Journal of
eISSN: 2373-6410


Case Report Volume 5 Issue 4
1Neurointerventional Unit General Air Force and Reserve Hospital, Greece
2Neurosurgical Department General Air Force and Reserve Hospital, Greece
Correspondence: Veranis Sotiris, Neurosurgical Department 251 General Air Force and Reserve hospital, Athens, Kanellopoulou - Katehaki 3, po box 11525, Greece
Received: November 22, 2016 | Published: December 30, 2016
Citation: Lagios K, Mpazinas T, Veranis S, Sphikas Sp, Kapetanakis A, et al. (2016) Hydrocephalus Treated with Embolization of a Tentorial DuralFistula. J Neurol Stroke 5(4): 00187. DOI: DOI: 10.15406/jnsk.2016.05.00187
We present a case of a 73years old, caucasian male patient who presented two years ago with progressive dementia, frequent falls, unsteady gait and somnolence. He suffered from diabetes type 2 and mild chronic renal insufficiency. He was diagnosed with obstructive hydrocephalus and tentorial dural fistula (Cognard type IV). He underwent brain angiography and embolization of the fistula. His symptoms improved remarkably postembolisation and he remains stable after two years of follow up.
Keywords: hydrocephalus, dural fistulas, tentorial davf, embolization, flow voids
Hydrocephalus is a pathological condition in which the ventricles of the brain are widened and is caused by abnormalities regarding the formation, flow or absorption of the cerebrospinal fluid. Dural fistulas is a well known cause of intracranial hypertension because of impairment of venus outflow (Borden type III, Cognard type III,IV,V) 1,2,3.On the other hand dural fistulas are rarely reported as a cause for obstructive hydrocephalus.
We present the case of a 73 years old, caucasian male patient who presented with progressive dementia and gait disturbances with frequent falls. Furthermore he was complaining for headache and somnolence. He have been suffering from diabetes type 2 and mild renal insufficiency. Brain MRI diagnosed obstructive hydrocephalus and multiple flow voids mainly at the subtentorial space (Figure 1). Brain four vessel angiography diagnosed a tentorial dural fistula (Borden type III, Cognard type IV) (Figure 2).
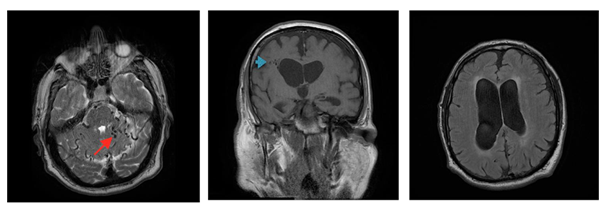
Figure 1 A) T2 brain MRI depicting multiple flow voids (red arrow) in the posterior fossa. B) T1 brain MRI obstructive hydrocephalus with remote fistula (blue arrow). C) T2 Flair dilatation of lateral ventricles.

Figure 2 a) Infusion through RICA in venous phase opacifies a small part of strait sinus (lower red arrow), there is absence of internal cerebral veins, vein of Galen and basal vein, there is opacification of subependymal vein (upper red arrow) b) Infusion inside ascending pharyngeal artery, a micro catheter was progressed through neuromeningeal branch and final embolization of DAVF performed with ONYX. Anastomosis of dural branch with posterior meningeal artery and dilated cerebellar veins can be seen. c) Infusion into EC and retrograde flow inside cerebellum veins, pontomedullary vein, basal vein and towards superficial veins of temporal and frontal lobe. d) Infusion into left vertebral artery leads to opacification of cerebellar veins through fistula from posterior meningeal artery. Cognard type IV.
Patient was sedated, paralysed and intubated. Femoral artery was catheterised on the left side and a four vessel brain angiography was obtained. A tentorial dural fistula was diagnosed. There were several distended tortuous veins depicting venous outflow hypertension. We proceeded with transarterial embolization of the feeding arteries using ONYX [5-8]. Patient remained stable throughout the procedure (Figure 2b&3).
Clinical results
Patient remained stable through the embolisation procedure. Afterwards his symptoms resolved and returned home 2 days later. His neurological examination at discharge was unremarkable. The patient has been under close follow up for the last two years without clinical or radiological remission.
Radiological results
The patient remained stable and did brain MRI once a year for follow up. There was resolution of hydrocephalus and disappearance of flow voids and tortuous vessels (Figure 4).
Dural fistulas is a well known cause of intracranial hypertension because of venous outflow obstruction. Hydrocephalus is a rare symptom of dural fistula. According to Sandro Rossitti 4 CSF pressure is equal to cerebral vein pressure. Dural fistula that cause elevated venous outflow pressure result in elevated CSF pressure and intracranial hypertension. In our patient we observed multiple tortuous dilated veins in the posterior fossa and we assume that this fact caused raised CSF pressure in the posterior fossa and obstructive hydrocephalus. We did not perform lumbar puncture and CSF pressure measurements because this was thought to be contraindicated due to obstructive hydrocephalus. It is not yet clear how dural fistulas affect CSF dynamic.
Hydrocephalus is associated with symptoms such as headache, gait disturbances and dementia. In our case ventricular dilatation markedly improved post embolisation. On the other hand it not sure if blockage of the venus outflow due to the tentorial dural fistula affected gait and memory in addition to hydrocephalus 9.
None.
None.
None.

©2016 Lagios, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.