International Journal of
eISSN: 2577-8269


Research Article Volume 6 Issue 6
1Bachelor of Accounting and Master of Administration from the Autonomous University of Zacatecas, PhD in Public Administration from the International Institute of Law and the State, Mexico
2Bachelor of Administration from the Autonomous University of Durango, Master of Administration from the Autonomous University of Zacatecas, Doctor of Public Administration from the International Institute of Law and the State, Mexico
3Pharmacobiological Chemist from the Autonomous University of Zacatecas, Master in Forensic Sciences from the Zacatecano Institute of University Studies, PhD in Forensic Sciences from the Zacatecano Institute of University Studies, Mexico
4Bachelor of Accounting and Master of Administration from the Autonomous University of Zacatecas, PhD in Public Administration from the International Institute of Law and the State, Mexico
5Degree in Psychology, Autonomous University of Durango, Mexico
6Graduate in Accounting from the Autonomous University of Zacatecas, Master’s Intern in Administration with terminal area in Finance from the Autonomous University of Querétaro, Mexico
Correspondence: Rosa Aida Rivera Cornejo, Bachelor of Accounting and Master of Administration from the Autonomous University of Zacatecas, PhD in Public Administration from the International Institute of Law and the State, Mexico
Received: November 24, 2022 | Published: December 7, 2022
Citation: Cornejo RAR, Berumen LEP, Briones RMM, et al. Reincorporation of victims of enforced disappearance in their workplace. Int J Fam Commun Med. 2022;6(6):331-336. DOI: 10.15406/ijfcm.2022.06.00299
The statistical increase in the commission of crimes such as Forced Disappearance in Mexico has generated a great social impact and despite the years, regulations and established strategies, it continues to grow constantly, affecting individuals individually, as well as in the scenarios in which unfolds on a daily basis. Approximately only 55% of people who have been victims of this crime are located alive and most of them are of working age, for which it is necessary in companies and institutions to train and develop protocols for human resources departments, seeking to be able to get involved in the prevention, care and intervention of the same, due to the bio-psycho-social sequelae that may affect the employee and consequently decrease productivity and quality within the company.
Keywords: forced disappearance, labor insertion, human resources
The perception of insecurity in Mexico is increasing. According to figures from the National Institute of Statistics, Geography and Informatics1 By June 2021, 66% of the population aged 18 or over considers it unsafe to live in the city that resides for fear of being a victim of a crime, being Fresnillo, Cancún, Ecatepec de Morelos, Coatzacoalcos Naucalpan de Juárez and Tonalá the cities with a higher proportion of their population that expressed feeling insecurity. 71% of the women interviewed expressed feeling insecurity, while the perception was lower for men at 60.9%. Many people have even experienced changes in routines and habits in the face of uncertainty. The emotional stability of people can be altered by the fear of what can happen, according to the perception of their environment regarding insecurity, even more so their instability grows when they have been the victim of a crime, which can limit their performance, their daily life, projects, generate disabilities, reduce their productivity and affect their work and interpersonal relationships. This investigation focuses its attention on victims of the specific crime of Forced Disappearance that affects not only people and their integrity, but also companies that suffer from its absence and, in future moments, the reintegration into the labor area, generating fundamental impacts. in their productivity and in the achievement of institutional objectives.
Goal
Propose from the legal point of view, the efficient incorporation of human resources in the labor area, supported by motivational theories and treatments, protecting the health and well-being of those who have been victims of enforced disappearance.
This research is descriptive, because it expresses the characteristics of the people who have been victims of forced disappearance and the working conditions they face. The documentary technique is applied as a source of indirect information, by resorting to the analysis of current legislation, reports, statistics and psychological and motivational theories that provide approaches to the area of human resources to propose adequate alternatives for labor reintegration for victims of forced disappearance.
General Law on Forced Disappearance of Persons (LGMDFP)2
Based on article 4, F VI and VII of the General Law on Forced Disappearance of Persons, Disappearance Committed by Individuals and the National System for the Search for Persons (SNB), it is understood as a person not located, that of the whose location is unknown and according to the information provided to the competent authority, it is not related to the commission of any crime. On the other hand, a Missing Person is one whose whereabouts are unknown and it is presumed under any indication that the event is related to the commission of a crime. Both the executive commission and the commissions of victims will provide the Disappeared Person and found alive according to their faculties and with the support of other institutions, in addition to the right to the truth, aid, assistance and care measures (arts. 136 and 137 ).
To protect their rights, personality and legal interests, to restore their assets and rights, to proceed against those who make use of their assets or carried out actions to deprive them of their assets or rights, to receive specialized treatment to overcome the damage suffered by them types of crimes, if possible, directly or with the support of their family, which will also enjoy the right to be informed and access specialized programs and services to care for and overcome the damage. In the same way, they have the right to receive immediately and without restriction: help, assistance and attention from the executive commission or the victims' commissions, as long as these are provided to them by the corresponding institutions. The declaration of absence must be granted within a period of no more than 6 months from the start of the procedure and its purpose is: to recognize and protect the legal personality and the rights of the disappeared person and broad protection to their relatives.
According to articles 145 and 146, the importance of reporting and processing the Special Declaration of Absence lies in the beneficial effects for the Disappeared Person, among others: Preserving parental authority and protection of assets and rights of their children under 18 years of age , as well as guard and protect minors, protect the assets of the Disappeared Person, set forms and deadlines so that the family can dispose of the assets of the disappeared person under judicial control, allow their beneficiaries to continue enjoying social security as a result of their work , provisionally suspend civil, administrative or commercial acts against their assets and rights, declare the temporary unenforceability of their duties or responsibilities, assign a legal representative during their absence,establish rules so that once it is located, their rights and obligations are restored, as well as the recovery of their assets.
Similarly, the victims of these crimes have the right to full reparation through the following measures:
Federal Labor Law (LFT)3
Based on articles 53 and 54 of the Law, the employment relationship ends when the physical and mental capacity or inability that the worker has manifested prevents him from continuing to provide his work. If the disability comes from a non-professional risk, the worker will receive one month's salary and twelve days for each year of service or, if possible and expresses it, another job is assigned according to his aptitudes, receiving training and training. necessary. It also allows employer and worker agreement to set the working day and distribute the necessary rest hours and, if possible, rest on Saturday afternoon or its equivalent, without violating legal provisions (art. 59).
It is important to mention that, for a worker, part of his obligations consist of carrying out his work with intensity, care, care, in the agreed manner and time, and giving immediate notice to the employer of the justified reasons that prevent him from attending his workplace. , except for reasons of force majeure. On the other hand, based on art. 132, employers are obliged to grant leave without pay to their workers declared missing, for whom a Special Declaration of Absence has been issued in terms of that law and in this sense, it is prohibited under these conditions, to dismiss or terminate the employment relationship (art. 133). When the disappearance of a worker as a criminal act, is related to or derived from the provision or due to his work, whatever the place or time in which it is provided, it will be considered as a work risk even when it occurs in commute from work to home or from home to work. These criminal acts, can generate in the worker, a temporary disability, when he loses faculties or aptitudes that partially or totally make it impossible to carry out his work for a while; partial permanent disability, when their faculties or aptitudes to carry out their work decrease or; Total permanent disability when he loses his faculties or aptitudes to perform any job for the rest of his life (Chapter Nine LFT).
Workers who suffer a work risk will have the right to receive medical or surgical assistance, rehabilitation, hospitalization, medicines and healing material, prosthetic and orthopedic devices, the employer being released from these obligations when the worker is intoxicated, under the influence of a narcotic unless there is a medical prescription and when the worker alone or with the support of someone else causes the work accident. In addition to the rights listed, you will receive compensation that is indicated below:
According to the consequences of the event, the degree of disability of the worker will be determined and the compensation will be calculated according to the daily salary that he received when the event occurred and the increases that occur later, according to the work he performed, and should not be less than the salary. minimum, considering for its determination the degree of disability and its temporality or permanence, also considering (art. 498) that the employer will reinstate the worker who suffered a work risk to his job as long as he has the capacity and presents himself within the year following the date your disability was determined.
Importance of human resources
A company can be conceived as a set of processes, systems and subsystems, significant and complex, that work at the same time and keep it running, thus, when some aspect or part of the system does not work, it tends to generate important changes in the rest of your gears. Throughout life, business systems become changeable depending on global developments. Companies have various types of resources that are combined to help their operation, development and achievement of goals throughout their lives, human resources being a fundamental part of these. To denote the concept of "human resources", from its simplest structure, according to the Royal Spanish Academy4 "resources", can be defined as the "Set of elements available to solve a need or carry out a company", in the same way it is understood by "human" the being that "has the nature of man (rational being)". Thus, the human resources department within a company can be considered as "that set of human elements available to solve the needs within the company". Derived from this, the Human Resources Administration, is conceived according to Mondy, R Wayne5 as "the coordination of the participation of individuals to achieve organizational objectives", thus within the company. Due to the above, the human resources department is considered one of the main nuclei in companies, since directly or indirectly any change in this resource has a favorable or unfavorable impact within them.
Aspects that influence human resources to achieve objectives
For the efficient control of human resources, companies face endless challenges, from the evolution of the markets that constantly change due to the economic situation, demand, globalization, government or health regulations, technological revolution, natural disasters, contingencies health, socio-cultural aspects, among others, that characterize the place where the company is established, also influencing the individual situation of each member of the company such as problems at home, stress, risks, illnesses, loss of loved ones, etc. As can be seen, any aspect, however large or small, that occurs in human resources, has an impact on productivity, stability or quality in companies. This is the case when a worker is absent, being the only person who knows how to manage any machine within the production areas, or who exclusively performs certain types of operations or functions, stops the productivity of the company. The reason why a worker is absent from work can be diverse; by will, tradition, illness, death, or any other cause of force majeure. The present investigation focuses on analyzing the insertion in the company of an employee who is absent involuntarily caused by his forced disappearance, the result of committing a crime and is located alive. Considering that there are extraordinary events for companies that leave their daily operations, the Human Resources Administration area requires proposals and alternative solutions to face problems faced by the victims of Forced Disappearance, seeking their adequate reintegration into the workplace.
It is therefore necessary to know the main characteristics that a victim of Forced Disappearance faces. According to the United Nations Human Rights Council (UN, nd) "victims can suffer for a long time the physical and psychological scars of this form of dehumanization and the brutality and torture that often accompany it." It is undoubtedly considered that not all people react in the same way to traumatic events, even when they become identical situations, just as not all forced deprivation of liberty produce the same psychological or physical effects on the victims, since it depends a lot on the balance and conditions of the same in this situation, conditions that can minimize the consequences of the traumatic event. Some physical conditions suffered by a person who is a victim of enforced disappearance are: lack of exercise, alteration of the circadian cycle (natural cycle of physical, mental and behavioral changes that a person's body experiences in 24 hours),6 due to the absence of and alterations due to the discrepancy of light and darkness, anorexia nervosa can arise, which inhibits appetite and hunger, injuries due to torture or the passage of time when being in unfavorable situations, among others. Within the psychosocial aspects, to understand the impact on the individual, according to Janoff - Bulman cited in the Journals Open Edition7 people have a belief system of the world and the environment that helps them relate, these beliefs are: trust in others, sense of control, feelings of invulnerability, recognition of self-worth, among others. These feelings or beliefs that remain constant in their way of thinking, feeling and acting help them to live in a structured way in society and their environment, as well as to give meaning to their existence; However, when a person is in an extreme situation or suffers a traumatic event, it has the ability to deconstruct the person and destroy their assumptions, causing conflicts in them.
Post-traumatic stress syndrome is one of the main consequences in victims of kidnappings and forced disappearance, it is then necessary to determine and denote its criteria, according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of mental disorders (DSM-5)8 establishes the following criteria to be taken into account for its diagnosis:
Having mentioned the symptoms and criteria to take into account to determine post-traumatic stress and returning to the fact that it is one of the main consequences of the victims of kidnapping and forced disappearance, we can say that, without a doubt, it affects performance, productivity and quality within an organized system in companies, due to the instability of the employee, as well as his current physical condition. It is considered extremely important that companies and human resources administrators are trained to face the difficulties that the recession of an employee who has been a victim of forced disappearance entails and thus provide adequate integration into the workplace.
Intervention of the human resources department in the reintegration of victims of forced disappearance
Abram Maslow9 is one of the referents within personality theories with his "hierarchy of needs", he proposed a pyramidal hierarchy locating five levels, which are divided into: 1) Physiological needs, 2) Need security, 3) Need for belonging and love, 4) Need for esteem and 5) Need for self-actualization. These needs are dynamic and constantly changing. As previously mentioned, a person who is a victim of Forced Disappearance and with post-traumatic stress is in an unstructured state, that is, if we return to the proposal made by Abram Maslow, it could be considered that a person with these conditions is at the bases of the hierarchy. of unsatisfied needs. It is in this way that the human resources department must evaluate and facilitate certain conditions for the employee who is the victim of Enforced Disappearance, since he needs to satisfy said needs. Within the main foci, physical needs would be considered, that is, if the employee requires medical attention (malnutrition, trauma). If the state of health is not favorable to carry out their activities within the company, the human resources department must evaluate whether it considers immediate reinsertion to the workplace favorable. In the aspect of security and belonging due to the condition of the employee, you can assess whether or not the application of security measures is considered necessary for the employee, such as follow-up calls, accompaniment if there is a personnel transport vehicle within the company, offer confidence in security within the facilities, identify the support networks that said employee has in the company (close colleagues, It is considered advisable that the human resources department can work together with professionals such as psychologists, security institutions, doctors and psychiatrists for the treatment of symptoms and syndromes that may affect the physical and psychosocial state of the employee, highlighting that, if Said company does not have professional personnel to treat this employee, you can channel it with external professionals who can provide this attention.
A worker with this syndrome or with mild symptoms can be considered an immature person within the "maturity theory" proposed by Chris Argyris,10 since his maturity was taken away by external factors, thus, the objective It could be collaborating so that it can return to the state of maturity in which it was found and develop functionally despite the mishap. Chris Argyris establishes that the development of a person goes from a situation of immaturity to a situation of maturity. An immature person is characterized by being passive, dependent, lacking confidence, and a tendency to be controlled by others. It is in this way that it seeks to increase and expand work responsibilities in an appropriate manner, allow greater variety in the tasks to be carried out and adjust supervision styles to allow greater participation and promote better human relations in order to increase the best business practice, that is, the better the development, the greater the productivity. In the case of victims of Forced Disappearance, it would be sought that the employee or the victim person have a transition from a passive employee to an active one, this would help to reduce the symptoms, increase the confidence and proactivity of the employee and therefore improve productivity. Achieving independence would be something significant in him, that is, working alone or in a group and contributing satisfactorily. In turn, it would seek to train a flexible and adaptable employee, awaken deeper and stronger interests in the workplace, generate awareness of past aspects and future objectives, seeking to generate greater awareness in the control of the "I" generating greater self-control.
Karl Lewin for his part, developed the so-called "Field Theory" where he explains that the human being acts under the influence of internal factors, as well as his environment, existing on the one hand motivating forces that drive him to face challenges and achieve objectives, on the other hand, inhibitory forces that limit or paralyze its progress or development.
For the application of this theory, Lewin proposes three stages that are perfectly applicable to organizations, which are indicated below:
Applying field theory to the issue of Forced Disappearance, when a worker has been a victim of this type of crime, it may be too complex to incorporate it into their organization or work area, since it may have a set of internal sequelae and triggers in their environment that arrive to limit it, such as periods of anxiety, mania, depression or little lucidity. However, the intervention of the human resources administration (human resources department) will be necessary to develop the possible changes, so that the worker gradually incorporates the change and develops a perception of physical, mental, psychosocial and economic improvement. which, consequently, will modify its development and potential within the work carried out, in the same way, the relationship with the members of the organization will improve and increase their productivity projecting in a general way in the company. In time, you will develop positive thoughts, optimism and security, which allow you to be functional in a personal way in any aspect to develop.
According to statistics from the National Registry of Unlocated Missing Persons (RNPDNO),11 the number of disappeared persons in the period from March 15, 1964 to December 13, 2021 was 234,914, of which 129,939 have been located alive, that is, approximately 55% Figure 1. According to the missing persons and those found alive, 56% correspond to the female sex, 44% to the male sex and less than 1% undetermined. Based on the ages of the Disappeared Persons, 174,001 range between 15 and 59 years of age, who will be considered for the purposes of this investigation as persons of working age. If to this total, the percentage of people that in global terms have been located alive, which is equivalent to 55%, is applied, then we will have approximately the following Figure 2:
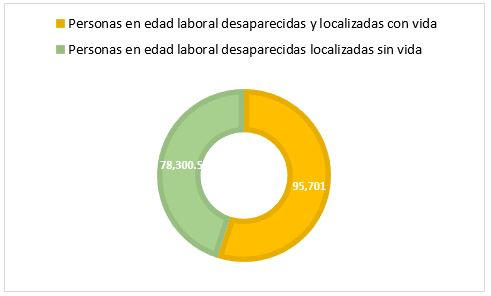
Figure 2 Persons of working age Disappeared.Font: Own elaboration based on statistical data CNPDNO 2021
If we start from these figures, 95,701 people who are considered to have been declared missing and found alive, would be in a position to rejoin working life. It is a considerable figure when imagining the impact it has on each of the companies that receives them to resume the activities they had been carrying out before their disappearance.
It is therefore important to analyze the agreement between the current legislation in Mexico regarding Persons Declared Disappeared who are located alive and the theories of the motivation of human resources in organizations.
Proposal
Based on the General Law on Forced Disappearance of Persons, Disappearance Committed by Individuals and the National Person Search System, within organizations, it is important to have controls that make it possible to identify when a worker is absent. Knowing that the causes are diverse, if it were a Missing Person, it will be important after the deadlines established by Law, to obtain the Declaration of Absence and in the case of being located alive, they must receive specialized care to restore their well-being and compensate the damage suffered, by the person who committed the crime, by victim support organizations or, where appropriate, the federal entities or the federal government in their jurisdiction, guarantee their attention if there was the direct or indirect participation of any public servant in the commission of the crime. In this way, the corresponding instance will plan the restitution of the assets and rights of the person who was located alive, in this case, the company's human resources department must receive the documentation that proves their location alive, since part of their rights can be incorporated into your work.
In accordance with the previous law and in compliance with the Federal Labor Law, the corresponding information must be provided to identify if the Disappearance of the Person was derived from a work risk or not, for once located after a physical assessment and It is determined if there is any partial or total disability and if it is considered temporary or permanent, thus, the company and/or the labor authorities deliver the corresponding compensation or pensions. The company, for its part, must prepare to incorporate it into the work that it had been doing before the event, if its health condition allows it, or in agreement between the employer and the worker, they can agree on different working conditions that facilitate the incorporation process. Knowing that there are other theories, in addition to those raised in this document, it is suggested that the human resources department obtain the results of the diagnosis that indicates the state of health of the worker, both physical and psychological, considering that his physiological needs, security and belonging are dissatisfied and displaced due to the traumatic event, which can lead to more complex syndromes or disorders such as post-traumatic stress, leading it to express immaturity behaviors, and it is important to consider that the behavioral and emotional aspects in where the employee is is due to the influence of the environment and how the problem is internalized at a conscious and unconscious level.
It is suggested that the human resources department have a protocol and visual and simple information available to employees (as it exists for fires, floods, etc.) to detect situations and prevent risks of Forced Disappearance. If it occurs, collect the documentation that allows timely compliance with the laws on the matter. It is proposed that companies train various members that are part of their staff to develop new skills or acquire knowledge that will facilitate the development of various functions within the organization, in this way, in the absence of a worker, it has someone trained to replace them in their tasks pending their location and insertion, in this way, companies will not see their operation, protection and productivity diminished, for the benefit and collaboration of the human resources administration of the company as a whole. To facilitate the reinsertion of a worker after being found alive, offer members of the organization preventive training and awareness about the psychological effects produced by this type of crime, as well as changes in behavior to facilitate interpersonal relationships, offer the Follow-up worker in overcoming the trauma from the company or channeling it with external specialists to provide support for as long as necessary. Carry out recreational activities or those necessary that allow the worker to change their perception of the facts, reduce their stress, fears, limiting ideas and increase their tranquility, optimism and well-being until they consider themselves fully functional. Flexible schedules and different functions can be temporarily offered while the worker transitions to a state of well-being, which translates into the recovery of his maturity, and a feeling of security, detonating favorable effects on his productivity and that of the organization as a whole.12,13
The Forced Disappearance of people in Mexico has been increasing despite the creation of laws on the matter and the increase in penalties imposed on those who participate directly or indirectly in the commission of the crime. The authorities, commissions created and measures implemented have been exceeded, since the socio-economic situation, which is difficult for many Mexicans, makes them vulnerable to participate in the commission or be a victim of it. Human resources are fundamental within organizations for the achievement of objectives and preservation of personnel, in this way people who have been declared missing and found alive, and who, in turn, may have physical disabilities and medical conditions psychological (such as post-traumatic stress), they can be adequately incorporated into the tasks they performed before their absence or the referral, depending on their state, to new activities. For this, companies need to develop protocols for prevention and attention to the occurrence of these crimes to protect their employees or incorporate them back into their working life, considering that an employer obligation is to respect and return the rights that had been suspended during their absence. In the same way, establish policies, professional support and administrative measures that facilitate their labor insertion, moving to a state of homeostasis and productivity in a less prolonged period. This business culture is recommended to be designed and implemented throughout the national territory, especially in federal entities or geographical areas where this crime occurs more frequently. The human being is a complex being, especially due to his rational character, considering that, from his way of thinking, his way of living, acting and relating is derived, hence the wisdom of popular sayings such as "a healthy mind in a healthy body".
None.
The autor declares there is no conflicto of interest.

©2022 Cornejo, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.