Journal of
eISSN: 2574-9943


Case Report Volume 2 Issue 2
1Department of Dermatology, Hospital Universitario de La Princesa, Spain
2Department of Pathology, Hospital Universitario de La Princesa, Spain
3Department of Microbiology, Hospital Universitario de La Princesa, Spain
Correspondence: Constanza Martinez Mera, Department of Dermatology, Diego de León 62, Postal code 28006, Madrid, Spain, Tel +3460 8771 695
Received: March 11, 2018 | Published: April 10, 2018
Citation: Martinez-Mera C, Capusan TM, Moyano-Herrero M, et al. Tinea capitis in 2 immunocompetent elderly patients. J Dermat Cosmetol. 2018;2(2):132-133. DOI: 10.15406/jdc.2018.02.00062
tinea capitis, trychophyton tonsurans, elderly, folliculitis, corticosteroids
Tinea capitis is classically considered as a childhood disease, however in recent years has been an increase in the involvement of adults. The prevalence of tinea capitis in adults is around 10% in southern of Spain.1,2 The population have been epidemiological that had conditioned the emergence of etiological agents in fluctuating form.3 We review the frequency of Trichophyton tonsurans in our hospital center and present 2immunocompetent elderly patients with tinea capitis in whom this agent is isolated.
Determine the prevalence of tinea capitis due to Trichophyton tonsurans in the elderly population of the University Hospital of La Princesa, Madrid.
A retrospective study was performed since 2009 to 2016. It were reviewed all the positive fungal samples of skin lesions and annexes sent to microbiology.
In total, 424positive samples for fungi with skin lesions and adnexa were collected. From these only 6 presented a culture of Trichophyton tonsurans, which corresponds to 1.4% of the total positive cultures. In 3 of the 6 cases had tinea capitis and 2 from the 3 patients were older than 65years.
The first case is an 87year‒old woman, without immunosuppressive factors and without risk environment, who started 18 months before with pruritic lesions on the scalp, alopecia, erythema, thick adherent scales, pustules and follicular black dots (Figure 1A) (Figure 1B). Fungal culture was positive for Trichophyton tonsurans. Serologies (VHB, VHC, and VIH) were negative and a complete blood count test and biochemistry analysis was normal. Histopathology showed a follicular involvement by a dermatophyte with an endothrix pattern (Figure 2A). Terbinafine 250mg/day was prescribed for 16weeks. A persistence of residual slight erythema was observed. Control cultures and KOH were negatives.

Figure 1(A,B) Tinea capitis with alopecia in bilateral frontal and parietal region. Erythema, thick crust adhered, pustules and follicular black dots.
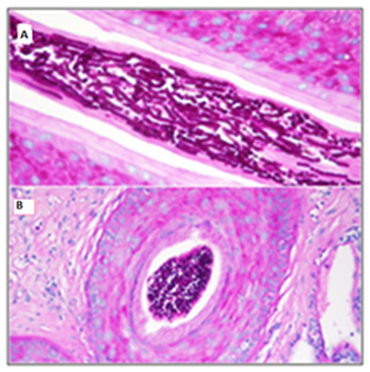
Figure 2 (A) Tinea capitis with endothrix pattern first case HE (Hematoxilin and eosin) x40.
(B) Tinea capitis with endothrix pattern second case HEx20.
The second case is a 90year‒old woman, without immunosuppressive factors and without a risk environment, which began 6months before with progressive pruritus on the scalp, with diffuse erythema, follicular hyperkeratosis, pustules and diffuse black dots. Numerous annular and circinate erythematous and squamous plaques were observed in the dorsal neck and scapular region (Figures 3A‒3C). Fungal culture was positive for Trichophyton tonsurans. Serologies (VHB, VHC, and VIH) were negative and a complete blood count test and biochemistry analysis was normal. Histopathology showed a follicular involvement by a dermatophyte with an endothrix pattern (Figure 2B). Itraconazole 200mg/day for 8weeks and eberconazole 1% topical was prescribed with progressive disappearance of the lesions.
In recent years Trichophyton tonsurans is becoming increasingly isolated, linked to immigration from Africa, among other factors.2,3 Related to our local epidemiology, it was observed that in the period 2009‒2016 there was a low prevalence of Trichophyton tonsurans, which could be explained by the limited foreign population that is treated in our hospital. Tinea capitis in adults predominate in postmenopausal women, prone by the use of topical corticosteroids.4 Desquamative lesions, alopecia and black dots have traditionally been related to infection by Trichophyton tonsurans.5,6 Exceptionally cases have been reported where the predominance of inflammatory lesions are seen as in the first case.7
It is important to exclude fungal infections in cases that simulate seborrheic dermatitis, folliculitis or impetigo with torpid evolution, because produce a delate in the diagnosis, as in our patient who being delayed a year and a half after the start of the clinic. Mostly is important to perform cultures prior to treatments, to make the right diagnosis, identify the correct etiological agent and know adequately the local epidemiology of tinea capitis of each center.
None.
This manuscript has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by another journal. All authors have approved the manuscript and agree with submission to the Journal of Dermatology & Cosmetology. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

©2018 Martinez-Mera, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.