Journal of
eISSN: 2373-6453


Editorial Volume 10 Issue 2
1Faculty of Medicine, Western University, Thailand
210th Zonal Tuberculosis and Chest Disease Center, Thailand
3Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Thailand
Correspondence: Attapon Cheepsattayakorn, 10th Zonal Tuberculosis and Chest Disease Center, 143 Sridornchai Road Changklan Muang Chiang Mai 50100 Thailand, Tel 66 53 140767, 66 53 276364, Fax 66 53 140773, 66 53 273590
Received: August 28, 2023 | Published: August 28, 2023
Citation: Cheepsattayakorn A, Cheepsattayakorn R, Siriwanarangsun P. Antibody response after booster vaccination after SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections in patients with advanced cancer. J Hum Virol Retrovirol. 2023;10(2):56-57. DOI: 10.15406/jhvrv.2023.10.00267
Even after triple COVID-19 vaccination, several population-based studies have demonstrated that patients with cancer continue to be at an increased risk of COVID-19 infections, depending on specific cancer types and different active therapies.1 Higher cumulative risk was identified in vaccinated patients with lung, colorectal, liver, and pancreatic cancer, whereas lower risk was seen in vaccinated patients with prostate, breast, and gynecological cancer.1 Data from several retrospective studies confirmed the improvement the short-term clinical outcomes by decreasing hospitalization and 30-day mortality among patients with cancer.2,3 Additionally, regularity-of-antineoplastic-therapeutics disruption can be caused by mild COVID-19 infection4 that is similar to hematological malignancies.5 A recent study revealed that antibody titers higher than 800 binding antibody unit (BAU) were efficiently correlated to SARS-CoV-2-variant-infection-immunological protection and severe symptomatic COVID-19 (Figure 1, 2).6
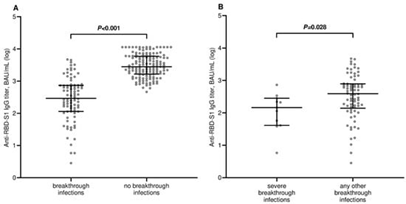
Figure 1 Demonstrating the comparison of scatter plot distributions and medians of antibody titers.
(A) Comparison of antibody titers between breakthrough infection cases and non-cases.
(B) Comparison of antibody titers between severe breakthrough infection cases and any other cases.RBD-S1, receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein (S1); binding antibody unit (BAU); log, logarithmic values. Bars represent median values with a 95% confidence interval (CI).6
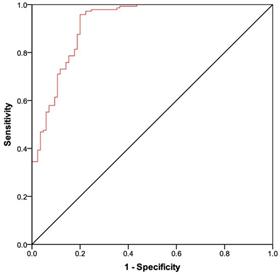
Figure 2 Demonstrating the ROC curve analysis of anti-RBD-S1 IgG titers on the SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections AUC relative value: 0.92 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.88–0.95), p < 0.001., receiver operating characteristic (ROC); RBD-S1, receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein (S1); area under the curve (AUC).6
In conclusion, in patients with advanced cancer, active treatment should be prioritized, whereas after COVID-19 third dose will enhance humoral antibody response to protect against COVID-19 breakthrough infections.
None.
None.
Author declares that there is no conflict of interest.

©2023 Cheepsattayakorn, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.