eISSN: 2575-906X


Research Article Volume 2 Issue 1
University of Guayaquil, Ecuador
Correspondence: Guido Poveda Burgos, Teaching researcher, Faculty of Administrative Sciences, University of Guayaquil
Received: October 29, 2017 | Published: January 5, 2018
Citation: Burgos GP. Demand of the Ecuadorian Pitahaya towards the Dutch market period 2014-2015. Biodiversity Int J. 2018;2(1):8-11. DOI: 10.15406/bij.2018.02.00035
Biodiversity in Ecuador is classified as one of the most diverse and exquisite in the world, especially in tropical fruits, and that is why the export of Ecuadorian pitahaya seeks new markets such as the case of Holland, the production of fruit is given in the Amazon region of the country also contains medicinal properties by its composition, also the fruit is used to create new products, such as juices, mousse and salads. The growth of the exports of the pitahaya has been possible thanks to the change of the productive matrix, the properties of the fruit are attractive for the European countries, so they prefer products with low caloric intake and carbohydrates, it also has a high content in vitamin C. The destination of the exports of pitahaya studied corresponds to the period 2014-2015. The level of competitiveness that Ecuador has with the fruit is very high, being more preferred the yellow pitahaya, which is desired by its sweet and tropical flavor, in such a way that it is consumed by countries of Europe like Holland.
Keywords: biodiversity, export, fruit, productive matrix, pitahaya, properties
The pitahaya, pitaya or dragon fruit is an exotic fruit that comes from a type of cactus and has a lot of beneficial nutrients for health. It is a cacti plant, and as such, very resistant to droughts. The plant is a succulent, rustic cactus, with long triangular stems, whose tentacles search the rocks incessantly for which they feel a special predilection, whether there is earth nearby or not; it usually gets entangled in the nearby trees feeding on the humidity of its bark and climbs freely through the branches at eight or ten meters from the ground without penetrating a single centimeter into the ground.
This paper analyzes exports of Ecuadorian pitahaya, Stenocereus queretaroensis, to the Dutch market, considering that the product is an exotic fruit that has a large exportable supply to European markets. Ecuador, through the change of the productive matrix, contributes to its products an added value, in such a way that the small producers realize a new product.
The pitahaya when considered an exotic fruit is very desired in the European markets, especially in the Netherlands. In addition, Ecuador has great potential in the production of pitahaya, especially in the Amazon and subtropical areas, where the characteristics of the climate are ideal for the development of the fruit, in relation to its color, size and taste. Ecuador is one of the exporters of yellow pitahaya, in such a way that there is interest in yellow pitahaya for the sweet taste.
The present research work has been carried out through the application of the descriptive method and documentary bibliographic research which has allowed to know the demand of the Ecuadorian pitahaya to the Dutch market during the period 2014-2015. The descriptive method allows to evaluate certain characteristics of a particular situation such as the case of the exportable supply of pitahaya, likewise describes a situation, phenomenon, process or social fact to formulate, based on this, precise hypotheses.
Brief review of the demography of the Netherlands
Holland is the 17th economy by volume of GDP, it is also in position 66 of the population table, composed of 196 countries In 2015 it had a population of 16,979,120 people, in 2014 it had 16,900,726 people. The Netherlands has a very high population density, with 409 inhabitants per km2. The net migration rate is 2.02 per 1000 inhabitants, each year its population grows 0.45% per year. The predominance of Holland in the Netherlands has been translated into regionalism by the other provinces, in addition to the population is not called Dutch but as Dutch. Holland has gained fame in consuming fruit pulp as its population likes the easy use that is given to the product in bakery foods, beverages, daily products, baby food.
Brief review of the geography of the Netherlands
The Netherlands is located on the west coast of the Netherlands. It is of temperate oceanic climate Divided into two provinces North Holland and South Holland. Geographical coordinates: 52° 30 'N 5° 45' E. Limita; North with the North Sea, South with Belgium, East with Germany, West with the North Sea. It has an area of 41,526 km2.
It has numerous rivers; the most important are the river Reno, Waal and Meuse also has lakes and an extensive inner channel. The lowest point of Holland is a polder, (terrestrial surfaces gained to the sea and are below the sea level); as is the case of; Zuidplaspolder, which is 6.75 meters below sea level, near Rotterdam. And the highest is Vaalserberg at 322 meters.
Some of the natural resources that it possesses are oil, salt, sand, natural gas, limestone, and the earth which uses it in arable land in a 21.96%, in permanent crops in 0.77%.
History and origin of pitahaya
Also known as dragon fruit, pitaya, cactus pitahaya, it is from the cactaceae family, which are found in very humid and dry places. Originally from the southwestern region of the United States and Mexico, taken to Vietnam by the French more than 50 years ago, it is found from 0 to 2,000 meters above sea level in areas of tropical, subtropical and deciduous forests.
It is also native to the Pacific Coast of Guatemala, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Bahamas, Bermuda, Vietnam, Thailand, Australia and Taiwan, also in countries such as Brazil, Uruguay, Ecuador, It is cultivated in some tropical and subtropical regions, some of the main world producers are Israel, Nicaragua and Mexico.
In Ecuador, the crop has great agro-ecological potential for the production of pitahaya, especially in the Amazon and subtropical areas. In 2003, the first association of pitahaya producers was created; called Asopitahaya with 70 partners, producing around 300 tons.
Types of pitahaya and its main uses
There are two types of pitahaya:
The pitahaya Contains ascorbic acid, calcium, phosphorus, carbohydrates, fiber, protein, iron. It is used for the health of people and its benefits are: It reduces cholesterol, It helps to prevent certain types of cancer and diabetes, It helps digestión
Market analysis
The Dutch market is characterized by having an open economy in such a way that trade with other countries is of great importance. The Dutch industries mainly produce products that are intended for the consumer, however, they also produce semi-finished products, such as: sugar, flour, cocoa and starch.
In the Netherlands, there is no direct production of fruit pulp, however, there is a sector of logistics services, processing, storage and sales representation. Ecuador is one of the countries with the highest pulp production of different fruits such as yellow pitahaya.1
The main cities in the Netherlands that demand pulp of Ecuadorian fruit are: Amsterdam, Rotterdam and Holland due to the proximity to the port. Within these cities you can find the processing and logistics of the product, since its ease of access to the port allows greater access to other countries.
The consumption of fruit pulp like pitahaya in the Netherlands is mainly aimed at an intermediate market, that is, restaurants, bakeries, natural and industrialized food and beverage producing companies that use the pulp as an ingredient in the process of making their final product. . The fruit pulp is easy to use and serves different products.1
Among the main uses that are used to fruit pulp are the following
Bakery: fruit bread, cookies, muffin cakes, among others. In drinks you can find fruit juices and nectar. Among the products of daily consumption are: ice cream, yogurt, pudding, fruit bar, among others. And baby foods include: cereals, desserts and fruit-based drinks.
Dutch economy
It is determined to be a stable industry, as well as unemployment and inflation subject. The agricultural sector, mostly industrialized, occupies only 2% of the country's labor force. That is, it obtains one of the largest sources of supplies for export (Table 1) (Figure 1 & 2).
Product Code |
Product Description |
Description |
Applied Rate |
Equivalent Rate of |
0810.90.40 |
Pitahaya (Cereus spp.) |
MFN Rights (Applied) |
0.00% |
0.00% |
Table1 Tariff Barriers and trade agreements in the Netherlands.
Source: Market Access Map; Elaborated by: Guido Poveda B.
Applies the following tariff for the importation of pitahaya with the Sub-program 0810.90.40
Note: It is detailed that the aforementioned commercial agreements are approved once the Certificate of Origin has been submitted for the corresponding confirmation to the Ecuadorian production of the assigned product.

Figure 1 Non-Tariff Barriers in the Netherlands.
Source: Market Access Map; Elaborated by: Guido Poveda B
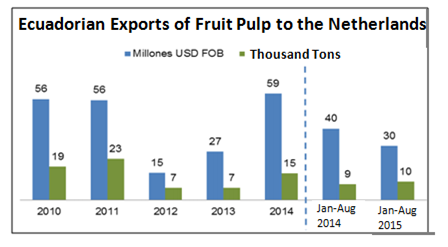
Figure 2 Exports of fruit pulp to the Netherlands.
Source: Central Bank of Ecuador; Elaboration: Commercial Intelligence and Investment Office, Pro Ecuador
Ecuadorian exports of fruit pulp to the Netherlands during 2014 were USD 59 million in FOB value and 15 thousand tons.
Destination of the ecuadorian exports of pitahaya
The main destinations for pitahaya exports in 2015 were the Asian countries. Hong Kong had a 53% stake with USD 1.7 million, Singapore 20% with USD 639 thousand, Indonesia 7% with USD 229 thousand. Other fruit importing markets from Europe are the Netherlands and France, with a share of 5% and 3% respectively (Figure 3).
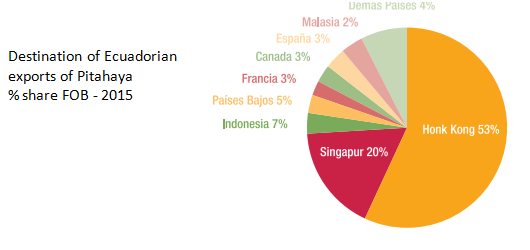
Figure 3Main destination of the Ecuadorian Pitahaya.
Source: Central Bank of Ecuador; Elaboration: Commercial Intelligence and Investment Office, Pro Ecuador
Competitive advantage of ecuador as a supplier of pitahaya
Among the advantages that ecuador has, we can cite the following: The pulp is soft and has a sweet flavor. The climate is an indispensable factor for the production of this fruit, for that reason there is seasonality almost all the year. It has 2 large harvests in the year, in the months of December - March and May - June. While the months of August - September are of lower production and in the remaining months the fruit can be harvested in Limited quantities.2 The Ecuadorian producers and exporters make sure to comply with all the quality standards demanded by the destination country, such as cleaning and sanitation of the fruit. Likewise, the price is competitive according to the quality of the fruit. In addition, the main exporting farms have the necessary certifications to export.
Channels of commerce
Structure of the marketing chain: The exporter has different alternatives for marketing, such as: Sell the fruit pulp to an importing agency, they are responsible for importing the product to Holland and deliver it to the buyer. Another option is to sell the product directly to the consumer or distributors. Another alternative is to sell the pulp in bulk to the processors, who use it as raw material and perform the packaging process for the final consumer. Depending on the request and need of the customer, during the pulp mix, you can use fruits of different origin, in search of balancing quality and price.1
Development of commercial channels in the Netherlands (Holland)
Food services is the most important sector in countries such as Holland, for this reason the distribution of fruit pulp starts in specialized channels, such as restaurants, organic and biological products, ethnic stores such as Chinese supermarkets, Arabs, as they offer variety of fruit pulp.
Transport
Taking into account the distance between Ecuador and the Netherlands, international transport is usually carried out by sea or air. The choice depends on the negotiation and needs of the exporter and the importer.
If done by air transport, the shipment allows faster, which is favorable for the transfer of products that require less volume or quantity. It should be noted that the transport risk is lower, since insurance costs are cheaper. While by maritime transport the quantity of the product must be in great weight and volume. It is generally applied to containerized loads, such as bulk products.
Evolution of export
Exports of the sector: The pitahaya is within the non-traditional fruit sector such as: papaya, pineapple, mango, passion fruit and among other more detailed in the portal of Proecuador,1 80.21 million FOB value was registered in exports. This Table 2 shows the exports of pitahaya around the world, where the FOB value was 3.2 million and in 344 tons in 2015. In addition, the pitahaya is considered within the non-traditional fruits that reached in 2015 the largest exportable supply. The Netherlands occupies only 5% share of the fruit, which indicates that it is a decreasing value for Ecuadorian exports, however, correctly analyze the Dutch market will be very useful to improve the exportable supply to that country (Figure 4).
Ecuadorian Exports of Pitahaya to the World |
|||||||
Thousands USD FOB |
Tons |
||||||
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
TCPA FOB |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
TCPA FOB |
759 |
1,243 |
3,249 |
107% |
99 |
128 |
344 |
87% |
Table 2 Exportation of Ecuadorian Pitahaya.
Source: Central Bank of Ecuador; Elaboration: Commercial Intelligence and Investment Office, Pro Ecuador
Destinations of pitahaya exports |
% Participation FOB 2015 |
Hone Kong |
53% |
Singapur |
20% |
Indonesia |
7% |
Paises Bajos |
5% |
Frania |
3% |
Canada |
3% |
Malaysia |
2% |
Demas Paises |
4% |
Table 3 Main importers
Source: Central Bank of Ecuador; Elaboration: Commercial Intelligence and Investment Office, Pro Ecuador
The pitahaya grown in Ecuador is much sweeter than the one produced in other countries, and its quality is very good, it also does not require so much harvest time and production; These are reasons to pound the potential of this fruit. Through the incentive to small producers can be carried out the continuous improvement of production processes, and increase exports to international markets. Exports between Ecuador and the Netherlands for this type of product have decreased gradually in recent years. Ecuador will have to improve the exportable supply to the Netherlands, implementing improvements in the product, such as striking packaging and more information on the fruit.
Exporting with an added value to the product allows competitiveness in international markets, in such a way that it contributes to the transformation of the productive matrix. In addition, international certifications such as Fairtrade or Fair Trade are crucial when closing a negotiation, because they are highly accepted by the Netherlands.3-5
None.
Author declares there is no conflict of interest in publishing the article.

©2018 Burgos. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.