MOJ
eISSN: 2572-8520


Mini Review Volume 3 Issue 2
Department of Buildings and structures design, Moscow State University of Civil Engineering, Russia
Correspondence: Sergey V Stetsky, Buildings and structures design, Moscow State University of Civil Engineering, Russia
Received: May 02, 2017 | Published: July 24, 2017
Citation: Stetsky SV. Stationary outdoor sun-protective canopies as a mean of improving of lighting environment in the premises of civil buildings in the hot and sunny climate with clear sky conditions. MOJ Civil Eng. 2017;3(2):266-269 DOI: 10.15406/mojce.2017.03.00064
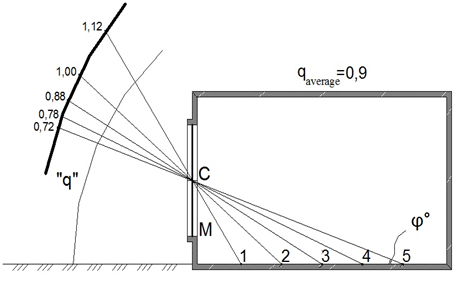
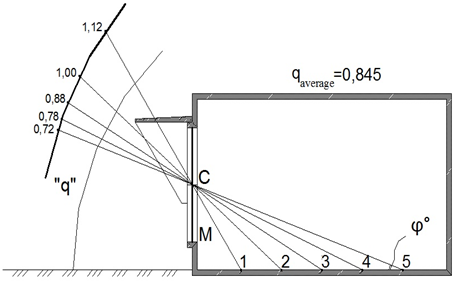
The design of natural lightings` systems in southern regions with sunny climate needs to consider an affect of external sun-protective devices, as well as a character of external lighting. The latter in the case considered much differs from the standard overcast sky conditions of Commission Internationale de l'éclairage (C.I.E.). In sunny climate the character of outdoor lighting is determined as lighting in «clear sky» conditions.1–4 The values of «q» factor, which determine the uniform luminance of sky vault with diffused and sun lighting in graphical form are shown on Figures 1–3. The curves shown have different character, depending on sky vault conditions, aspect of window openings and presence or absence of sun-protective devices. Date of «q» factor values are quoted in Table 1.5–8
A-without external sun-protection devices.
B-with external sun-protection devices
Figure 1 Non-uniform luminance of sky-vault under diffused external lighting a premise considered, observed from design points.
«C» -The middle point of a window opening.
«M» - Design point of insolation.
1, 2, 3,4, 5 - Design points for daylight factor’ calculations

А - South-eastern aspect.
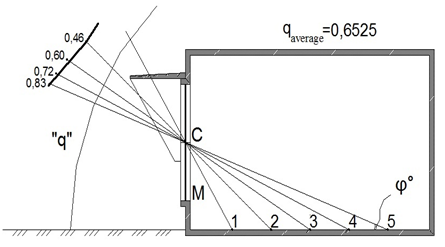
В -Southern aspect.
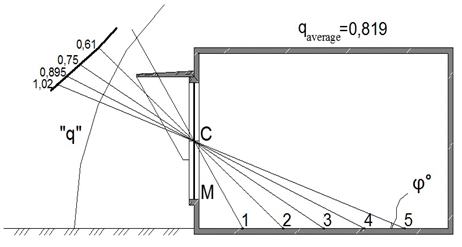
С - South-western aspect.
Figure 2 Non-uniform luminance of a sky-vault under sunny external lighting for a premise considered without external sun-protection devices, observed from design points.
«C»’ –The middle point of a window opening.
«M»’ – Design point of insolation.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5 – Design points for daylight factor’ calculations.

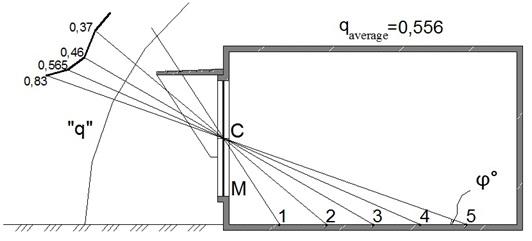
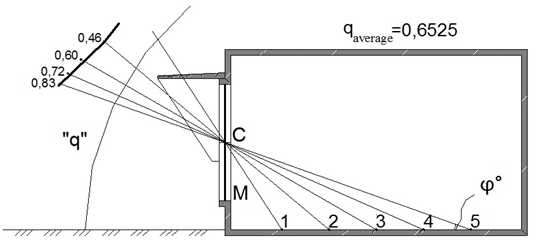
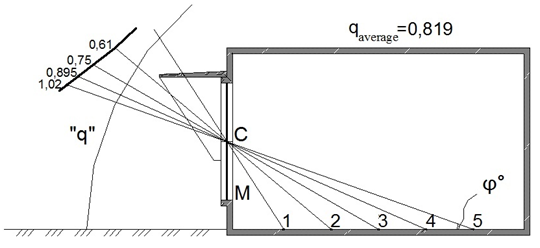
Figure 3 Non-uniform luminance of a sky–vault under sunny external lighting for premise considered with external sun-protection devices, observed from design points.
№№ of design’ points |
Angle |
Values of «q» factor |
|||
|
Under sun-lighting with different windows aspects |
||||
South-eastern |
Southern |
South-western |
|||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
1 |
54 |
1,12 |
0,305 |
0,37 |
0,49 |
2 |
42 |
1,0 |
0,37 |
0,46 |
0,61 |
3 |
32 |
0,88 |
0,46 |
0,60 |
0,75 |
4 |
25 |
0,78 |
0,565 |
0,72 |
0,895 |
5 |
20 |
0,72 |
0,83 |
0,83 |
1,02 |
Table 1 The values of «q» factor, showing the non-uniform sky’ luminance under different sky-vault conditions for a premise concerned
The theoretical and field investigations were conducted, based on examination of real residential premise in Beirut, Lebanon, which was chosen as an experimental site. In the room considered, which originally had no sun-protection, a temporary model of sun-protective canopies over a and below window were constructed. The canopies were painted in a light-grey colour. These permits to conduct lighting researches with sun-protective devices, as well as without these units see Figures 4 & 5. As a result of scientific investigations, the positive role of sun protection in form of canopies (awnings) on the natural lighting of interiors levels in the premises of civil buildings in the sunny climatic conditions with respect of external lighting on «clear sky» basis.
None.
The author declares that there are no conflicts of interest.
None.

©2017 Stetsky. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.