Journal of
eISSN: 2373-6453


Editorial Volume 10 Issue 2
1Faculty of Medicine, Western University, Thailand
210th Zonal Tuberculosis and Chest Disease Center, Thailand
3Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Thailand
Correspondence: Attapon Cheepsattayakorn, 10th Zonal Tuberculosis and Chest Disease Center, 143 Sridornchai Road Changklan Muang Chiang Mai 50100, Thailand, Tel 6653140767, 6653276364, Fax 6653140773, 6653273590
Received: July 18, 2023 | Published: July 18, 2023
Citation: Cheepsattayakorn A, Cheepsattayakorn R, Siriwanarangsun P. Humoral and cellular immune response in kidney transplant recipients after COVID-19 vaccination. J Hum Virol Retrovirol. 2023;10(2):47-48. DOI: 10.15406/jhvrv.2023.10.00265
With different mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in immunocompromised patients, such as kidney transplant recipients (KTRs), solid organ transplant recipients (SOTRs), etc., binding and neutralizing antibodies measurement clearly revealed lower levels, compared to healthy persons.1–5 A number of previous studies demonstrated that KTRs or non-KTRs with renal failure markedly reduced vaccine response, whereas adaptive protocols of mRNA COVID-19 vaccination or alternative adjuvant vaccines is now not known yet.6,7 Whereas protective immunity is further impaired immunosuppressants, thus fully restoring adaptive, cellular immunity and renal function in KTRs cannot occur and increase susceptibility to viral-related malignancies and infections.8–10 After two doses of mRNA-COVID-19 vaccines, the seroconversion rates in KTRs were relatively low that varied from 4% to 57%11,12 and decreased with increasing age.12,13 A recent study demonstrated that everolimus (EVR), a mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor had a higher seroconversion after mRNA-COVID-19 vaccination among KTRs, in comparison to mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) therapy (Figure 1).14
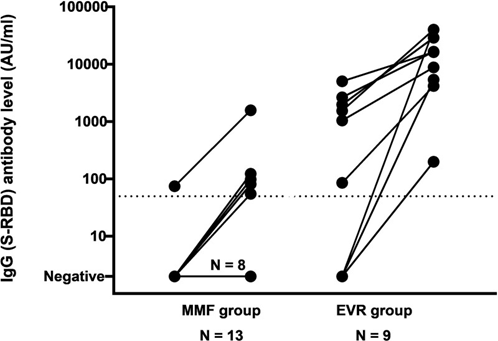
Figure 1 Demonstrating spike receptor-binding domain [S-RBD])-IgG-antibody-level changes between second and third mRNA-COVID-19 vaccination. The threshold for serocoversion is indicated by dotted line. Maximal threshold of quantification is 40 000 AU/mL.
(AU, arbitrary units; EVR, everolimus; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil).14
In conclusion, immune response, particularly humoral immunity in elderly-post-transplant KTRs after COVID-19 vaccination was associated with EVR treatment and higher seroconversion.
None.
None.
Author declares that there is no conflict of interest.

©2023 Cheepsattayakorn, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.