Journal of
eISSN: 2379-6359


Case Report Volume 7 Issue 4
1Consultant Head Neck oncosurgeon, India
2Surgical oncologist Curie Manavata cancer centre, India
3Consultant Oral Facio maxillary surgeon Indore, India
Correspondence: Mohammad Akheel Consultant Head Neck oncosurgeon, India, Tel 9584284566
Received: January 25, 2017 | Published: June 13, 2017
Citation: Akheel M, Nagarkar R, Roy S, Wadhwania A (2017) Huge Nodular Goitre with Retrosternal Extension- A Rare Case Report. J Otolaryngol ENT Res 7(4): 00215. DOI: 10.15406/joentr.2017.07.00215
Retrosternal goitre is very rare condition which account for 5 to 20% of thyroidectomy patients. Though rare, it can be better managed surgically. In this article we report a rare case of 55year old female who had nodular goiter with huge retrosternal extension associated with hyperthyroidism. Majority of retrosternal thyroid can be removed safely by conventional cervical approach. Our patient had around 12cm mass which was impossible to remove it from conventional approach and hence total thyroidectomy by a combined cervical/sternotomy approach. Procedure was uneventful and patient is doing fine in 2months of follow-up. The role of thyroidectomy in patients with retrosternal goitre provides yet another area of surgical controversy.
Keywords: thyroid neoplasm, retrosternal goiter, sternotomy
Retrosternal goiter is defined when 50% of the thyroid is below the thoracic inlet. This can also be called as intrathoracic goiter.1‒5 Retrosternal goiter is a very rare condition which account for 5 to 20% of thyroidectomy patients. Mediastinal extension is more common in huge goiters with a peak incidence in 5th to 6th decade. This is usually rare when the patient has associated hyperthyroidism which may increase the risk of complications. The reported incidence of goiters with thyroid malignancy is around 3 to 17%. Retrosternal goitre occurs when the thyroid enlarges downwards into the chest. Although the great majority of retrosternal goitres are extensions from the neck, pure intrathoracic goitres are very rare. Retrosternal goitres are more likely to be left sided and very rarely a left sided cervical goitre descends into the right side of the chest which is called a "crossed substernal goitre". With few exceptions huge goiters can be removed by cervical approach but less than 2% patients require cervical/sternotomy approach. All these factors will influence the perioperative management of the patient. In this article we report a rare case of 55year old female who had nodular goiter with huge retrosternal extension associated with hyperthyroidism. The tumor was removed surgically by a combined cervical/sternotomy approach.
A 55year old reported to our cancer centre with a chief complaint of difficulty in breathing and eating from 2years. General examination was insignificant. Local examination revealed a diffuse swelling of left lobe of thyroid (Figure 1). Her medical history revealed hyperthyroidism from 2years. A provisional diagnosis of Thyroid swelling was made. Radiological examination was done. Computed tomography of neck revealed 12 x 8 x 7cm retrosternal mass arising from left lobe of thyroid with tracheal compression (Figure 2). There was no cervical lymphadenopathy.6‒10 Thyroid function test (T3, T4 and TSH) were done. T3 was 2.11nmol/l, T4 was 228.86nmol/l and TSH was less than 0.06uIU/Ml. Fine needle aspiration of the lesion gave a final diagnosis of nodular colloid goitre with cystic changes. Since T4 was high, patient was started on Tab Neomarkazole 2.5mg, Tab Inderal 80mg and Lugol Iodine solution orally for 5days to avoid Thyrotoxicosis. After 5days T3 was 0.98nmol/L, T4 was 180.36nmol/L and TSH was less than 0.05Uiu/Ml. Patient was taken for surgery.
Fibreoptic laryngoscopy was done to visualise the tracheal patency. Awake intubation was done. General anesthesia was administered. Necklace incision was given 2cm above the sternum. Strap muscles were dissected.
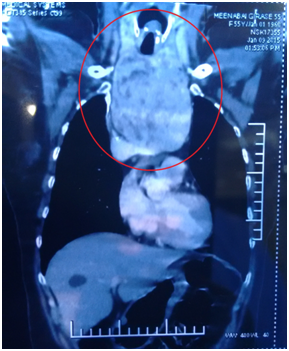
Figure 2 Computed tomography of neck revealed 12 x 8 x 7 cm retrosternal mass arising from left lobe of thyroid with tracheal compression.
Thyroid gland was exposed. First left thyroid gland was mobilized followed by right thyroid gland. Bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve was identified and preserved (Figure 3). The left thyroid mass was dissected. Sternotomy was done to enucleate the retrosternal mass from anterior mediastinum. Thyroid gland along with retrosternal mass was excised (Figure 4). Hemostasis was achieved. Drains were kept and closure was done in layers. Postoperatively patient was started on Tab Neomaracazole 2.5mg and Tab Inderal 80mg. Postoperative T4 was 145nmol/L. Patient was discharged on 4th postoperative day.
The definition of retrosternal goiter is not uniform and often varies among authors. Goldenberg and Lindskog defined retrosternal goiter as a lesion of the thyroid gland extending downward the fourth thoracic vertebra on chest imaging or a structure with an inferior margin extending down to the level of the arch of the aorta. According to Katlic and colleagues retrosternal goiter is defined when more than 50% of the mass lies distally to the thoracic outlet. Patients often complain with slow and progressive growth commonly seen in 5th or 6th decade of life. When the age of clinical presentation advances there is increased medical co-morbidity implying that surgery at an earlier stage may be associated with reduced complications related to co-existing disease.
Other symptoms can be cough, dyspnoea, dysphasia, strider, and symptoms of choking which are absolute indications for surgery. Our patient had all these clinical symptoms. Radiological Imaging indicators may include compression of trachea, tracheal deviation, compression of other adjacent vital structures. Imaging often helps in correlating the symptoms with size of goiter, presence of tracheal deviation or extent of retrosternal extension. The cause for acute airway obstruction/orthopnoeaneeds to be considered which may be due to haemorrhage within the thyroid gland or may be secondary to prolonged mechanical pressure with acute laryngeal edema and congestion. Although rare these acute problems can contribute for around 5-11% and may lead to catastrophic consequences providing a clear indication for thyroidectomy in patients with retrosternal goiter.
The majority of nodular goitres, limited to the neck and including a retrosternal component are often benign in nature. Clinical and ultrasonography examination can be done for cervical goitres and needle biopsy of suspicious areas can be taken, with cytological determination of malignant nodules, leading to patient selection for surgery.11 Retrosternal or subternal components of goitres are not easily imaged by ultrasound due to artefact generated by bony structures and needle biopsies are difficult to perform in routine practice. This can lead to exclusion of malignancy thought with difficulty in retrosternal goitres. Prospective studies reveal the incidence of development of malignancy in goitres is 1.3-3.7 new cases per 1000 patients. A recent review of evidence-based management of substernal goitres concluded the incidence of malignant transformation is equivalent in retrosternal goitres to those residing entirely in the neck.12‒14
With few exceptions huge goiters can be removed by cervical approach but less than 2% patients require conventional cervical approach combined with sternotomy/ manubriotomy/ thoracotomy. Review of the literature regarding the complications of recurrent laryngeal nerve injury, hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyroidism and tracheomalacia after retrosternal goitre excision reveals conflicting results as to whether these specific complications are increased by comparison to cases of excision of simple cervical goitre. Total Thyroidectomy for retrosternal goitres with associated medical co-morbidities should be performed by surgeons who are experienced in thyroid surgery to prevent complications and a cervical approach is successful in the maximum number of cases.
Graves disease is one of the most common cause for thyrotoxicosis or thyroid storm. It can be precipitated by systemic insults like trauma, surgery, trauma, myocardial infarction, pulmonary thromboembolism and severe infection. In the past, thyroid storm was most commonly caused in thyroid surgery patients who had uncontrolled hyperthyroidism. Though this condition has been decreased by newer imaging modalities, but has not been completely eliminated the incidence of thyroid storm.
Preoperative management of the thyrotoxic patient includes preparation for elective or nonurgent procedures and preparation for emergent procedures. When the case is nonemergent, there must be control of thyrotoxicosis to achieve euthyroidism before surgery.15 In this cases, thionamide therapy preferably Neomercazole would be recommended and would facilitate euthyroidism within several weeks. The use of iodine (lugols iodine) as a method of decreasing thyroid vascularity and friability before thyroid surgery (Table 1). Postoperatively Beta adrenergic receptors may be required for a period of 1 week. In our patient, Tab Neomarkazole 2.5mg, Tab Inderal 80mg and Lugol Iodine solution orally were given for 1 week preoperatively to avoid Thyrotoxicosis followed by 5days postoperatively.
Medication |
Dosage |
Mechanism of Action |
Conditions of Use |
||||
Inhibition of new Hormone Production Propylt Hiouracil |
200-400 mg po q6-6ha |
Inhibits a new Hormone Synthesis: Decreases T4-T3 Conversions |
First-Line Therapy |
||||
or Methimazole |
20-25mg po q 6ha |
Inhibits a new hormone synthesis |
First-Line Therapy |
||||
Inhibition of Thyroid Hormone Release Potassiumiodideb SSKI |
5 drops q 6 h |
||||||
Lugol's Solution |
4 drops po q 6-8-h |
Blocks release of hormone from gland |
Administration at least 1 hr after thionamide |
||||
Sodium Iodatee (308 mg Iodine/500mg tab |
1-3 po qd |
Blocks release of hormone from gland |
Administration at least 1 hr after thionamide |
||||
Iponic Acide |
1g po q 8 hr or 24 h then 500mg po q 12 h |
Blocks release of hormone from glandT3-toT3 conversions |
Administration at least 1 hr after thionamide |
||||
Beta Adrenergic Blockade Propranolol |
60-80 mg po q 4 h or 80-120mg q 6 h |
Blocks release of Hormone from GlandT3-toT3 Conversions |
|||||
Cardio selective agents: |
500-200mg po qd |
||||||
Atenolol |
100-200mg po qd |
Beta adrenergic blockade |
|||||
Metaprolol |
40-80mg po qd |
||||||
Nadalol Intravenous agent: |
|||||||
Esmolol |
50-100/kg/min |
Beta adrenergic blockade |
|||||
Table 1 Management of thyroid storm
There is always a controversy to perform a Total thyroidectomy in patients with retrosternal goitre. There was historical surgical dogma to operate the patient with retrosternal goitre. But due to increased use of radiological investigations, particularly advanced Computed tomography scans have identified the often asymptomatic retrosternal goiter.16,17 These developments have prompted some thyroid surgeons to challenge the traditional surgical doctrine. Today it remains generally accepted that patients of retrosternal goitre with clinical symptoms of stridors/dysphagia and/or radiological evidence of significant tracheal narrowing, oesophageal compression or SVC syndrome.
Total Thyroidectomy in retorsternal goitre with hyperthyroidism patients must be performed with utmost precautions. Thyrotoxicosis and thyroid storm pose a critical diagnostic and therapeutic challenge to the clinician. Recognition of life-threatening thyrotoxicosis and prompt use of the arsenal of medications aimed to prevent the thyrotoxic process at every level is essential to successful management. Surgery is usually associated with increased risk of complications and hence must be performed by an experienced surgeon.
None.
Author declares there are no conflicts of interest.
None.

©2017 Akheel, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.