The spondylometry data is shown in Figure 1. Following the above mentioned method, the average values were analyzed. When using different methods for the SK determination, the maximum difference was 1,20, the average of the module difference for all clinical cases 0,2840±0,0460, that indicates a high results comparability (correlation r=0,97). A visual analysis of the distribution allows to suggest that the optimal function with the least number of coefficients is a parabola
. During the relevant calculations, the assumption is confirmed by a sufficiently high value of the coefficient of determination (R2=0,8914). Model characteristics is defined in the third iteration. As a result, the function is revealed which describes the nature of the dependence of the analyzed indicators the most effectively:
The analysis of the correlation matrix demonstrates quite convincingly the absence of unnecessary components of the reduced formula (Table 1). Attention is paid to the sufficiently high value of correlation
and
coefficients of the model, which is naturally explained by a fairly narrow range of initial values (Table 2). The residual analysis results (Figure 2) are also testified in favor of adequacy of the received model. Thus, the evaluation demonstrates a sufficiently high representativeness and predictive efficiency of the obtained dependence. The next stage of the analysis was to assess the nature of the deviation of real indicators from the predicted values. The visual evaluation of the graph of distribution (Figure 1) allows to mark out 3 ranges
t which
shows the specificity of dispersion relative to.
The following tendency revealed:
- Range
is characterized by moderate module the deviation of SKfin indicators relative to the prognostic curve with both positive and negative values.
- Range
shows a more significant difference of residues, but mainly with a tendency to negative values.
- Range
makes the largest dispersion in both the positive and negative directions.
With the purpose of objectifying boundaries of these groups, which are differ in their correlation of SKfin и SKint we used the cluster analysis with K-means method. The obtained results are shown in Figure 3. The statistical reliability of the analysis is presented in Table 3. Taking into consideration that the cluster analysis findings are characterized by a high level of the statistical significance, we determined the boundaries of the clusters at the
, which were as follows: 1-st cluster:
; 2-nd cluster:
;3-d cluster:
. Consequently, the obtained data allows considering the intraoperative range
as the optimal for saving the indicators of correction in the late postoperative period (Figure 4). Subsequently, the biomechanical verification of the results was executed. It was analyzed 3 finite- element models of the cervical spine. The SK of spine segment with fusion system were corresponded to the centers of the obtained clusters and arranged -1,80; -4,60 and -7,80. Models marked as “
“, “
and “
“.The maximum values of equivalent von Mises stresses were estimated in the following model elements: the upper laminar plate of C6 vertebra body, the lower laminar plate of C4 vertebra body; arcs roots and articular masses of C4 and C6 vertebrae, screws fixing the anterior plate that are located in the bodies of C4 and C6 vertebrae. The peak values of the equivalent stresses were registered in the analyzed model elements and are shown in Figure 5.
The load distribution analysis in the contact zone of the vertebral plates with the implanted body-replacing system reveals the following regularitie
Compression action on the operated cervical spine causes the maximum loading of the lower locking plate of the C4 vertebral body during the formation of
. Thus, the value of the equivalent tension is 8,4MPa, that is 2,3MPa more than the SK-4,60 model and 1,9MPa more than the
. Loading of the upper laminar plate of the body C6 during compression demonstrates some other results. Consequently the values for
and
models are almost identical and arrange respectively 7,2MPa and 7,.3MPa, while the minimum values of segmental kyphosis provide tension of 6,3MPa. The extension load provokes the following redistribution of von Mises equivalent tension on the analyzed models. The lower laminar plate of C4 vertebra shows the highest values with SK equal to -7,80, that is manifested by the peak value of the tension of 8,6MPa. The minimum tension is fixed with
and it is arranged 7,5MPa. In the model
the corresponding value is registered at the level of 7,7MPa. The maximum value of the stress on the upper surface of the body C6 was recorded at
and is 7,5MPa, while for the models
and
this figure is less, respectively, 0,4MPa and 0,2MPa. In a series of the load tests, the flexion emulation impact demonstrates the highest von Mises stress. So, on the lower laminar plate of C4 the analyzed value was calculated for models
,
and
respectively 9,7MPa, 8,1MPa and 11,2MPa. A similar pattern was observed in the analysis of stress on the upper surface of the body C6. The minimum value is registered when loading
model and made 6,5MPa. The maximum was observed in
MPa, while the value of 7,9MPa was observed with
. The modelling of the rotational load demonstrates the expected low values of the equivalent stress of the anterior support complex in the area of the operated vertebral segment. So, on the lower surface of the body of C4 models
,
and
peak values arranged, respectively, 3,5MPa, 3,3MPa and 4,1MPa. A similar pattern is recorded in the analysis of the equivalent stress in the contact zone of the implanted system and the upper surface of the body C6. The maximum value of 3,4MPa is marked at
, the minimum one is registered at
and is 2,6MPa.
The tension distribution on the C4 and C6 vertebrae arcs roots with the different loading options of the analyzed models is the followin
The C4 vertebra is the least loaded in a case of compression effect with the
, the equivalent tension is 5,9MPa. The highest load value of the analyzed zone was noted in the model  and amounted to 6,8MPa. In contrast, the roots of C6 vertebral arc of all analyzed models demonstrate significantly higher values of the analyzed parameter. Thus, the maximum amount is observed in the model
and arranged 18,2MPa, the lowest value of 16,9MPa was in the kyphosis formation -1,80. The extension loading causes peak values at the roots of arcs in all analyzed models. For the C4 vertebra the equivalent stress was 9,2MPa, 10,0MPa and 12,4MPa for models
,
and
respectively. The C6 vertebra is loaded more significantly. Thus, for the model
the value of the arc root von Mises equivalent tension was 25,3MPa, which is the maximum of all values obtained in the experiment. Model
demonstrates lower data – 22,4MPa. The most biomechanically favorable is the formation of sagittal kyphosis -4,60, which provides the load of the analyzed zone no more than 20,2MPa.The flexion of the cervical spine almost completely unloads the elements of the rear support complex. At the same time, for C4 vertebrae, the equivalent stress on the roots of arcs of all analyzed models is practically the same and is 0,8MPa, 0,9MPa and 1,1MPa, respectively,
,
and
. Almost identical pattern was observed in the analysis of the C6 arc root: 0,9MPa, 1,1MPa and 1,2MPa. The changes of the SK operated segment practically does not affect the arc root load of the C4 vertebra under the rotational action. Thus, the values of the equivalent tension were 5,8MPa, 6,0MPa and 6,2MPa for models
,
и
. A lightly different pattern was observed when loading of the root of the vertebral arch, located below the resected one. Thus, the maximum tension value is calculated in the model
and was 8,2MPa, while for SK equals to -4,60 the analyzed parameter is 6,0MPa.
and amounted to 6,8MPa. In contrast, the roots of C6 vertebral arc of all analyzed models demonstrate significantly higher values of the analyzed parameter. Thus, the maximum amount is observed in the model
and arranged 18,2MPa, the lowest value of 16,9MPa was in the kyphosis formation -1,80. The extension loading causes peak values at the roots of arcs in all analyzed models. For the C4 vertebra the equivalent stress was 9,2MPa, 10,0MPa and 12,4MPa for models
,
and
respectively. The C6 vertebra is loaded more significantly. Thus, for the model
the value of the arc root von Mises equivalent tension was 25,3MPa, which is the maximum of all values obtained in the experiment. Model
demonstrates lower data – 22,4MPa. The most biomechanically favorable is the formation of sagittal kyphosis -4,60, which provides the load of the analyzed zone no more than 20,2MPa.The flexion of the cervical spine almost completely unloads the elements of the rear support complex. At the same time, for C4 vertebrae, the equivalent stress on the roots of arcs of all analyzed models is practically the same and is 0,8MPa, 0,9MPa and 1,1MPa, respectively,
,
and
. Almost identical pattern was observed in the analysis of the C6 arc root: 0,9MPa, 1,1MPa and 1,2MPa. The changes of the SK operated segment practically does not affect the arc root load of the C4 vertebra under the rotational action. Thus, the values of the equivalent tension were 5,8MPa, 6,0MPa and 6,2MPa for models
,
и
. A lightly different pattern was observed when loading of the root of the vertebral arch, located below the resected one. Thus, the maximum tension value is calculated in the model
and was 8,2MPa, while for SK equals to -4,60 the analyzed parameter is 6,0MPa.
The loading of the articular masses of the vertebrae which are adjacented to the resected one is similar to the nature of the load distribution on the arcs roots, but in some cases has its own characteristics
The articular masses of C4 vertebrae of the analyzed models demonstrate the highest values of equivalent stresses under compression and extension. Thus, the compressive load causes the analyzed parameter to 3,2MPa, 2,8MPa and 2,4MPa, respectively, for
,
и
. In the modeling extension, the maximum value was noted in the
model and was 5,5MPa, while for
,
the values were 4,5MPa and 3,8MPa, respectively. At a flexion load, the values of the equivalent tension are corresponding to the range of 0,3-0,6MPa while the highest value is noted in the model
. Similar to the arc root C4, the change of SC practically does not affect the level of loading of the articular masses of the C4 vertebra during rotation, the equivalent stress values correspond to the range of 0,9-1,1MPa. A similar pattern was observed with analysis of C6 vertebra. Under the compression, the highest indices were registered in the model
and amounted to 3,2MPa, the lowest 2,6MPa in
. The extensional loading demonstrates the clear advantage of
, which is manifested by the value of the analyzed indicator 3,5MPa in comparison with 6,5MPa and 6,8MPa for
and
respectively. The cervical spine flexion naturally demonstrates the minimal stress values of the articular masses of the vertebrae, the range of values corresponds to 0,1-0,2MPa. With the rotation, the analyzed zone of model
is less loaded –2,2MPa, while for
and
this index is 2,9MPa and 3,2MPa, respectively.
The analysis of the equivalent tension on fixing screws allows to reveal the following features
Under compression loading, the upper pair of screws shows the highest values of equivalent stress in the model
, that was 9,2MPa. The load in
is 0,1MPa less. The most biomechanically favorable for the analyzed value was
, the load made 8,2MPa. A similar pattern was observed in the analysis of the lower screw pair: 3,2MPa, 2,8MPa and 2,7MPa for
,
and
respectively.The еxtension in all cases is accompanied with decrease of tension in the screw pairs, that is caused with the load transfer to the rear support complex. Thus, for
and
, the values of von Mises equivalent tension on the top pair of screws were decreased in comparison with the compression load by 1,5MPa and 0,4MPa and amounted to 7,7MPa and 7,8MPa, respectively. In the model
no changes are observed and the tension is 9.1MPa.The lower screw pair is also characterized by the load reduction. The highest indices, however, were registered in
model and arranged up to 2.8MPa, while for
and
the equivalent stresses were determined as 1,1MPa and 1,5MPa, respectively. The flexion load causes a significant increase in the stress on the fixing elements of the anterior plate. Thus, the highest rates were registered when modeling -7,80 SC and amounted to 11,2MPa on the upper screw pair. For
,
, these values are corresponded to 10,2MPa and 9,5MPa, respectively. The lower pair of screws in the modelling front bending remains less loaded. The values of equivalent tension for model
,
and
correspond to 4,5MPa, 3,2MPa and 4,8MPa.The rotation modeling for the upper screw pair shows the maximum load at kyphosis -7,80 (10,0MPa), while the lower screw pair is significantly overloaded with a minimum value of SK. So for
the equivalent stress was 7,2MPa, while for models
and
only 4,2MPa and 4,3MPa.
Consequently, summarizing the finite element analysis data, it is possible to identify the following patterns:
- biomechanically, the most favorable for all the analyzed models is the compression load, which provides a more uniform distribution of stress on the supporting elements of the model.
- The rotary load leads to critical values of equivalent stress on the fixing screws.
- The model with SK corresponding -4,60 provides the minimum critical value of the equivalent stress in the analyzed basic structural elements.
- The least favorable is the formation of segmental kyphosis with a value of -7.80.
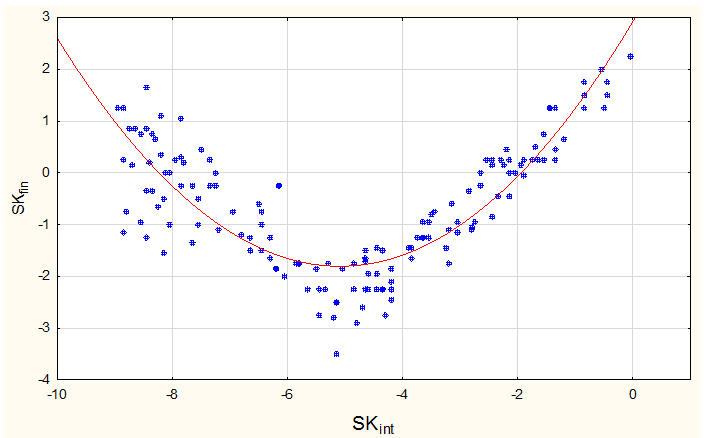
Figure 1 N=57; Epidemiological distribution of the pathological fractures, traumatic fractures, and nonunion.

Figure 1 Dependence of sagittal kyphosis values of the operated segment in the delayed postoperative period on the value of intraoperative correction and prognostic SKfin=f(SKint).
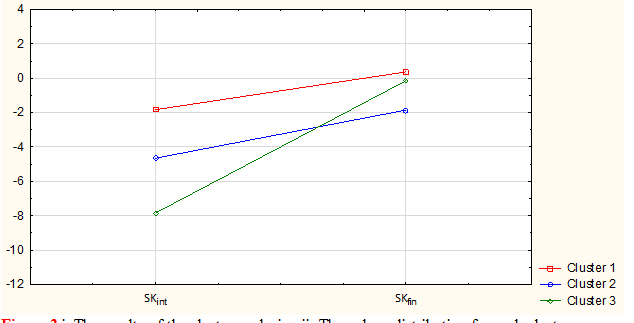
Figure 3 i. The results of the cluster analysis. ii. The values distribution for each cluster.

Figure 4The pattern of the finite-element model “SK -4,60” with the different loading options: (A) compression, (B) extension, (C) inflexion, (D) rotation.
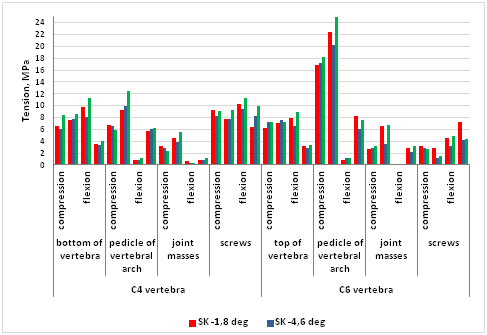
Figure 5 The maximum values of equivalent von Mises stress in the models’ elements.
|
A |
B |
C |
A |
1,000000 |
0,974551 |
0,819138 |
B |
0,974551 |
1,000000 |
0,913061 |
C |
0,819138 |
0,913061 |
1,000000 |
Table 1 The correlation matrix of the calculated coefficients of the model
|
Аverage value |
Standard
error |
t (df = 148) |
p |
Confidence interval (alpha=0.05) |
low |
top |
a |
0,182626 |
0,008965 |
20,37046 |
0,00 |
0,164909 |
0,200342 |
b |
1,857933 |
0,090267 |
20,58268 |
0,00 |
1,679555 |
2,036311 |
c |
2,921429 |
0,195262 |
14,96161 |
0,00 |
2,535568 |
3,307289 |
Table 2 The reliability estimation of the calculated coefficients of the model
|
Sum of squares of the deviations between the cluster centers |
df |
Sum of squares of the deviations of objects from cluster center |
df |
F |
Importance, p |
SKint |
838,5718 |
2 |
101,9286 |
148 |
608,8019 |
<0,000001 |
SKfin |
140,4024 |
2 |
80,4737 |
148 |
129,1077 |
<0,000001 |
Table 3 Results of the dispersive estimation based on cluster analysis
Since the first successful anterior decompression-fusion cervical surgery and up to the present time, the technical aspects of performing surgical correction remain very discounted. The corporotomy with subsequent stabilization at subaxial level despite the relatively high risks in some cases remains the only effective method of decompression spinal cord in traumatic injuries and neoplastic and inflammatory processes in vertebral bodies, degenerative changes of the cervical spine, which are provoking the compression of the ventral spinal cord and it is accompanied by the myelopathy. For a quite long period, the use of tricortical auto graft was the gold standard of the spinal surgery. Further researches, however, showed a fairly high rate of adverse results, that were manifested by lysis of the implanted bone fragment, its fracture, migration, loss of achieved intraoperative correction and, in some cases, aggravation of neurological disorders. The combination of auto graft with a anterior plate partially solved these problems. The next significant milestone in the development of spine surgery is the use as the body replacing system as hollow vertical cylindrical mesh implants. The first clinical experience with the use of mesh-systems without additional fixing wasn’t met with significant success because of the extremely high frequency of prolapse of the system in the body of the vertebrae adjacent to the resected ones. The combination of mesh and rigid ventral plate has demonstrated rather high clinical efficiency.
The literature data allows to reveal a significant number of works devoted to the evaluation of the effectiveness of this combination. The authors consider both biomechanical, clinical and radiological aspects. At the same time, the results are extremely variable. A number of researchers demonstrate 100% efficiency and safety of the stabilization method, others - indicate the frequency of unsatisfactory results up to 30%.
Such results dissociation appears to be due to a number of factors
Firstly, until now, there have not been developed sufficiently clear criteria that would allow to evaluate the effectiveness of the surgical intervention. It is known that clinical symptoms often do not correspond to the x-ray picture. Thus, progressive kyphotic deformation in the postoperative period may not be accompanied by neurological disorders for a long time. At the same time, the effective fusion with preservation of the sagittal contour and optimized distribution of the load on the cervical spine in case of severe trauma may not lead to an obvious regression of neurological disorders. Considering the SK state of the operated segment as a criterion of efficiency of the fusion, which is emphasized in this research, it should be mentioned that the different authors’ interpretation of the results is very ambiguous. Thus, K. Narotam and co-authors, based on a 4-year retrospective study, estimate the correction loss up to 40 as an excellent and 50-90 as a good one.12 At the same time, a number of authors allow the increase of kyphotic deformation up to 100 in comparison with intraoperative parameters.13 In other publications can be found a quite reasonable statements about such loss of correction in traumatic lesions of the cervical spine, it is quite significant local CSF flow and vascular disorders, in addition to the violation of the congruence of the facet joints in combination with the defeat of the ligamentous apparatus of the rear support complex can lead to one- or bilateral dislocation, causing enough risk of the vascular lesions compression of neural structures at the level of the operated segment. Secondly, the vast majority of publications devoted to the combined use of mesh and ventral plate evaluate the result of the performed surgery, but not the result of the treatment of a certain pathology. For example, some clinical studies include the patients with traumatic spinal cord injury and patients with compression myelopathy due to degenerative changes of the spine. This approach, obviously, does not allow to carry out the comparative biomechanical analysis of the produced fusion in full objectively. It is known that decompressive-fusion surgery performed in patients with isolated traumatic injury of the anterior support cervical spine complex biomechanically has no equivalent to similar surgical manipulation performed in the treatment of cervical myelopathy.
For example, the absence of traumatic injury of ligamentous apparatus of the posterior supporting complex verified with MRA or CT doesn’t give a total assurance of the absence of this pathology and it does not exclude, however, the distension of the ligamentous-capsular apparatus of the concerned spine segment. Results of search in the National Center for Biotechnology Information database using keywords “cervical mesh cage” for the period of last 5 years shows that the vast majority of publications is devoted to the application of the analysed combination in treatment of cervical myelopathy. As for the traumatic injuries treatment, the majority of authors prefer the 3600-fixation. Along with this, however, there is some tendency to minimize surgical exposure. Thus, a number of works convincingly demonstrate the effectiveness of isolated anterior fusion even with significant damage to the front and rear support structures of the subaxial section of the cervical spine. This data is fully correlated with our research results. The retrospective analysis demonstrates rather convincingly high clinical efficiency of the described method of surgical treatment under condition of technical adequacy of execution with the subsequent clinically and biomechanically reasoned stages of rehabilitation. This approach, undoubtedly, can reduce both the economic loading and the surgical trauma, reducing the postoperative complications risk and negative iatrogenic effects.
Thirdly, the most important factor is the lack of a unified approach to the surgical operation technique. In fact, considering the use of mesh, there are two different approaches that have an impact on the final results.12 A number of surgeons, during the system installation, prefer to use the partial resection of the endplates of the vertebral bodies, which significantly increases the coherence with the implantable structure. However, due to the cortical layer removal, this approach requires the use of endcaps, in order to increase the bearing surface of the implant and prevent the system prolapse into the vertebral body. Another approach is to maximize the preservation of the cortical layer of the endplates, that eliminates the use of additional structural elements. In our research we applied this surgical modification that for a number of reasons was considered as more expedient. Thus, the structure teeth impression in the cortical layer of the endplate and a kind of adaptation in the implant-bone system. It creates additional stabilization and prevents dislocation of the structure. The use of endplates inevitably reduces the contact area of the filler of mesh with bone tissue and in some way prevents the bone block formation. Thus, the mesh-system, which is actually a cage for a filler and is designed to consolidate with the bodies of the vertebrae, is that case loses its main advantage and turns into simple spacer. Taking into consideration the fact of true fusion formation, i.e. bone fusion, is the most optimal and most stable outcome of surgery, and the use of end caps is impractical. Besides, a certain role in forming the biomechanical pattern of anterior fusion plays the type of screws for cervical plate fixation. Our retrospective data consists of cases with fixed screws, so the model has the appropriate type of fusion system. Using non-fixed or variable type screws obviously impacts the stability of fixation and can be studied further. Presented data demonstrates the reasons of wide range the final results of the similar surgical interventions, that are given in the literature. The obtained in our study data is partly consistent with some of them. At the same time, it should be mentioned that the concept of the maximum possible preservation of the physiological curvature of the cervical spine formed the basis of this research. It which is unconditionally proved, even when the deviation from the desired SK values do not have visible negative clinical consequences within the analysed observation period.


![]() and amounted to 6,8MPa. In contrast, the roots of C6 vertebral arc of all analyzed models demonstrate significantly higher values of the analyzed parameter. Thus, the maximum amount is observed in the model
and arranged 18,2MPa, the lowest value of 16,9MPa was in the kyphosis formation -1,80. The extension loading causes peak values at the roots of arcs in all analyzed models. For the C4 vertebra the equivalent stress was 9,2MPa, 10,0MPa and 12,4MPa for models
,
and
respectively. The C6 vertebra is loaded more significantly. Thus, for the model
the value of the arc root von Mises equivalent tension was 25,3MPa, which is the maximum of all values obtained in the experiment. Model
demonstrates lower data – 22,4MPa. The most biomechanically favorable is the formation of sagittal kyphosis -4,60, which provides the load of the analyzed zone no more than 20,2MPa.The flexion of the cervical spine almost completely unloads the elements of the rear support complex. At the same time, for C4 vertebrae, the equivalent stress on the roots of arcs of all analyzed models is practically the same and is 0,8MPa, 0,9MPa and 1,1MPa, respectively,
,
and
. Almost identical pattern was observed in the analysis of the C6 arc root: 0,9MPa, 1,1MPa and 1,2MPa. The changes of the SK operated segment practically does not affect the arc root load of the C4 vertebra under the rotational action. Thus, the values of the equivalent tension were 5,8MPa, 6,0MPa and 6,2MPa for models
,
и
. A lightly different pattern was observed when loading of the root of the vertebral arch, located below the resected one. Thus, the maximum tension value is calculated in the model
and was 8,2MPa, while for SK equals to -4,60 the analyzed parameter is 6,0MPa.
and amounted to 6,8MPa. In contrast, the roots of C6 vertebral arc of all analyzed models demonstrate significantly higher values of the analyzed parameter. Thus, the maximum amount is observed in the model
and arranged 18,2MPa, the lowest value of 16,9MPa was in the kyphosis formation -1,80. The extension loading causes peak values at the roots of arcs in all analyzed models. For the C4 vertebra the equivalent stress was 9,2MPa, 10,0MPa and 12,4MPa for models
,
and
respectively. The C6 vertebra is loaded more significantly. Thus, for the model
the value of the arc root von Mises equivalent tension was 25,3MPa, which is the maximum of all values obtained in the experiment. Model
demonstrates lower data – 22,4MPa. The most biomechanically favorable is the formation of sagittal kyphosis -4,60, which provides the load of the analyzed zone no more than 20,2MPa.The flexion of the cervical spine almost completely unloads the elements of the rear support complex. At the same time, for C4 vertebrae, the equivalent stress on the roots of arcs of all analyzed models is practically the same and is 0,8MPa, 0,9MPa and 1,1MPa, respectively,
,
and
. Almost identical pattern was observed in the analysis of the C6 arc root: 0,9MPa, 1,1MPa and 1,2MPa. The changes of the SK operated segment practically does not affect the arc root load of the C4 vertebra under the rotational action. Thus, the values of the equivalent tension were 5,8MPa, 6,0MPa and 6,2MPa for models
,
и
. A lightly different pattern was observed when loading of the root of the vertebral arch, located below the resected one. Thus, the maximum tension value is calculated in the model
and was 8,2MPa, while for SK equals to -4,60 the analyzed parameter is 6,0MPa.


