocytic Index By Removing Carbon Partical From Blood |
Albino Mice |
125mg/Kg |
|
19 |
Haematological Activity |
Koenimbidine, Mahanimbicine, |
No Adverse Effect Against Food Efficiency Ratio |
Rats |
85mg/Kg |
|
20 |
Antipyretic Activity |
Murrayacine, Murrayazolinine. |
Decrease In Fever |
Albino Rat, Rabbit |
200mg/Kg |
|
21 |
Nephroprotective Activity |
Koenimbidine, |
Reno-Protective Activity Against Unilateral Renal Ischemia |
Male Wistar Rats |
150mg/Kg |
|
22 |
Cardio-Protective Activity |
Girinimbine, Girinimbiol |
Cadmium-Induced Oxidation Is Reduces |
Swiss Albino Mice And Rat Cardiac Tissue |
100 Mg/Kbw |
|
23 |
Anti-Cytotoxicity Activity |
Girinimbine, Koenoline, Mahanine, Pyrafoline-D And Murrafoline-I |
Exhibiting The Cell Death Resulted As The Mortality Of The Cell |
Swiss Albino Mice |
150mg/Kg |
|
24 |
Inotropic Activity |
Girinimbiol |
Positive Inotropic Effect |
Frog Heart |
100mg/Kg |
|
25 |
Hepatoprotective Activity |
Girinimbine, Mahanine, Mahanimbine, Isomahanimbine, Murrayazolidine, Murrayazoline |
Oxidative Stress Inducer |
Wister Rats |
90mg/Kg |
|
26 |
Anti-Lipase Activity |
Mahanimbin, Koenimbin, Koenigicine And Clausazoline-K |
Reduced Total Cholesterol (Tc) And Triglyceride (Tg) Levels |
Albino Rats And Wister Rats |
120mg/Kg |
|
27 |
Anti-Alzheimer's Activity |
Isomahanimbine, Murrayazolidine, |
Improves The Values Of Protective Antioxidants |
Young And Aged Mice |
150mg/Kg |
|
28 |
Anti-Analgesic Activity |
Girinimbine, Mahanine, Mahanimbine, Isomahanimbine |
Anti-Nociceptive Effects |
Mice |
25mg/Ml In Combination With Diclofenac |
|
29 |
Effecte Digestive System |
Mahanine, Murrayafoline |
Stimulates Digestive Enzymes |
Mice |
50mg/Kg |
|
30 |
Neuro-Protective Activity |
Koenimbin, Koenigicine And Clausazoline-K |
Decreasing Glycemic Levels |
Mice, Rats |
100mg/Kg |
|
31 |
Anti-Inflammatory Activity |
Girinimbine, Mahanine, Mahanimbine, Isomahanimbine, |
Cox-Inhibitory Property |
Albino And Wistar Rats |
50mg/Kg |
Table 4 Pharmacological use of Murraya koenigii.
Other uses
Murraya koenigii is a leafy medicinal as well as green leafy plant that belongs to family Rutaceae. The various pharmacological activities of the plant has been seen such as such as activity on Anti diabetic, cholesterol reducing property, antimicrobial activity, antiulcer activity, Antioxidative property, cytotoxic activity, anti-diarrhoea activity, anti-cancer activity with many other phagocytic activity. The chemical composition of the Murraya koenigii consists of essential oil alkaloids and terpenoid. Thus Curry leaves merits further phytochemical, pharmacological and clinical investigations for development of an effective natural plant.
None.
The author declares no conflict of interest.

©2017 Jain, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.