MOJ
eISSN: 2641-9297


Research Article Volume 1 Issue 4
1Department of Business Administration, Islamic Azad University, Naragh Branch, Markazi, Iran
2Researcher of Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences, Shahrekord, Iran
3Department of Business Management, Islamic Azad University, Iran
Correspondence: Alireza Nojoomi, Department of Business Management, Islamic Azad University, Electronic Education Unit. Tehran, Iran, Tel 9128181699
Received: July 30, 2018 | Published: August 6, 2018
Citation: Rasoulian M, Ghannadi AA, Rajabi-Vardanjani H., et al. Study of factors affecting the risk-taking of Tehran’s active insurance companies in 2017. MOJ Curr Res & Rev. 2018;1(4):175-178. DOI: 10.15406/mojcrr.2018.01.00028
The insurance industry is considered as one of the crucial factors for the development and progress of countries, and insurance condition is an indicator of this phenomenon. In the present study, among 60 senior managers and experts, descriptive statistics in the field of demography such as gender, background, and educational level of respondents were studied, and next they were asked for the confirmation and rejection of statistical assumptions in the form of known criteria and opinions of experts and decision-makers. In the statistical sample, the results demonstrated that all seven criteria including equality of competition between provider organizations (40/60, p=0.0021), sales expertise in serving the service (46/60, p=0.0011), variety of services provided (54/60, p<0.001), informing people about the diversity of current services (lack of appropriate advertising) (43/60, p=0.0019), prices variations of organizations to attract customers (58/60, p<0.001), government policy and lack of inflation in the community (60/60, p<0.0001) were significantly effective in risk taking of life insurance. In order to prioritize the factors from the hierarchical analysis process for factor ranking, the results indicated that inflation, governmental policies and lack of expertise were the major factors impacting on risk taking in the industry of life insurance.
Keywords: insurance industry, life insurance, risk factors
Nowadays, the insurance industry is considered an eminent factor in the development and progress of countries, and also insurance is a determining factor during the development of countries. Insurance has a prominent role along with other economic sectors and increases the incentive to invest by covering possible losses caused by various economic activities, and increasing investment also plays a significant role in the country's growth and development, as well as the study of the growing trend of insurance in general and life insurance in particular over the past decade have been indicating the increasing role of life insurance in the families’ economy in developed and developing countries .1 The risk is the cause of insurance contracts, and if the assumption of risks is generally eliminated, the conclusion of the insurance contract is also meaningless. The risk is always with itself, bitterness and negativity, and the meanings of present kind are reminded and precisely in the face of luck.2 Therefore, it is noted that the risk existence is crucial in concluding insurance contracts, and insurers are the most obsessive individuals present at the contractual stage of the contract, it is a matter of accurately identifying the risks surrounding the insurer. Basically, most risks have the ability to create insurance coverage, and insurance companies perform it in the normal process of making insurance coverage. However, in some cases, some risks are not fundamentally or impossible to create coverage, such as those that are the product of intentional or intentional insurer's fault, which do not come from the first place within the scope of coverage. Or, if it is not and can create an insurance umbrella, insurance companies can receive an excessive amount of additional premium on the organization from the applicant in order to provide him with the coverage of the desired insurance. Risk is a major and effective component of the contract. As long as the increase and decrease of risk which affects the legal fate and, as the case may be, it creates rights for the insurance and the insurer. In present research, the identification and ranking of factors affecting the risk taking of insurance companies in Life insurance industry was assessed.1−3 The purpose of the present study was to identify the factors affecting the risk taking of active insurance companies in Tehran city in the life insurance industry.
Risk-taking means the eventual occurrence of an unpredictable event in the future, a situation that may be risky or has adverse consequences and incidents. Basically, life insurance and survivors cover two general risks in human life including sudden and unexpected death (risk of death): Present risk is especially crucial in the case of the death of the family's guardian and breadwinner. In many families, the economic life of the family depends on its breadth and, with the sudden death of other members; it is deprived of its material and spiritual support. Revenues from his business and works are cut off and the family is subjected to severe economic and social injuries. Life expectancy is higher than expected (life risk): In the face of the risk of death, there is a risk that a person and his family will be exposed to severe economic and social conditions due to his long life span. The reason is that with increasing age and reaching the retirement age, the income of individuals decrease, and on the other hand, the expenses also increase as a result of increased costs of treatment due to illness and aging problems.4 The aim of this study was study of factors affecting the risk-taking of Tehran's active insurance companies in the life insurance industry in 2017.
The present study is a cross-sectional cohort or exploratory survey using quantitative parameters. The purpose of exploratory research is to create a suitable ground for better understanding of different phenomena or a particular problem about which the investigator have no sufficient information. Exploratory research may be carried out in different ways. The present research was implemented according to interviews with individuals, and consultation with professors and experts. In addition, since present research is about a real, objective, vivid, and dynamic subject, and its results can be scientifically applied, it is also an applied research. The statistical population of the research was considered by senior managers of life insurance of active insurance companies in Tehran city. Determining the sampling plan to be used and selecting sample volumes are key issues in designing a survey. In present research, simple random sampling was used. For this purpose, according to the Morgan table, a population of 70 subjects was estimated, and the number of samples obtained as 60.
Data collection methods included
According to the responses of managers and experts, seven studied factors were included described later. In present study, the indicators used to confirm the interview were used. In order to study the weights and priority of variables, the hierarchical analysis process method and the paired matrix questionnaire were followed. Reliability is the technical characteristics of the measuring instrument. The reliability of a measuring instrument indicates the extent to which the results of the measuring instrument are stable and consistent. In present research, the cronbach coefficient Alpha was used to examine the reliability of the instrument. Regarding the concept of validity and reliability of the questionnaire mentioned in present study, in order to investigate the reliability of the questionnaire, a questionnaire was developed based on the Likert spectrum and seven identified options distributed among the statistical samples. The Cronbach Alpha Test was also used for analysis of results.
The present study aimed to identify and rank the factors affecting the risk-taking of active life insurance companies in Tehran city based on a statistical sample of 60 senior managers and experts. To this end, by reviewing literature and research background, all seven factors were identified according to interviews with the experts of each of the seven factors, then using the hierarchical analysis process method and using the available spectra in the method, the questionnaire was completed by the sample statistical analysis.
Ethical approval
This manuscript has been submitted to this journal by the consent of all authors and has not been considered for publication in any other journal. This work was ethically approved by Department of Business Management, Islamic Azad University, and Electronic Education Unit.
First, using descriptive statistics, cognitive status of demographic characteristics of respondents was obtained and then, by approving the criteria and factors, the ranking of these criteria was done using the hierarchical analysis process. Of the 60 people, the highest number of respondents was men (80%). The majority of subjects had a master's degree (54%) and the least of them had a doctorate (8%). Moreover, the majority of subjects had a history of between 10 and 20 years (81%) and the least of them were between 20 and 30 years (8%). According to the responses of managers and experts, using statistical analysis, all seven factors studied including equality of competition between provider organizations (40/60, p=0.0021), sales expertise in serving the service (46/60, p=0.0011), variety of services provided (54/60, p<0.001), informing people about the diversity of current services (lack of appropriate advertising) (43/60, p=0.0019), prices variations of organizations to attract customers (58/60, p<0.001), government policy and lack of inflation in the community (60/60, p<0.0001) were significantly effective in quality of life insurance. Then, with the corresponding calculations and column mean of the final results, the final values of each index were presented in Table 1. Finally, the values and effeteness of each factors from calculations and according to the matrix obtained, and the hierarchical analysis process technique, are presented in Figure 1.
In addition to the existing conditions in the country's insurance market (tariff liberalization, privatization, entry of new rivals and all of which lead to increased competition), which strengthen the necessity and need for the establishment of a risk management system for controlling and monitoring the risks in the insurance companies of the country, there are issues in the market and institutions of the country providing insurance without a management system There is no risk of solving them. The statistical survey of the state of the insurance market as well as the study of the financial situation of the country's insurance companies indicates an increase in risk in the insurance companies of the country. In a society where there is no risk, there will be no insurance or risk, there are different types and forms, but with many variations and in spite of its variety, it has a stable result. Risk assessment is, of course, different in each of the individuals' insurance, and the path to education varies from one to the other. In life insurance, the premium is calculated on the basis of the death table, which is for normal risks. In the stock market of developed countries, there are markets responsible for securing the risk of fluctuations in stock prices. These markets are called stock market trading, while comparing the stock options agreement and the insurance contract, present paper examines the possibility of reducing the risk of purchasing shares in the stock market is based on insurance contracts. In this regard, after introducing the general framework of the study, the theoretical consideration of the subject has been examined using domestic and foreign sources. Then, using the field method, the data were gathered, obtained from a questionnaire distributed among the shareholders in the Exchange Hall and analyzed using the software. The results showed that the shareholders tend to be insured. They believe that the involvement of the insurance industry in the stock market as a reliable security market can increase the amount of investments. At the end, proposals are presented with regard to the results. To control and hold risk management and to implement methods of coping with risk should be considered, in other words, risk management is applied to the set of actions with assets of an institution to maintain firm.5
The environmental complexity, the intensity of competition, the advent of new and advanced technologies, the advancement and development of information and communication technology, the new ways of supplying goods and services, environmental issues and the orientation of organizations from intangible assets are among the major factors which has caused organizations and businesses to face a lot of risks and high and even unpredictable risks during their lives. For this reason, in order to reduce the risk and compensate for the resulting losses, scientific literature of various types of risk management, such as risk management, business risk management and strategic risk management, is presented in everyday literature.6 Obviously, each organization experiences different risks depending on its nature. In today's changing environment, the success of each firm is basically the ability to control its risks and management type.7 Time risk management implies that conditions are likely to suffer losses and uncertainties. Present kind of management includes a wide range of areas that include financial, operational, commercial, strategic, and wider areas of risk incidents. Overall, risk management is the risk measurement process, and then the risk management strategy, the thinkers have identified four common strategies for risk management: risk transfer (acceptance of risk by another), risk avoidance (non-performing risk-taking activity), Risk reduction (methods that reduce the severity of losses), and acceptance of risk (acceptance of losses at occurrence), but the main thing in our economic firms is that there is no strategic look at identifying risk management in them, so that There is no specific place for this kind of management in our organizations and firms.8
In this study, by alpha cronbach analysis, all seven criteria including equality of competition between provider organizations (40/60, p=0.0021), sales expertise in serving the service (46/60, p=0.0011), variety of services provided (54/60, p<0.001), informing people about the diversity of current services (lack of appropriate advertising) (43/60, p=0.0019), prices variations of organizations to attract customers (58/60, p<0.001), government policy and lack of inflation in the community (60/60, p<0.0001) were significantly effective in risk taking of life insurance. Some previous studies have evaluated risk-taking of markets, banks, directors' and officers' liability insurance and deposit insurance.9–12 Over the past few years, the financial industry worldwide has had its share of recession. Given the widespread reporting of unpredictable business failures and the global financial closure of the economy, the debate about the size of insurance companies and excessive risk appetite has become a concern for economic operators.13,14 Recent research has shown that the size of the company and the ratio of the company's capital have had a significant impact on the risk of insurance companies. Given the widespread reporting of business unpredictable failures and the global financial closure, the debate over the size of insurance companies and excessive risk appetite has become a concern for economic operators.15–17
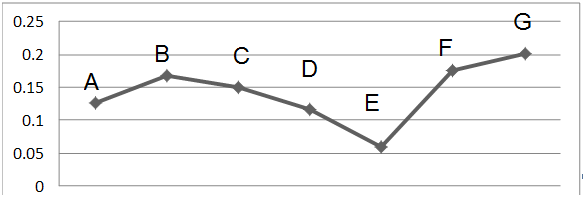
Figure 1 The values and effeteness of each factor from calculations and according to the matrix obtained, and the hierarchical analysis process technique, A: Inequality of competition between the organizations; B: the lack of sales expertise in providing the service; C: The lack of diversity in the services provided; D: Failure to inform people about the variety of current services (lack of appropriate advertising); E: Prices between different organizations to attract customers; F: Government policies; G: Inflation in society.
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
A |
1 |
0.25 |
9 |
2 |
7 |
0.11 |
0.2 |
B |
4 |
1 |
9 |
6 |
3.03 |
0.33 |
0.14 |
C |
0.11 |
0.11 |
1 |
1 |
5 |
7 |
0.33 |
D |
0.5 |
0.16 |
1 |
1 |
0.2 |
0.33 |
5 |
E |
0.14 |
0.33 |
0.2 |
5 |
1 |
0.33 |
0.2 |
F |
9 |
3.03 |
0.14 |
3.03 |
3.03 |
1 |
1 |
G |
5 |
7 |
3.03 |
0.2 |
5 |
1 |
1 |
Table 1 column mean of the final results, the final values of each index, A: Inequality of competition between the organizations; B: the lack of sales expertise in providing the service; C: The lack of diversity in the services provided; D: Failure to inform people about the variety of current services (lack of appropriate advertising); E: Prices between different organizations to attract customers; F: Government policies G: Inflation in society
Life insurance provides a social peace for the community and economic security and the prosperity of financial markets for the economy of a country. At the community level, the life insurance insurer, in return for payment of a premium, ensures the receipt of the amount of insurance capital in the future. Insurance companies with a significant source of their mathematical savings can invest in different sectors that lead to the dynamics of the economy. There are factors such as inflation, government policies, and lack of expertise in the key priorities for impact on risk taking in the life insurance industry. Factors which could affect and help in bettering conditions included equality of competition between provider organizations, sales expertise in serving the service, variety of services provided, informing people about the diversity of current services (lack of appropriate advertising), prices variations of organizations to attract customers, government policy and support and lack of inflation in the community. Some limitations are considered in this study such as refrain in terms of providing accurate responses by interviewing, prolongation and time consuming of all the questions which performed at various times, possibly affecting the accuracy of the responses by the managers or experts.
This study was supported by Islamic Azad University, Naragh Branch, Isfahan, Iran.
Author declares that there is no conflict of interest.

©2018 Rasoulian, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.