Advances in
eISSN: 2378-3168


Research Article Volume 12 Issue 3
1Kulvinder Kaur Centre For Human Reproduction, India
2Scientific Director, Ex-Rotunda-A Centre for Human Reproduction, India
3Consultant Neurologist, Swami Satyanand Hospital, India
Correspondence: Kulvinder Kochar Kaur, Dr Kulvinder Kaur Centre For Human Reproduction, 721,G.T.B. Nagar, Jalandhar-144001, Punjab, India
Received: April 29, 2022 | Published: June 15, 2022
Citation: Kaur KK, Allahbadia G, Singh M. De Novo lipogenesis inhibitors: as the other innovative agents for therapy of metabolic diseases (obesity, NAFLD/ NASH, CVD). Adv Obes Weight Manag Control. 2022;12(3):78-93. DOI: 10.15406/aowmc.2022.12.00367
For survival fatty acids are necessary, working as substrates for bioenergy generation, structural constitutents along with signaling molecules. With their key part, evolutionary modes bycells for fatty acids formation from alternative carbon resources via a event labelled as de novo’’ lipogenesis ( DNL). In spite of the knowledge of significance regarding its up regulation abnormalities being correlatedwith numerous types of pathological conditions. Attempt at hampering core DNL enzymes inclusive ofcitrate/iso citratecarrier(CIC), ATP citrate lyase ( ACLY), acetyl CoA carboxylase(ACC) along with fatty acid synthase( FAS) apparently should turn out to be a good therapeutic approach. Although numeroushurdles anticipated regarding effectiveness, selectiveness besides safety variable newer classes of synthetic DNL hampering agents have reached clinical stage generation besides becoming the basis for a newer class of treatment substances. Having earlier reviewed numerous articles regarding obesity along with its co-morbidities type2 Diabetes mellitus (T2DM) NAFLD /NASH here we have presented a narrative review regarding the evolutionary generation of DNL hampering agents as potential treatment agents. For this we review utilizing search engine pubmed, google scholar; web of science; embase; Cochrane review library for which we have extracted data from earliest data with the recognition of significance of various enzymes besides their allosteric, covalent, transcriptional control of fatty acids generation & the problems encountered for their generation till date. Apart from obesity associated therapeutics their utility extends to acne vulgaris, various cancer thrapies besides treating neurod generational diseases.
Keywords: de novo’’ lipogenesis ( DNL), FAS hampering agents, evolutionary generation
DNL, de novo’’ lipogenesis; FA’s, fatty acids; ACLY, ATP citrate lyase
Fatty acids (FA’s) represent necessary cell survival parts since they act like crucial constitutents of cell membrane and significant signaling molecules. Fatty acids further are maximum calorie rich energy storage types with transformation of escalated glucose confers protection against glucotoxicity, besides provision of a significantly greater reserve for energy in contrast to glycogen in the periods of scarcity of nutrients. With the knowledge of parts of FA’s with the evolutionary modes now cells possess the capacity of sustenance of enough amounts. This is inclusive of modes for cells uptake of exogenous FA’s, besides possessing capacity of FA’s formation from other alternative carbon resources via stepwise enzymatic responses, an event preserved over phyla that is referred to as de novo’’ lipogenesis(DNL).1
DNL initiation takes place if escalated accessibility of substrates exists contrasted with cellular energy requirements resulting in enhanced mitochondrial citrate getting exported from the mitochondria to cytosol utilizing citrate/iso citratecarrier(CIC)(alias CTP/SLC25A1) (Figure 1). Subsequently this cytosolic citrate gets transformed to FA’s by stepwise biogenerational reactions getting catalysed utilizing ATP citrate lyase( ACLY), acetylCoA carboxylase( ACC/ ACACA) and fatty acid synthase( FAS/ FASN). Variable expression of these enzymes, takes place over tissues and generational stages (like proliferation, besides quiescence). Furthermore the expression action are further controlled both in acute orchronic way via transcriptional regulation and Histone post-translational modifications having correlation with the nutritional status (like fasting /food intake) and accessibility of substrates (like suppression of DNL by FA’s).
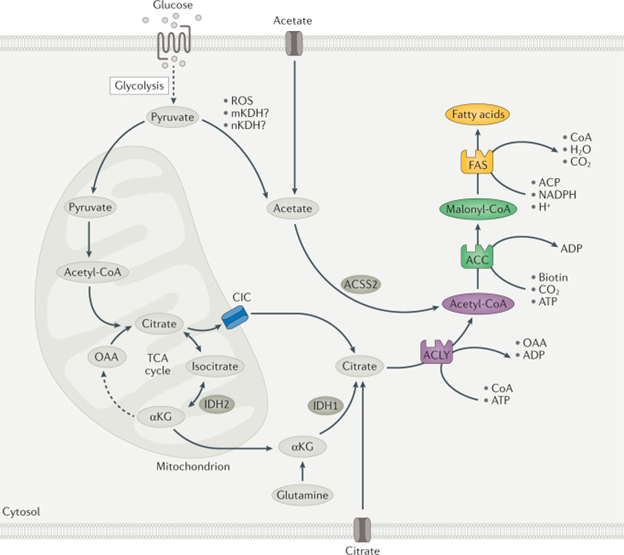
Figure 1 Overview of DNL.
Courtesy ref no-2-A series of coordinated enzymatic reactions takes place during fatty acid biosynthesis. Typically, pyruvate produced by glycolysis is converted in the mitochondrion into acetyl-CoA, which enters the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle to produce citrate. In conditions of carbohydrate excess, citrate is exported to the cytosol by the citrate/isocitrate carrier (CIC) and is broken down to acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate (OAA) by ATP-citrate lyase (ACLY). Acetyl-CoA is subsequently carboxylated by acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) to generate malonyl-CoA, which is considered the first committed metabolic intermediate in fatty acid synthesis. Utilizing seven malonyl-CoA molecules and one acetyl-CoA primer, the synthesis of palmitate (16:0 fatty acid) is completed by repeating a cycle of condensation, reduction, condensation and dehydration catalysed by fatty acid synthase (FAS). An alternative carbon source of de novo lipogenesis (DNL) is acetate, which can be produced de novo from glucose through non-enzymatic and enzymatic reactions. Acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 (ACSS2) catalyses the reaction of acetate and CoA to form acetyl-CoA, which is subsequently used for fatty acid biosynthesis. With hypoxia or CIC deficiency another alternative pathway for DNL is reductive carboxylation of glutamine via cytosolic isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) and mitochondrial IDH2. αKG, α-ketoglutarate; ACP, acyl carrier protein; mKDH, mitochondrial ketoacid dehydrogenase; nKDH, nuclear ketoacid dehydrogenase; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
Despite DNL being key for the sustenance of full body besides cellular homeostasis, correlation of chronic enhancement with generation of wide diseases spectrum andconditions, inclusive of cardiovascular disease (CVD),2 Non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)3–5 type2 Diabetes (T2D),5 multiple cancers,6 viral infections,7 autoimmune diseases.8 This Physiological glucose metabolism pointed that pharmacological hampering might prove to be advantageous over numerous diseases. Different natural products got isolated regarding DNL hampering agents and these acting as mainstay for formation of synthetic hampering agents which reveal greater bioavailability, escalated effectiveness besidesspecificity. Recently approval imparted tocertain substances regarding hyperlipidemia9 treatment, or latter stages of NAFLD generation and cancers.
Nevertheless, even now no clarification existent regarding numerous queries if systemic /organ particular hampering of DNL requires targeting and the extent of hampering is essential for avoidance of probable adverse actions like abnormalities in fetal formation,10 generation of platelets11 or impairment of muscle function.12 Clarification isstill not apparent in which situations hampering of the canonical DNL pathway might get bypassed in the foraging of alternative carbon resources via acetylCoA synthetase,13 ketoacid dehydrogenase14 or isocitrate dehydrogenase.15 Hence ifcombination treatments or diet alterations requirement present. Despite the differentkey targets indirectly impacting lipogenesis (like fructokinase, glucokinase or glucagon receptor, sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c(SREBP1c), and liver X receptor(LXR)16 are implicated in downstream processing (egSCD, DGAT1, DGAT2).17 In this review our objective has been the formation of hampering agents which target directly the core constitutents in the lipogenic pathways, basically(CIC, ACLY besides FAS).
Physiological besides pathological parts of DNL enzymes
The physiological control ofDNL is complicated, variable widely amongst cell kinds besides nutritional status. Observational studies conducted in mice with genetic absence of citrate carrier Slc25a1, Acly, Fas Acc, Acaca, besides Fas have corroborated the existence of DNL in lipogenic tissues like liver, adipose tissue (AT), however without anticipation of biological effects on cell kinds believed to possess restricted ability for DNL. These observations pointed to much wider parts of DNL in controlling the generation of lipids in a wide spectrum of physiological functions as compared to prior realization (Figure 2). N9 detailed description of complicated lipogenesis physiology control18 here just crucial physiological, pathological parts of DNL enzymes is described. Significantly provision of the knowledge obtained from genetic studies imparts key understanding regarding the chances /problems of generation of DNL hampering agents.
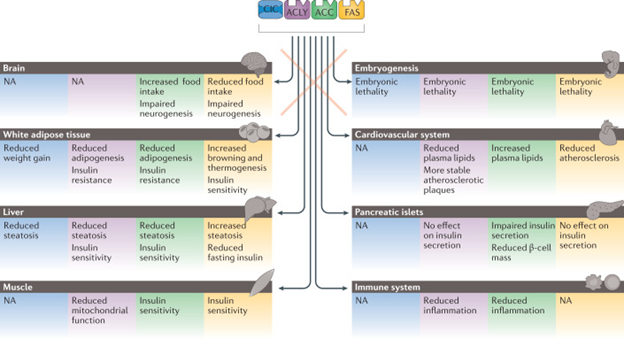
Figure 2 Tissue-specific actions of DNL.
Courtesy ref no-2-Important insights into distinct actions of citrate/isocitrate carrier (CIC) and de novo lipogenesis (DNL) enzymes in various tissues have been postulated from studies that employed animal models that lack one of these core components of the DNL pathway. The actions of each enzyme is colour coded: CIC-mediated effects are in blue boxes, ATP-citrate lyase (ACLY) in purple boxes, acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) in green boxes and fatty acid synthase (FAS) in yellow boxes. NA, not available.
Energy consumption besides energy expenditure
Apparently DNL pathway actions control energy consumptionbesides energy expenditure. Like mice possessing Fas absence consume lesser food,19 while escalated food consumption in mice with absent Fas, Accseen.20 The distinctive variation in modes of actions of ACC besides FAS on food consumption can be reasoned out by differential actions on malonylCoA, on stereostatic administration of malonylCoA decarboxylase(MCD), into the hypothalamus results in enhanced food consumption,21 while food consumption reduction occurs in mice with constitutive activation of ACC 1/ ACC 2 isoforms.22 These outcomes pointed to hampering of FAS results in suppression of food consumption, while ACC hampering in enhancement.
Activation of brown adipose tissue (BAT) in humans besides mice in reaction to escalated nutrients(diet induced thermogenesis or (cold adaptive thermogenesis).23 In rodents besides humans BAT activation results in enhancement of glucose uptake, nevertheless studies conducted recently astonishingly observed that primary function of glucose was not for supporting glycogenesis, however rather for fuel provision for DNL.24 Corroborating this posit cold exposure besides greater carbohydrate accessibility enhances DNL in BAT25 pointing to utilization of triglycerides(TG) regarding thermogenesis. Conversely as a paradox decrease in AT Fas results in decrease in body mass26 secondary to enhanced local action of sympathetic nervous system(SNS) leading to browning of white fat forsubjects.27 These outcomes pointed to contradictory hampering of DNL in AT might cause escalated energy expenditure in full body. Further studies need selective ACLY, ACC besides FAS hampering amongst BAT besides White adipose tissue (WAT) for directly quatifying DNL pathway significance for controlling futile cycles besides energy expenditure.
Lipids accumulation inNAFLD-NASH
The biggest factor responsible for escalated lipids accumulation inNon alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) patientsis their greater DNL rates.4,5 Corroboration of these findings the enhanced expression of CIC ACLY, ACC, besides FAS in liver of patients with NAFLD or Non alcoholic hepatic Steatohepatitis (NASH).28 In mice fed high fat diet (HFD), liver particular Slc25a1 gene elimination resulted in decreased hepatic steatosis.29 ob/ob mice receiving high carbohydrate diet, temporary genetic ACLY hampering utilizing small interfering RNA(siRNA) resulted in decreased liver lipid amounts.30 Akin to that selective ACLY elimination from hepatocytes of NASH stimulated by HFD/high fructose diet, decreased hepatic steatosis [not published ). Conversely life long hampering of liver Acly in mice receiving high fructose amounts do not cause fat reduction possibly secondary to up regulation of acetate formation by gut microbiota(GM) besides compensatory part of acetyl CoA synthetase 2(ACSS2) upregulation.31 Nevertheless, noticeably utilizating high fructose amounts do not result in obesity, NAFLD/ NASH, facilitation hence therapeutic significance of these observations requires clarification. Genetic hampering of liver Acc132 or Acc1 /Acc233 results in reduction of liver fat in mice receiving high carbohydrate diet independent of adiposity alterations. In mice with essentially active ACC 1 /ACC2 isoforms secondary to absence of 5’ AMP-activated protein kinase(AMPK) hampering phosphorylation formed more steatosis besides fibrosis compared to controls receiving a high carbohydrate diet.34 These outcomes pointed to ACC hampering can result in positive impact on steatosis besides fibrosis reduction. Nevertheless a significant result of liver ACC hampering is generation of hypertriglyceridemia becausedecreased liver polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA’s) result in enhancement of SREBP1c and expression of glycerol 3phosphate acyl transferases (GPAT), the rate restricting enzyme for TG generation. Despite maximum studies pointing to positive action of hampering ACC on hepatic steatosis in a study genetic hampering resulted in enhanced liver lipids secondary to hyperacetylation of mitochondrial protein, probably because acetyl CoA accrual besideslesser fatty acid oxidation.35 The phenotype of the liver particular ACC null mice was akin to mice with FAS absence further presenting with escalated steatosis secondary to decreased fatty acid oxidation.36 Thus these studies in ACC besides FAS null mice emphasized the complicated crosstalk might restrict the therapeutic applications regarding NAFLD / NASH.
Insulin sensitivity besides T2DM
Insulin resistance (IR) is a bench mark of type2 Diabetes (T2D). An inverse correlation is existent amongst DNL in liver with hepatic besides full body Insulin sensitivity in humans.37 Liver particular elimination of Slc25a1 results in recovery of glucose tolerance in ob/ob mice in receipt of a control high carbohydrate diet /HFD.28 The ACLY expression following its suppression modulated by siRNA resulted in decreased fasting glucose besidesrecovery of glucose tolerance in ob/ob mice receiving a control high carbohydrate diet.38 On selective eliminationof ACLY from the hepatocytes in mice receiving HFD /high fructose diet for 16weeks akin findings were seen. Genetic hampering of ACC2 in muscle or ACC 1 /ACC2 in liver resulted in enhanced muscle and liver Insulin sensitivity respectively, while mice with basic active ACC 1/ACC2 isoforms possessed most deleterious IR.34,38 These outcomes pointed that hampering of DNL and/or upregulation of fatty acid oxidation amongst muscle besides liver of mice possessed the capacity of enhanced Insulin sensitivity.
Besides muscleand liver AT is equally key for controlling Insulin sensitivity.39 DNL rates in WAT are akin to that in liver at the time of postprandial period.40 Nevertheless, with obesity reduction in DNL in AT occurs in rodents41 & humans42 though modest glucose decrease.43 Recently studies pointed that decreased DNL in AT occurs at a rapid pace with progression of reduction with deterioration of obesity besides IR which is correlated with decreased expression of ACLY, ACC, FAS,44 and carbohydrate response element binding protein(ChREBPβ),45 pointing that hampering AT DNL might be deleterious for total body Insulin sensitivity. In corroboration with this posit on challenging ACLY fat-particular null mice with a high sucrose diet female mice generated lipodystrophy like phenotype, which correlated with hepatic lipid accrual besides IR.46 Akin findings were seen in ACC1fat - particular null mice. These outcomes pointed to a significant part of AT DNL in sustenance of total body Insulin sensitivity, probably by conferring protection to liver from formation of steatosis. Additionally, studies with properties of temporary knockouts of ACLY /ACC in totally differentiated adipocytes of adult mice with obesity instead of lifelong elimination7,46,47 had the capacity of being more advantageous in provision of protection regarding AT DNL part in IR.
Absence of the capacity of pancreatic β cells liberating adequate insulin amounts for euglycemia sustenance is the cornerstone of T2DM. Corroborating proof pointed that ACC might be significant for pancreatic βcells function since ACC elimination causes dysfunctional glucose induced insulin liberation ex vivo besides in vivo insulin tolerance.47 The mechanism being enrichment of βcells, while FAS expression is weak, causing enhancement of malonyl CoA amounts subsequent to glucose stimulation.48 This results in fatty acid oxidation hampering by escalated malonyl CoA resulting in enhanced accessibility of cytosolic long chain fatty acyl CoA (LCFA CoA) for lipid signaling to cellular events implicated in insulin liberation.49 Additionally observation of recent studies is the ACC significance in facilitating β cells in mice.47 These outcomes pointed that hampering of ACC in pancreatic islets might cause dysfunctional insulin liberation besides reduction of β cell mass leading to T2D.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
Liver DNL escalation results in enhanced plasma VLDL/LDL, the main risk factors for CVD mortality.50 Observation of incidental heart failure (HF)51 inrecent studies possess a positive correlation with enhanced FAs obtained from DNL. In agreement with this posit, genetic variants in ACLY are correlated with a reduction in plasma LDL besides reduction in cardiovascular processes. Akin to that polymorphisms of ACLY/ACC are correlated with lesser triglycerides subsequent to supplementation with dietary fish.52 Astonishingly no evaluation of actions of genetic hampering of Acly, Fas, or Acc on generated models of atherosclerotic formation were conducted. Nevertheless having the knowledge of the actions of hampering ACC for facilitation of hypetriglyceridemia it might be predicted to escalate atherosclerosis. Conversely liver ACLY deficiency causes triglycerides reduction in mice {unpublished). Clarification on explanation regarding opposite actions of ACLY and ACC hampering on circulating TG is not existent, nevertheless it might be associated with simultaneous cholesterol generation suppression distinctive to ACLY hampering or corresponding actions which ACLY and ACC hampering possess on amounts of acetylCoA which might be significant for reinforcing protein acetylation. These outcomes pointed that whereas hampering of ACC might be efficacious in reduction of hepatic steatosis, it possesses deleterious actions on risk factors for CVD which require management regarding other lipid reduction treatment like fish oil, hampering of DGAT or PPARα agonists like fenofibrate.
Furthermore, macrophages possess key part in atherosclerotic CVD generation since uptake besides lipid storage occur in them, stimulating inflammation within the atherosclerotic plaque. Enhancement of action of ACLY and FAS occurs amongst atherosclerotic plaques in mice and humans, pointing that hampering might be advantageous. In agreement with this posit genetic hampering of Acly, or Fas amongst macrophages of ApoE mice decreases atherosclerosis. Astonishingly no studies have evaluated the actions of genetic elimination of macrophage ACC on atherosclerosis.
CIC- Control besides structure
CIC gets encoded by the SLC25A1 gene with ubiquitous expression, maximum of which is in liver, reproductive organs, Gastrointestinal Tract(GIT) and AT. It resides within the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM). Basically it catalyzes expulsion of tricarboxylateslike citrate& isocitrate getting exchanged for dicarboxylates besides phosphoenol pyruvate.53 LCFA CoAhampers CIC- in a reversible way, competing with citrate,54 whereas acetylation can result in escalated allosteric activation by citrate (Figure 3).55
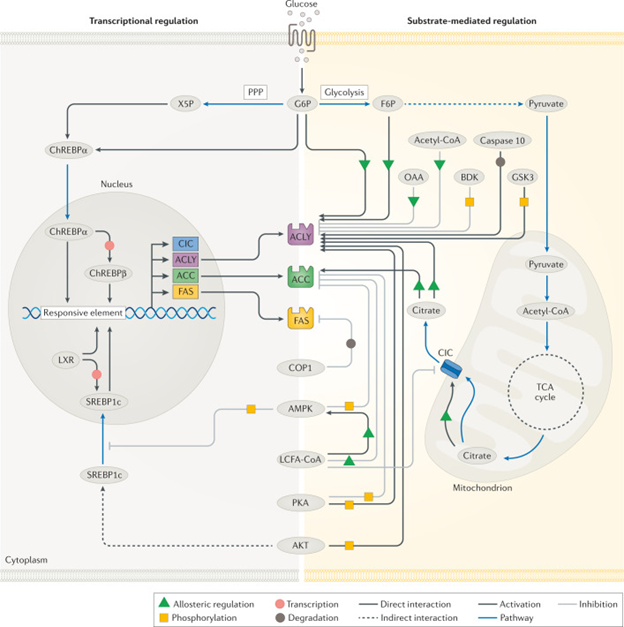
Figure 3 Physiological regulation of DNL.
Courtesy ref no--Regulatory mechanisms of de novo lipogenesis (DNL) involve allosteric regulation, covalent modifications and transcriptional changes. Allosteric activators include citrate, glucose 6-phosphate (G6P) and fructose 6-phosphate (F6P) while oxaloacetate (OAA) and long-chain fatty acyl (LCFA)-CoAs are allosteric inhibitors. Regulatory phosphorylation is facilitated by several enzymes including AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), AKT, branched-chain α-keto dehydrogenase kinase (BDK), glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) and protein kinase A (PKA), whereas caspase 10 and constitutive photomorphogenic 1 (COP1) facilitate the degradation of ATP-citrate lyase (ACLY) and fatty acid synthase (FAS), respectively. Transcriptional modifications are regulated by two major transcription factors, sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP1c) and carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein (ChREBP). Additional transcription factors, such as liver X receptor (LXR) are also implicated in the transcriptional regulation to varying degrees of importance depending on the cell type. ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; CIC, citrate/isocitrate carrier; FAS, fatty acid synthase; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; X5P, xylulose 5-phosphate.
Insight is lacking regarding mode of structural constitutents of CIC impacting the physiological control of action. Structurewise, eukaryotic three homologous domains constitute, of which every one generates two hydrophobic membrane spanning α helices which are bridged by hydrophilic loops which span from the inter membrane space to the mitochondrial matrix (Figure 4).53 A minimum of two citrate binding regions located at variable depths amongst the membrane act as the binding regions of CIC hampering agents. Residudes of regions 1 /2 generate six and, 8 hydrogen bonds with citrate respectively.56 CIC region 1 is dynamically available to anions from the inner surface besides estimates specificity to the internal substrates on moving via the CIC.57 Following binding to region 1 citrate gets shifted to region 2 prior to liberation into inter membrane space where its diffusion occurs via a voltage-based anions transportation channel amongst the outer mitochondrial membrane(OMM) into the cytoplasm.
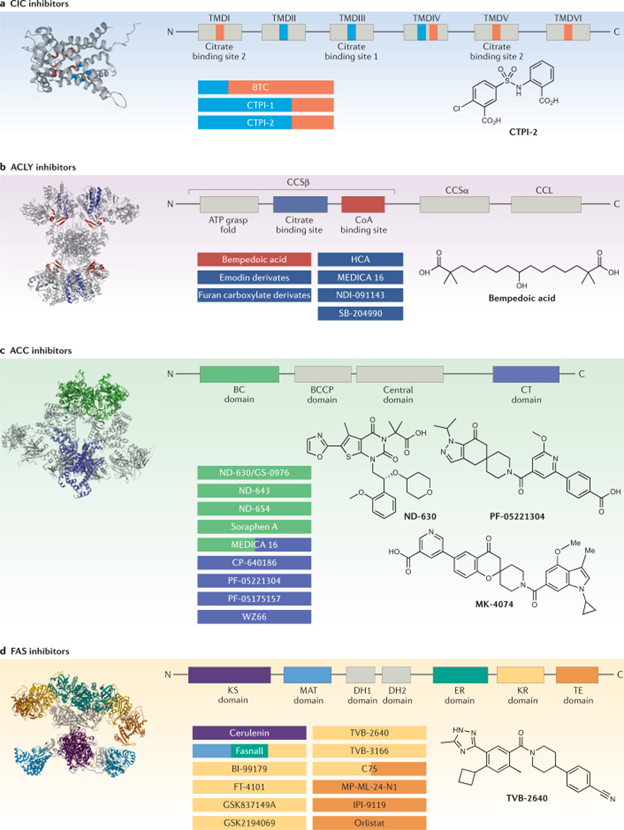
Figure 4 Structural domains and binding sites of DNL inhibitors with chemical structures of the most advanced inhibitors.
Courtesy ref no-2-Lipogenesis inhibitors interact with one or more druggable sites of the enzyme to exhibit an inhibitory effect. Linear organization and model representation of each enzyme are shown with known inhibitor binding sites in colours. Inhibitors with known enzyme binding sites are colour coded with their respective interaction sites. a | Citrate/isocitrate carrier (CIC) inhibitors: compounds that bind to citrate binding site 1 are shown in light blue and those that bind to citrate binding site 2 in orange. The chemical structure of CTPI-2 is shown. b | ATP-citrate lyase (ACLY) inhibitors: compounds that interact with the CoA binding site are highlighted in red and those that interact with citrate binding site in dark blue. The chemical structure of bempedoic acid is shown. c | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) inhibitors: compounds that target the biotin carboxylase (BC) domain are highlighted in green and those that target the carboxyl transferase (CT) domain are highlighted in violet. Chemical structures of clinical stage inhibitors are shown. d | Fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitors: inhibitors that bind to the β-ketoacyl synthase (KS) domain are highlighted in purple, inhibitors that bind to malonyl-acetyl transferase (MAT) are in blue, inhibitors that bind to enoyl reductase (ER) are in green, inhibitors that bind to β-ketoreductase (KR) in yellow and those that bind to thioesterase (TE) in orange. The chemical structure of TVB-2640 is shown. BCCP, biotin carboxyl carrier protein; BTC, benzenetricarboxylate; CCL, citryl-CoA lyase; CCS, citryl-CoA synthetase; DH, dehydratase; HCA, (−)-hydroxycitric acid; TMD, transmembrane domain.
Pharmacological hampering agents
The 1st generation CIC hampering agent possessing greater affinity for the transporter contrasting to any substrates was benzenetri carboxylate (BTC)53 that hampers CIC in a vying and nonconflicting way.53,58 Structurally BTC is akin to citrate and basically crosstalks with citrate binding region2 (Figure 4).58 Despite wide utility of BTC, regarding studying, structural and functional properties of CIC, its probable binding to other citrate binding protein has restricted its therapeutic generation.
CTP1-1 alias compound 792949, represents a next generation competing CIC hampering agent whose Identification occurred through in silico screening of small molecules accessible commercially. It possesses minimally greater affinity for CIC compared to BTC besides binding residues from citrate binding regions simultaneously.58 The Identification of this hampering agent occurred in yeast CIC with subsequent observation of suboptimal binding to human CIC in view of amino acids variation in the citrate binding regions amongst species.59
Attempting optimization of substances particular for human CIC caused isolation of CTP1-2, which demonstrated 20times enhanced binding affinity compared to CTP1-1 and hampered citrate transportation at lesser amounts.59 Furthermore, it was illustrated to possess various advantageous actions in preclinical models described further.
Metabolic diseases - Cytosolic citrate reduction would be anticipated to hamper DNL by reduction of accessibility of substrates and allosteric ACC/ACLY activation.60 Corroborating this posit BTC decreased triglycerides amounts in primary hepatocyte. Escalated CIC expression in liver in NASH subjects besides CTP1-2 therapy of mice receiving HFD caused reversal of steatohepatitis and liver damage with a simultaneously decreased serum cholesterol besides triglycerides.29 Additionally, CTP1-2 led to fasting glucose reduction with normalization of glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity its target being gluconeogenesis. Nevertheless, since CTP1-2 further led to reduction of body mass via modes unclear this might have aided in enhanced glucose homeostasis, acute hampering of glucose induced insulin liberation in INS1cells and islets;61 nevertheless, in vivo actions on pancreatic islets were not elucidated. These outcomes pointed that hampering of CIC might cause advantageous actions on obesity, NAFLD, T2DM. For the estimation of modes which aid in advantageous actions on hepatic steatosis and glucose homeostasis require further elucidation.
Probably the mode of CIC hampering agents in impacting metabolic diseases positively independent of body mass decrease might implicate hampering of inflammation. Proinflammatorystimuli like lipopolysaccharides (LPS), Tumor necrosis factor alpha(TNFα), interferon γ(IFNγ) induce metabolic reprogramming in macrophages and natural killer cells(NKCells) results in escalated CIC expression pointing that hampering might induce antiinflammatory actions.62 CTP1-1 hampered inflammatory reaction in cultured macrophages stimulated by TNFα/IFNγ.62 Akin to that CTP1-2 blocked infiltration byinflammatory macrophages in liver of obese mice in association with reduction in circulating proinflammatory cytokines.29 These outcomes pointed that hampering of CIC might cause decreased inflammation which impact metabolic diseases positively.
A. ACLY: - Control besides Structure2
Maximum ACLY expression occurs in AT &liver, with least in skeletal muscle. Despite, ACLY being mainly a cytoplasmic enzyme it further was observed in nucleus. Their are4 steps implicated in activation of ACLY i)Mg-ATP binding ii) phosphorylation of His760 catalysing the generation of enzyme bound citryl phosphate with subsequent CoA attack that generated a citryl CoA intermediate and ultimately citryl CoA cleaved into last products acetylCoA besidesoxaloacetate(OAA). Activation of this allosteric reaction occurs by glycolytic intermediates glucose -6- phosphate(G6P)/fructose-6 phosphate(F6P), latter possessing greater robustness (Figure 3).63 Citrate further results in activation of ACLY allosterically, whereas products (acetylCoA /OAA) hampered enzymes action.60
Besides activation allosterically, earlier studies observed insulin64 besides glucagon65 enhanced serine /threonine phosphorylation on ACLY(fig3) with following studies illustrating Thr446/ Ser450 phosphorylated by glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3)66 while Ser450 phosphorylation occurs by protein kinase A66 besides insulin stimulated kinase,67 whose later Identification was as AKT(protein kinase B).68 Furthermore mammalian target of rapamycin complex2inhibitors (mTORC2) phosphorylated ACLY Ser454, an action requiring AKT.69 Further recent observation of branched chain ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase phosphorylated Ser454, hence associated ACLY action needed amino acids accessibility besides IR.70 Despite, earlier studies observed phosphorylating Ser454 possessed least ACLY activity, greater studies demonstrated phosphorylation of this residue caused reduced sensitivity towards activation allosterically by G6P and F6P. Future studies in different cell lines corroborated the significance of phosphorylation process in escalated ACLY activity.51 Additionally, ACLY is controlled by cleaving the enzyme post transcriptionally.71
Clarification of structural footing of chemical reaction modulated by ACLY needs evaluation.60 ACLY constitutents are 2 modules, ACLY-A /ACLY –B, existent in different domains(heteromeric ) in prokaryotes, yet homomeric in animals generating a functional tetrameric structure (Figure 4).63 Every monomer comprises of a N-terminal citryl CoA synthetase(CCS) module, possessing CCSβ and CCSαsites with a C- terminal citryl CoA lyase(CCL) domain. The ACLY-A module generates the CCSβ area whereas, ACLY –B generates the rest of the domains of the monomers with Ser/Thr phosphorylation taking place amidst a linker site amongst modules In studies conducted recently provision of structural reason in details regarding the multiple step catalytic mode of ACLY illustrating the citrate binding to CCSβ area, whereas CCSα sites act as a CoA binding area.60 The requirement of binding this existent extra CoA binding area in CCL domain is controversial.60
Pharmacological hampering agents
Secondary to tactical location at FA, cholesterol& carbohydrate metabolism intersection ACLY targeting is promising. Dependent on simultaneous modulating hampering of FA and cholesterol generation numerous ACLY hampering agents were identified, whereas FA β oxidation activated. The initially isolated was (-)hydroxy citric acid(HCA) a citric acid derivative observed in Garcinia cambogia and Hibisscus subdariffa.72 HCA hampered ACLY by battling citrate,72 causing simultaneous DNL and cholesterol biogeneration repression.73 Nevertheless, HCA contained bad physicochemical characteristics, subsequently observed to cause ACC allosteric activation.74 Despite multiple tries for enhancing HCA scaffold, no success was yielded secondary to observed off target actions.75 Isolation of ACLY hamperors on screening of natural products like Purpurone76 besides Pennicillium sp. Anthrones /Anthraquinones was feasible.77 Radicicol, a 14 member macrolide initially Identified in Monosporum bonorden78 besides cucurbitacinB; cucumber obtained bioactive compound79 enriched on the chemical scaffold of a natural products namely emodin.80 Despite, ACLY hampering by numerous substances in biochemal assays no specificity and clarification regarding mode of actions existed.81 Numerous hamperors got fashioned dependent on the alternative approach with objective of interfering with stable citric acid intermediate bound to the active region production. SB-201076 was an attractivesubstance illustrating actions subsequent to purifying rat ACLY proved to beinactive in cell –dependent DNL assays due to bad cell permeability.82 Enhancing cell permeability attained by production of a a lactone prodrug analogue SB-204990 via hydrolysis and activation on gaining access to the cell with active metabolite SB-201076 production.83 Nevertheles this series generation stopped prior to clinical generation. Recently4 kinds of furans/ benzofurans Identified byin silico sceening hampering ACLY further binding to citrate binding domain.84 An innovative chemical scaffold invented via virtual high through put screen(HTS)caused isolation of MS-303141, a2’hydroxy –N aryl benzenesulfonamide.85
This substance hampers ACLY, besidesACC1 and ACC2 at about 100 times lesser robustness.85 Nimbus Therapeutics Constructed on BMS-303141 chemical scaffold-rational computer aided design utility, generated new series of ACLY hampering agents. The substances possessing maximumn robustness, NDI-091143 hampered human ACLY combatantly contrasted to citrate. Utilization of cryo electron microscopy demonstrated unanticipated allosteric mode of hampering, where NDI-091143 bound adjacently with citrate binding regions in a hydrophobic cavity causing considerable conformational alterations causing avoidance of citrate binding to enzyme. Despite, no documentation regarding cell- dependent or in vivo outcomes, the observation of this innovative allosteric mode gave provision of newer strategy of inventing innovative ACLY hampering agents on enhancing drug like characteristics.86
MEDICA 16 was the initial synthetic fatty acid -like ACLY hampering agent. This substances fashioning implicated manipulating long chain dicarboxylic fatty acids forming ββ’-methyl-substituted αω- djcarboxylic acids for sustenance of lipid- controlling characteristics of β oxidation natural long chain fatty acids while enhancing drug like characteristics by avoidance besides enzymatic esterification.87 ACLY hampering contesting with citrate88 besides ACC contending with acetylCoA /ATP89 achieved by MEDICA 16. Generation of akin dicarboxylic acid, 3-thia dicarboxylic acid occurred by replacing dimethyl substitution in β position with sulphur atom. Hampering ACLY/FAS reduced plasma triglycerides besides cholesterol.90 None of these molecules progressed further than preclinical studies.
A phenotypic screen utilization dependent on fatty acids hampering besides sterol generation in primary rat liver cells Esperion therapeutics invented a liver- particular hampering agentETC-1002, 8 hydroxy-2, 2, 14, 14-tetramethylpentadecanedonic acid (Bempedoic acid) besidesESP55016.91 Robust hampering by Bempedoyl CoA of Recombinant human ACLY in competition with CoA was illustrated with the prodrug(Bempedoic acid being inactive.92 Significantly transformation into CoA conjugate is based on very long chain acetylCoA synthetase (ACSVL1, FATP2/SCL27A2)an enzyme with greater expression in liver however not maximum in other tissues inclusive of skeletal muscle, hence aiding liver - particular effects of Bempedoic acid.92 Whereas Bempedoyl CoA further hampers ACC9 besides activating AMPKβ possessing heterotrimers,92 no illustration regarding its importance as robustness towards ACC is low comparatively with Bempedoic acid persistent in repressing liver DNL despite the lack of AMPKβ isoforms.92
Obesity: Rodent preclinical studies observed HCA reducing body mass via a mode associated with calorie limitation93 an action not seen in humans.94 Further corroboration of association amongst weight reduction and ACLY by 2 more advantageous ACLY hampering agents withproperties well studied- Bempedoic acid besides BMS-303141 werecausing body weight accrual reduction besides adiposity independent of food consumption alterations, in preclinical models.85,91,95 Proofs from pooled evaluation of clinical trials showed Bempedoic acid stimulated modest weight reduction in humans.96 Greater studies regarding probable modes via which ACLY hampering agents evoke weight reduction are required.
NAFLD-NASH besides T2DM: A direct association amongst liver lipids and insulin sensitivity exists with intricate association amongst NAFLD besides T2D. MEDICA 16 results in reduction of liver lipid amounts,87 hepatic glucose formation besides enhancing peripheral insulin sensitivity97 in unique rodents obesity models with stimulated insulin resistance(IR). Bempedoic acid further resulted in decreased hepatic triglycerides besides inflammation markers in Ldlr-/- mice receiving high fat, high cholesterol diet. The lipids decreasing actions of Bempedoic acid was independent of activating liver AMPK92 In numerous mouse models Bempedoic acid further decreased fasting glucose, fasting insulin besides glucose intolerance, pointing to enhanced insulin sensitivity.95 Meta-analysis of randomized trials regarding Bempedoic acid decreasing new incidence/ Diabetes deterioration pointed to apparent translation in humans.98 Need for evaluating Bempedoic acid possessing efficacy against NASH besides fibrosis exists.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD): Evaluation regarding pharmacological ACLY hampering of CVD performed knowing the double influence on cholesterol besides fatty acids biogeneration. Prior studies in animal models illustrated the wide lipids decreasing actions of MEDICA 1698 on circulating cholesterol besidestriglycerides amounts correlated advantageous actions on myocardial vascular injuries. Studies on BMS-303141, SB-204990 corroborated ACLY being hyperlipidemia targets since both substances efficaciously decreased circulating triglycerides/ cholesterol in hyperlipidemia animal models.83,86 Bempedoic acid further repressed hepatic cholesterol besides fatty acids biogeneration,95 with illustration of hypolipidemic effects in hyperlipidemic hamsters,96 obese zucker rats,91 mice deficient in ApoE or LDL- receptor,99 associated with atherosclerosis reduction as well. In case of humans Bempedoic acid facilitated dose based LDL- cholesterol decreasing actions in monotherapy besides combined with ezetimibe.100 Apparently the basic actions in humans is decrease in plasma LDL- cholesterol contrasted to rodents where Bempedoic acid possesses robust actions in reducing cholesterol besides triglycerides.180 The absence of plasma triglycerides actions might be secondary to lesser DNL in humans contrasted to rodents. Besides reduction of LDL- cholesterol Bempedoic acid further declines numerous markers correlated with atherosclerotic CVD like total cholesterol(TC), non HDL cholesterol, plasmaApoB, LDL- particle numbers with high sensitivity CRP.100 Recently illustration regarding its safety besides being effective treatment for patients receiving statins,101 / statins intolerant patients.102 Bempedoic acid received approval for patients with heterogenous familial hypercholesterolemia(HeFH)(requiring extra decreased LDL- cholesterol adjunctive to diet besides statins were maximum tolerated contrasted to lone or with rest of decreasing lipids treatment for intolerant patients/statins contraindication. Cardiovascular mortality and co-morbidities actions have not been illustrated as yet.
Control besides structure: 2 Major ACC isoforms present in mammals, ie ACC 1(ACCα) besides ACC 2( ACCβ) possessing variable tissue expression. ACC 1 is existent in cytoplasm of all cells, with predominant expression in lipogenic tissue like ATACC 2 resides in the mitochondria, besides being abundant in oxidative tissue (like skeletal muscle heart, breast, liver) ACC isoforms illustrate akin amino acids sequences of82% and76% in their biotin carboxylase(BC) and carboxyl transferase (CT) domains respectively,103 with the major variation amongst 2 is N-terminal extension in ACC2 causing greater molecular weight ( contrasted to ACC1) in regulating fatty acid oxidation, as intricate to carnitine palmoyl ltransferase I, which ishampered allosterically by malonylCoA.103 Genetic proofs corroborated regarding overlap amongst ACC isoforms controlling fatty acid oxidation besidesDNL[rev in2] pointing comparative significance of every isoform controlling DNL besides fatty acid oxidation is associated with tissue particular expression profiles instead of cellular residence.
The modes associating tricarboxylic acid(TCA) intermediates with enhancement in DNL were initiallyrevealed in 1962 on observation that citrate caused stimulation of action of ACC [rev in2](Figure 3). Identification of the modulationof facilitation of the enzymes in the following studies namely an act hampered by LCFA CoA.104 Besides the allosteric regulation gets inactivated by phosphorylation,104 that is adequate for overcoming the allosteric activation during physiological amounts of citrate (Figure 3).105 This pointed that phosphorylation, not allosteric regulation, might be the major mode controlling ACC activity. Phosphorylation and hampering of ACC occurs by the AMPK at Ser79.106 Akin to that hampering of ACC2 by phosphorylation, at a homologous region (Ser221). Mutations in ACC1 and ACC2 in hepatocyte were essential for impacting maximum action on DNL along with fatty acid oxidation.107 Intriguingly, the observation of a direct activation of AMPK by LCFA CoA in a recent study,108 hence demonstrating bimodal modes implicating allosteric and covalent hampering of ACC action regarding hampering DNL along with escalated fatty acid oxidation.
This ACC enzyme comprises of 3 domains: i)BC, biotin possessing carboxyl carrier Protein(BCCP) and CT-that get packaged together in a single chain in maximum eukaryotes i. e. inclusive ofmammals (Figure 3). In case of eukaryotes functioning of ACC is in form of dimers, besides greater oligomers with the BC and CT domain dimers residing at the top and bottom of this structure, respectively, whereas BCCPis localized amongst the CT active region.v in2]. 2 steps are implicated in the ACC reaction i) an ATP-based carboxylation of biotin constitutent by the BCCP with subsequent shift of a carboxyl group from biotin to acetylCoA for the generation of malonylCoA with in CT[rev in2]. Structural studies conducted recently have described the dynamic crosstalk occurring amongst the polymerization state as well as the filament structures following citrate and palmitoyl CoA exposure that locks with efficacy the enzyme into a catalytically ingenious/or ingenious conformational states respectively[rev in2]. Occurence of phosphorylation at Ser79 in ACC1 and probably in Ser221 in ACC2 results in induction of a conformational alterations implicating the BC dimers interface, that facilitates the dissociation of the dimers and inactivation[rev in2]. Hence allosteric controlling of ACC by citrate and palmitoyl CoA besides phosphorylation of AMPK control enzymatic action via changes in the conformational state.106,109
Pharmacological hampering agents
Hampering of ACC results in reduction of malonylCoA that is further an allosteric hampering agent of carnitine palmoyl transferase I, the rate restricting enzyme, regulating the flux of fatty acids into the mitochondrial βoxidation. Hence hampering of ACC apparently is a promising strategy for concomitant repression of DNL along with escalated fatty acid oxidation. With the information regarding embryonic lethality correlated with ACC1 hampering differential tissue particular expression profiles with probable compensation by the alternate isozyme particular(ACC1or ACC2) and non particular(ACC1 and ACC2) hampering agents along with tissue particular hampering agents have got persisted with.
The first generation regarding ACC hampering agents assessed were soraphen A andTOFA(5-9tetradecyloxyl)2-furancarboxylic acid). Soraphen A represents a macrocyclic polyketide initially Identified from the soil myxobacterium Sorangium cellulosum regarding its robust antifungal effects. Subsequently it was observed tobe a hampering agent for yeast &rat ACC[rev in2]. In eukaryotes binding of Soraphen A occurs with BC domains, that allosterically hampers enzymes action by interfering with oligomerization; nevertheless this doesn’t takes place in prokaryotes secondary to structural alterations amongst theBC domain.110 intracellular transformation ofTOFA into an ester occursto TOFyl- CoA, that works as an allosteric ACC hampering agent, however causes reduction of cholesterol generation111 pointing that it further hampers ACLY. With the knowledgeof restricted bioavailability and specificity if one of them got generated commercially. Pfizer Identified a series of non particular hampering agents that subsequent to stepwise optimizations resulted in CP-640186.112 A complex of CP-640186 with the crystal structure ofCT domain,113 pointed that the substance possessed tight correlation with theactive region of the enzyme that blocked the binding of biotin to theCT domain.114 Taisho&TakidaPharmaceuticals115 further formed derivatives of CP-640186, but these possessed little stability with following reductions in lipophilicity resulted in greater advantageous pharmacokinetics,116 introducing 7-methoxy group causes greater robustness along with metabolic stability, yet neither reached clinical stage, WZ66 one more agent binding CP-domain, a structure-dependent drug fashion studies by China Pharmaceuticals University that hampers Recombinant human ACC1 and ACC2 in cells in rodents was developed.117 Clinical evaluation of different pan ACC hampering agents has started recently in humans. MK4074, was llustrated in studies by Merck to be a selective ACC hampering agent, that dose based hampered DNL along with reduction of liver lipid in rodents and humans.33 Despite, the precise citrate binding region of the substance not published, it does’nt seem that clinical generation is persisted with secondary to the finding of hypetriglyceridemia being induced.33 Subsequent to the studies by Pfizer regarding CP-640186, Pfizer generated PF-05221304. In the form of a selective drug with oral bioavailability andreversible ACC hampering with preferential organizations in liver,118 thus avoidance of probable toxicity associated with the generation of platelets11 and generational abnormalities.10 PhaseII clinical studies with lone PF-05221304 or combined with a DGAT hampering agent PF-06865571 in NAFLD/ NASH has finished[rev2]. Compared to PF-05221304 binding to the CTdomain, Nimbus therapeutics generated different robust hampering agents by concentration on substances binding BC domains withblockade of dimerization. Human ACC2 BC domain in a complex with soraphenA short utilizing crystal structure besides optimizing noncovalent crosstalk withdimerization area, reversible ACC hampering agent ND-630wasformed.119 Compared to prior ACC hampering substance this interfered with subunit dimerization bysimulating AMPK phosphorylation.119 An alternate substance from series ND-646, illustrated akin robustness besides hampering mechanism like ND-630 was generated for wider organization in peripheral tissues.120 ND-654 modifications( third substance) for aiding in escalated hepatic uptake.107 ND-630/ GS-0976(Firsocostat) started clinical generation presently in Phase II Clinical trials for NASH.
Besides the description of pan ACC hampering agents, isozyme particular ACC hamperors got generated. Takeda Identified innovative monocyclic[rev2] besides carboxamide derivatives,121 illustrating specificity for ACC1>ACC2. Abbot laboratories generated series of ACC2 particular hamperors: maximum robust besides selective was A-908292, demonstrating over 1000 times selectivity against ACC2 contrasted with ACC1. This substance dose-based resulted in reduced malonylCoA in rodents muscle however not in liver.122 An initial safety evaluation illustrated neurological besides cardiovascular adverse actions whose resolution occurred via alkyne constitutent replacement with heteroaryl linker.123 Laboratory constructing on this series isolated a chain of new molecules selectively hampering ACC2 contrasted without toxicity.124,125 Neither of these have reached Clinical trials.
NAFLD-NASH besides T2DM: Preclinical proof corroborated how ACC hampering is advantageous regarding liver steatosis however they further llustrated probable on-target responsibilities. Reduction of liver steatosis in rodents by soraphen A correlated with enhanced insulin sensitivity.126 This enhanced insulin sensitivity didn’t translate to decreased glucose, agreeing with ACC null mice studies. Hampering ACC decreased Pancreatic β cellsinsulin liberation.125 Avoiding this issue WZ66, a TOFA derivatives like generated for preferably achieving liver organization, decreased hepatic steatosis besides activating hepatic stellate cells in diet induced obesity( DIO)mice.117 CP-640186 further decreased hepatic steatosis Insulin resistance in mice fed HFD, but might be caused by decreased obesity[rev 2]. Short time therapy of db/db mice with a selective ACC hamperer (S)-9c decreased muscle malonylCoA amounts besides intramyocellular lipids, whereas longtime treatment enhanced muscle glucose uptake, glucose tolerance, while decreased HbA1c amounts, postprandiall glucose besides plasma triglycerides amounts.60 These studies pointed that ACC hampering correlated with decreased liver steatosis besides partial enhancement of glycemic regulation.
Information of attractive actions of genetic and pharmacologic hampering of ACC in liver caused advancements in clinical trials for NAFLD-NASH. PhaseI clinical study on PF-05175157 decreased DNL escalated total body fatty acids use.127 Further clinical trials got stopped secondaryto extra hampered hepatic action resulting in reduced platelets amounts.11,118 Liver optimization of PF-05221304, hampered DNL fatty acid oxidation and decreased triglyceride accrual in primary hepatocyte and decreased DNL, hepatic steatosis besides immune cells activation in preclinical models.128 Preclinical studies fashioned for evaluating liver targeting attained via PF-05221304was a maximum decrease of hepatic DNL by 82%, contrasted with 33% in lung and Bone marrow.128 PhaseI clinical trials PF-05221304, hampered DNL in dose based way without impacting platelets, agreeing with its maximum actions.118 In PhaseII clinical trials for NAFLD PF-05221304, dose base decreased liver fat to 65% at maximum dose tolerated besides reduction of HbA1c[rev2]. On Studying utilizing liver particular hamperor MK-4074 rodents besides humans agreed with treatment probability of robust ACC hampering however extra queries were raised regarding on target responsibilities. PhaseI clinical trials illustrated hepatic steatosis reduction by36% via MK-4074 following, 4wks of therapy.48 Its clinical generation was stopped.
Preferable dissemination of ND-630119 in liver besides illustrating advantageous actions in preclinical/ clinical rodents studies dose base decreased hepatic steatosis besides hyperinsulinemia.119 Independent group corroborated in animals fed western diet, besides decreased fibrosis.129 Agrreably it decreased hepatic stellate cell activation for decreasing fibrogenic action.130 Well tolerance seen in Phase I clinical study, hampered hepatic DNL in individuals with obesity /over weight.131 In open labeled non placebo controlled study, NASH patients treatment with ND-630 saw 22% median decrease of hepatic DNL besides significantly decreasing hepatic fat besides liver stiffness following12wks treatment.4 Following larger placebo controlled randomized study, decreased hepatic steatosis by21%seen.132 Evaluation in combination with apoptosis signal controlling kinase(ASK1) hamperor selonosortib and farsenoid X receptor(FXR) agonist clofexor in patients with bridging fibrosis/ compensated cirrhosis with combinations llustrated recovery in NASH instead of lone ND-630.133 PhaseII studies of ND-630 withGLP1R agonist semaglutide are on presently.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD): Asignificant risk factor for CVD circulating triglycerides, preclinical studies in mice numerous ACC hampering drugs like A-908292[rev2][CP-64018[rev2] (S)-9c,124 ND-630119 decreased plasma triglyceride amounts. In humans ACC hampering drugs in dose based way escalate plasma triglycerides/orVLDL, like initial detailing for MK-4074,33 however seen with PF-05221304[rev 2], this escalation of circulating triglycerides modulated declined liver PUFA for stimulating SREBP1c activation causing enhanced GPAT, VLDL liberation.33 ND-630 further escalated triglycerides,131 reducing triglycerides clearance.133 For avoiding this deleterious action preclinical studies use combination of ACC hamperors with drugs like omega 3 FA’s /PPARα agonists like fenofibrate.133 Akin DGAT2 hampering further blocked PF-05221304 from escalating liver SREBP1c besides circulating triglycerides whereas impacting extra action on liver fibrosis in rodents model.134 Significantly in PhaseII clinical trials DGAT2 hampering further ameliorated PF-05221304 stimulated escalated triglycerides in ApoC3.134 These outcomes pointed combining approaches might be efficacious for recovery from cardiovascular risk factors in patients with NASH.135–140
FAS- control besides structure
Abundant Human FAS expression is existent in AT besides reproductive organs. Compared to ACLY, ACC, rare allosteric besides covalent modes controlling FAS action got detailed (Figure 3). In yeast, Ser 1140, Ser 1640 Ser 1827 Phosphorylation correlate with escalated 18:0-CoA generation[129], whereas in breast cancer cell line, FAS gets phosphorylated at Tyr66 in complex with human Epidermal Growth factor receptor(EGFR) [rev 2]. Additionally, FAS breakdown occurs by E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 in existence of adaptor proteins SHP2 besides deubiquitinated by ubiquitin particular protease2a.141 These outcomes pointed to specific situations besides cell kinds, FAS controlling might beby covalent besides ubiquitination modes. Apparently primary controlling FASmode is transcriptional.
FAS evolution in structural besides functional different variants gets it classified into 2 kinds dependent on the distribution of their catalytic units-i)type 1 and type 2 FAS.135 In eukaryotes the expression of complex of FAS 1 which is multifunctional occurs in cytosol controlled by a single gene[rev 2]. Type 2 FAS exists in mitochondria, functioning independent of cytosolic FAS 1 totally.135 Type 1 FAS canonically forms palmitate alone, whereas, FAS2 causes distinctive FA’s generation; made of 2 multifunctional polypeptides possessing 7 functional domains besides2 non enzymatic/pseudo domains/chain[rev 2] all needed for FA biogeneration (Figure 4).
Pharmacological hampering agents
Numerous natural products, their derivatives have been observed to hamper FAS. Cerulenin, an antifungal antibiotic initially obtained from Cephalospporum cacruleus hampers FAS in mammals besides bacteria.Cerulenin hampers FAS by covalent binding to active cysteine thiol in the β-ketoacyl synthase(KS) domain (Figure 4), further hampers HMG- CoA synthetase action137 blocking sterol generation. Absent reactivity besides sensitivity of Cerulenin caused generation of synthetic analogue C75 binding KS138 thioesterase(TE) domain of human.139
Numerous innovative small- molecule FAS hampering agents got generated for hampering the TE domain. Orlistat (tetrahydrolipostatin), a derivative of lipstatin, a natural existent Pancreatic lipase hamperor seen to hamper FAS via irreversible binding via TE domainof enzyme.140 Secondary to poor bioavailability and metabolic nonstability, numerous repeat formulations got started, inclusive of nanoparticle delivering method,12 poly(ethylene glycol), conjugated poly (lactic –co- glycoic acid) nanoparticles141 and folate receptor targeted micellar nanoparticles,142 neither of them reached clinical generation. Fasnall, a thiophenopyrimidine derivative further targets co- factor binding areas in numerous domains besides pharmacokinetic /toxicity studies illustrated no toxic actions.143 Recently triazole urea dependent substituted Fasnall led to isolation of MP-ML-24-NI, hampering FAS via TE domain besides possessing > cellular permeability[rev 2]. IPI-9119 hampered irreversibly the TE domain by facilitating acetylation of catalytic serine residues, besides demonstrated >robustness/ selectiveness against FAS besides > pharmacologic characteristics[rev 2]. FAS hamperors targeting the β-ketoacyl reductase(KR) domain, further formed with initiating clinical evaluation. GSK isolated GSK 2194069 utilizing HTS strategy dependent on substance competition with NADPH regarding binding in KR domain. Hamperor bound XRay crystal structure llustrated regarding substance generating hydrogen bonds with Ser 2021&Thyr2034, whereas studies in various cell lines pointing > cellular action against DNL hampering. Another substance formed with akin strategy BI 99179, a robust, selective hamperor presumably bound KR domain144 illustrated in> microsomal metabolic stability with >bioavailability in rats.144 An oral bioavailable, reversible, robust, selective FAS hamperor presumably hamperedKR domain.145 A> advanced substanceTVB-2640 has entered clinical generation.146 Furthermore, FT4101 hampered human FAS besides hampering KR domain.147
Obesity- Clarification amongst association amongst FAS hampering with body weightreduction is not there. Prior findings pointed to implicated enhanced energy expenditure with repressed appetite. Despite, the approval of FAS hamperor Orlistat for weight reduction in obesity, noticeably its low bioavailability, Pancreatic lipase hampering instead of FAS is the basic weightreducing mode. Outcomes of selective FAS hamperors like TVB-2640 don’t agree with weight reducing association.
NAFLD-NASH besidesT2DM: Prior studies illustrating C-75 led to hepatic steatosis reduction [rev 2] besides blood glucose in mouse models of TVB-2640, that decreased DNLby90% in subjects of obesity&IR.147–155 In-NASH subjects PhaseII clinical studies are on. Evaluation of FT4101in human obesity patients, decreased DNL& steatosis.156 Clinical formation stopped without reasons given. Despite, these studies agree for probable therapeutic advantages of FAS hampering in NASH outcomes from continuing PhaseII studies is must for getting >insight regarding safety& effectiveness is mandatory.
Over past 5 decades considerable propagation have been made regarding acquisition of insight over biochemical modes, physiological importance of DNL in controlling cellular metabolism besides total body energy homeostasis. Significant steps inclusive of isolating crucial metabolic biochemal intermediates in transformation of glucose into fatty acids, the molecular cloning of the crucial enzyme controlling this event besides invention of crucial allosteric besides covalent modes which control flux via this pathway. Following studies in genetically manipulated mice illustrated physiological part of DNL, widening insight of complicated associations existent in numerous cellular events beside tissues much away from only the storage of abundant calories in AT. Advancements in structural biology put the basis for the molecular reinforcement via which natural products and newer generation small molecules hampered enzymes action. In toto this knowledge caused a burst of innovative small molecules, formed &assessed in preclinical models regarding cardiometabolic disease, NAFLD-NASH, cancer &others. Despite variation amongst these substances regarding their molecular targets, chemical structure, physicochemical characteristics, the sharedeffect hampering DNL agrees with the posit, regarding advantages for avoidance& treatmentof a wide disease kinds. Nevertheless the generation, evaluation of newer generation of remarkably selective&effective small molecules has illustrated astonishingly newer biological understanding regarding safety, effectiveness, requirement for combining treatments for moving to Clinical trials.
Moreover, realization is important for correlating deleterious actions with use of these i)like most important is formation of embryonic generational abnormalities. ACLY homozygous deficient mice [rev 2]/ ACC1[rev 2]/ FAS[rev2]demise at embryonic generation, while CIC deficiency correlates with robust neurodevelopmental disease[rev 2]. ACC hamperor PF-05175157 further caused generational toxicity (IUGR, dysmorphogenesis correlating interference with midline fusion) inrats&rabbit.10 Thus avoidance of systemic DNL hampering in pregnancy is significant.
Other big issue is DNL hampering in organsrelated to lipogenesis like liver, AT is causing redirecting carbon inrest body with > toxicity. Initiation of this was seen inMK-4074 that dose based way escalated SREBP1c &serum TG-an on target action inmice with genetic absence of ACC in liver possessing akin phenotype.9 Following studies with ND-630,132 PF-05221304118 in human NASH subjects illustrated akin actions. Significantly serum TG enhanced by PF-05221304 hampered with concomitant delivery of DGAT2 hamperor.134 Intriguingly hampering ACC by AMPK activation148 decreased TG cholesterol action. Akin actions were seen with hampering ACLY as well.96,101,102
Greater insight of mode for variable reaction with hampering liver is significant for unraveling, avoidance of these worrying side effects. Furthermore attention is required for upstream and downstream sequences correlated with blocking DNL at variable steps in pathway of DNL causing accrual of metabolic intermediates. Like hampering FAS results in malonylCoA enhancement, that disrupts physiological angiogenesis through malonylation of mTOR[rev 2], further malonylation responsibile for different metabolic pathway151 Histone modifications[150], reprogramming immune cells,151 pointed that hampering FAS might illustrate wider biological actions compared to presumed hampering DNL. Problems associated with CIC hampering are escalated citrate/isocitrate in mitochondria, correlated with robust neurometabolic actions. Finally hampering ACLY causing reduction of acetylCoA, implicated in acetylation of numerous Histone, gene expression epigenetic reprogramming.152 Hence attention is required for actions of metabolic intermediates when generating DNL hampering agents regarding treatment.
Another issue is differential reactions in rodents &humans. Like in case of PF-05175157 no toxicity in rodents visualized, however dose enhancement illustrated reduction in platelets amounts.20,118 Following studies illustrated platelet reduction was secondary to ACC hampering amongst Bone marrow causing dysfunctional megakaryocyte maturation[rev in2] pointing to need for DNL in human, & not in rodents, an astonishingfact with knowledgethat DNL in tissues like liver, AT is considerably greater in rodents compared to humans.152 Avoidance of these actions was feasible with newer formation of liver targeted ACC hamperors like ND-630132 & PF-05221304.118 Genetic ACLY hampering in muscle, ATcaused muscle weakness & lipodystrophy respectively, however avoidance of generation due to formation of Bempedoic acid –liver targeted prodrug. Liver particular hampering of DNL might be advantageous for preventing probable deleterious action of hampering DNL in AT. DNL hampering on total body insulin sensitivity with information that AT has direct association with insulin sensitivity.36,153 Finally hampering FAS correlates with alopecia an action decreased by formation of newer generation of liver targeted FAS hampering agent TVB-2640[rev2], FT-4101.154 These till date outcomes pointed hampering FAS, ACC& ACLY is feasible safely via liver targeting, nevertheless if chronic hampering DNL in other organs/cell kinds feasible safely needs future evaluation.
In the last decade numerous hurdles have been tackled resulting in clinical generation of DNL hampering agents initiated for CVD, NASH, canceretc. We reviewed different modalities for obesity therapy besides that for NAFLD/NASH,155–166 yet no drug has been approved for obesity/ NAFLD/NASHtherapy. Today when single cell evaluation of cellular metabolism is feasible a thrilling research aspect estimated if particular cell kinds having DNL upregulation in variable pathological situations is existent. Isolation of these probable cell kinds might result in cell particular DNL hampering, whose clinical applications at the time of some windows of generation to ameliorate or possible avoidance of disease.
Further attention regarding balancing effectiveness besides safety since enhanced robustness might result in more upregulation/or toxicity in eg regarding ACC hampering agents where DNL hampering intricately parallels simultaneous enhanced circulating triglycerides besides platelet hampering. Since DNL upregulation is temporary following a meal, methodology of probably avoiding upregulating compensatory pathway&/or toxicity might implicate utilization of hampering agent possessing shorter half life for DNL sustenance at basal amounts. Finally if DNL hamperors are utilized with sufficient proven safety & effectiveness for utilization as monotherapy or requires combination with different therapies for escalating effectiveness for offset responsibilities, like posited for ACC hampering agents in NASH, will base outcomes of clinical trials. Regarding this ACLY hamperor Bempedoic acid observations are good as they pointed that chronic DNL hampering in liver has safety on lone use or with other management practices. If DNL hampering agents targeting other cell kinds& organ system get widely accepted as a hallmark for treatment of other disease indications apart from CVD, NASH require determination.
None.
The authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
None.

©2022 Kaur, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.