Journal of
eISSN: 2376-0060


Editorial Volume 9 Issue 3
1Faculty of Medicine, Western University, Thailand
210th Zonal Tuberculosis and Chest Disease Center, Thailand
3Department of Pathology, Chiang Mai University, Thailand
Correspondence: Attapon Cheepsattayakorn, 10th Zonal Tuberculosis and Chest Disease Center, 143 Sridornchai Road Changklan Muang Chiang Mai 50100 Thailand
Received: October 18, 2022 | Published: October 19, 2022
Citation: Cheepsattayakorn A, Cheepsattayakorn R, Siriwanarangsun P. Covid-19-cardiovascular-disease patients treating with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir inducing cardiovascular-drug interactions. J Lung Pulm Respir Res. 2022;9(3):63-64. DOI: 10.15406/jlprr.2022.09.00282
Low-dose ritonavir in combination with nirmatrelvir (NMVr), a SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)-produced-protease enzyme anti-retrovirals in delaying its hepatic metabolism and prolonging its duration of action1 by inhibiting cytochrome P (CYP)3A4 and P-glycoprotein (P-gp),2 whereas ritonavir inhibits CYP 450 enzymes, especially CYP3A4 and a lesser degree of CYP2D6.1 The CYP 450 enzymes are responsible for several medication-oxidative metabolisms, whereas ritonavir induces other CYP 450 enzymes to a lesser degree, contributing to reduced-various-medication levels.1 Primary inhibition and subsequent induction with time by the effect of ritonavir on P-gp can induce relevant cardiovascular (CV) drug-drug interactions (DDIs) in COVID-19-cardiovascular disease (CVD) patients.2 The proposed decision-making algorithm is demonstrated in Figure 1.3
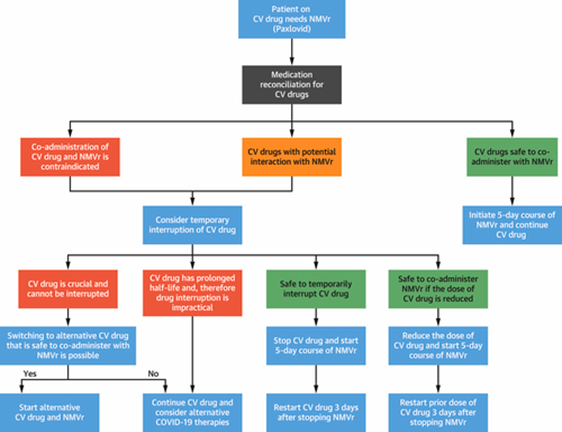
Figure 1 Demonstrating the algorithm for proposed decision-making for Covid-19-CVD patients with NMVR need.
Source: Cardiovascular drug interactions with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in patients with COVID-19 : JACC review topic of the week. JACC. 2022.3
In conclusion, for prevention of CV-DDIs, discontinuation or dose adjustment during the NMVr treatment and 3-5 days after completion of treatment in COVID-19 patients.
None.
There are no conflicting interests declared by the authors.

©2022 Cheepsattayakorn, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.