Journal of
eISSN: 2377-4312


Research Article Volume 13 Issue 1
Centro de Medicina Equina Integrado, CEMEI Araçatuba, Brazil
Correspondence: Luiz Alberto da Silva Vasconcellos, Centro de Medicina Equina Integrado, CEMEI Araçatuba, SP, Brazil
Received: May 31, 2024 | Published: June 13, 2024
Citation: Vasconcellos LAS. Use of cattles with cervical tumors as an experimental model of oropharyngeal neuropathies in equines. J Dairy Vet Anim Res. 2024;13(1):49-52 DOI: 10.15406/jdvar.2024.13.00348
In order to better understand the pathophysiology of diseases of the oropharynx in horses, endoscopy was performed in the oropharyngeal region of dairy and meat producing cattle, with the presence of tumors in the eyes, infra-auricular region or both regions (experimental model), analyzing what these tumors could cause in the innervation of their oropharynx and problems were observed in cattle very similar to those found in equine athletes such as epiglottic entrapment, collapse of the palatine arch, chondritis of the cuneiform recess, loss of palatal tone, but without respiratory symptoms, which we conclude that this model deserves more attention and can help us understand the nervous segments involved as well as the anatomical structures affected.
Keywords: tumor in cattle, endoscopy in cattle, endoscopy, bovine respiratory disease, equine respiratory disease, equine endoscopy
The most common tumors found in cattle in Brazil are lymphoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which can affect the eye, skin and regional lymph nodes.1 Ocular squamous cell carcinoma is one of the most frequent neoplasms in cattle around the world, being responsible for large economic losses due to the reduction in reproductive life or the condemnation of carcasses in slaughterhouses.2,3
Usually, the age of cattle affected by ocular squamous cell carcinoma is between 5-7 years, however older animals can also be affected.2–4 For management reasons, females are affected more frequently.4 Metastases are rare and generally seen in animals with large tumors. In these cases, emboli of neoplastic cells initially reach the head lymph nodes before reaching the bloodstream through the thoracic duct. In addition to regional lymph nodes, metastases have been observed in the lungs, heart, pleura, liver and kidneys.5 Intracranial invasion by squamous cell carcinoma is rarely reported.6,7
The ocular innervation is quite complex and with some anatomical particularities, where some nerves such as the pterygopalatine and its pterygopalatine ganglion, the innervation of the muscles tensor veli palatini, levator veli palatini, rostral pharyngeal constrictors, pterygopharyngeus and palatopharyngeus as well as the lingual and pharyngeal branches of the cranial nerves (XII, IX respectively).9,10
In a very similar way to cattle and horses (anatomy books), when affected by ocular tumors and or even regional metastasis in the lymph nodes of the parotid region (infra auricular region), caused by direct compression or invasion of tumor cells, lead to clinical signs with neurological manifestations not visible externally, but with loss of palatal tension, difficulty swallowing, pharyngolaryngeal hyposensitivity, non-productive cough, aspiration pneumonia,7 also affecting the X and XI pairs as well as their regional branches (vagus and accessory, respectively), due to their anatomical location and proximity.10–12
In horses with athletic function, the most common injuries found on examination of the upper respiratory tract (oropharynx) during physical activity are collapse of the arytenoid cartilage, collapse of the vocal cord, palatal dysfunction, epiglottic disorders, anterior collapse of the palatopharyngeal arch, medial deviation of the epiglottic arytenoid folds.10,11,13,14
On the other hand, we can also find in athlete horses, examining their upper respiratory tract when at rest, epiglottic entrapment, arytenoid asymmetry, palatal dysfunction, nasopharyngeal collapse and some other pathologies very similar to the observation of the same region during movement,11,15 which raises questions about the cause and which anatomical structure is actually involved in the pathological process, in a highly complex location that is the equine oropharynx, therefore a decision is needed on what to do and how to treat the conflicting findings. a better understanding of the pathophysiological processes involved.11,16
For this study, female cattle were used, meat producers of the Nelore breed (02) and milk producers of the Jersey breed (03), with the presence of ocular tumors and some with metastasis in the regional lymph nodes, in the parotid region (infra auricular, Figure 1 and 2). where the main nerve bundles of the IX, X, XI and XII pairs of cranial nerves are located, as well as their branches and the innervation of the oropharyngeal muscles, as previously described. For the examination, the animals were kept in places with only mechanical restraint, without any use of sedatives or local anesthetics, where they were then examined with the aid of an endoscope. These same animals did not show any signs of pathological nasal discharge, chest auscultation and temperature were within physiological limits. Another precaution was to keep the animals in an environment protected from the sun or shaded, where the respiratory rate was kept as low as possible, therefore exempting the cattle from the study from heat stress and tachypnea, which could mask or induce some anomalous result, even without know what the findings would be in these chosen animals. In these animals chosen for the study, we cannot confirm the presence or absence of a metastatic lesion in the lung or in another parenchymal organ, as it was not researched and this was not the purpose of the experiment.
For the endoscopic examination, the right nostril was used as being the easiest to introduce the optical fiber and the animals were restrained using a halter and a "nasal ant" (Figure 3); all findings (photos and videos) were recorded on a memory card; the device used was a Full Color Screen Endoscope, with 5.5 mm in diameter, 5 m fiber length, we can say that the same protocol for endoscopy in the equine species.
In the animal with an ocular tumor and infra-auricular metastasis (Figure 1), we noticed the collapse of the palatopharyngeal arch, epiglottic entrapment, vascular increase of the left pharyngeal wall (corresponding side of the tumor), flaccidity of the rostral pharyngeal constrictor muscle, palatal flaccidity, where all the findings are consistent with the innervation corresponding to pairs IX, X and XII, where we cannot fail to mention the muscles that tense and elevate the soft palate, which in Figures 4 and 5a,b) shows its complete collapse.
Figures 4, 5(a, b), 6 We notice complete epiglottic entrapment, collapse of the palatal arch, vascular enlargement of the right pharyngeal wall -side of the tumor.
In no case were anomalous secretions found in the endoscopies performed on these animals, and their image recording of the turbinate region (Figure 6), showing no evidence of an infectious process (mucopurulent discharge) in the upper respiratory tract (nostrils and oropharynx), which we cannot rule out the same animals as being serologically positive for viral infections such as herpesvirus, viral bovine lymphoma, tuberculosis, as well as latent infections not yet manifested, as serological diagnosis was not performed as a selection criterion for animals, but rather the presence of tumor in the eye and/or its metastasis in the parotid or infra-auricular region, the same can be said regarding the diagnosis and type of tumor as well as its malignancy or not.
The complex innervation of the oropharyngeal region has its main origin in pairs IX, m.elevator veli palatini, m.constrictor pharyngeus rostral, m.pterigo pharyngeus and m.palatopharyngeus8–12 which may be of great importance in the equine species and still very little studied as the findings in the bovine species are very compatible with respiratory problems in horses with low performance, such as epiglottic entrapment and palatal collapse. In cattle with epiglottic entrapment (Figure 5a and 5b) we can say that the palatal tensor no longer maintains the aforementioned functional structure, but in cattle of little clinical importance or still little known, but in equine athletes of vital importance; the IX pair arises outside the central nervous system in the posterior region of the parotid gland, which explains the choice of cattle with tumors in this region, as well as the VII, VIII, X, XI and XII pairs, as well as all their respective branches that from what this experiment showed, based on the endoscopies performed, the lesions mainly in the muscles that tension the soft palate, dorsal palatal region, even with unilateral tumoration have a response, in the oropharyngeal muscles examined, bilaterally, but more accentuated on the corresponding side of the presence of the tumor (Figure 7).
Comparatively, we can make some parallels between the images of equine epiglottic entrapment (Figure 7–10), collapse of the palatal arch (Figure 7), low muscle tension of the soft palate (Figure 10), unilateral edema of the cuneiform recess (Figure 7) , in cattle with findings in horses with low performance with etiology in the upper portion of the airways or oropharynx, where the comparative study proved to be an interesting model for the study of the anatomical structures involved in the "sagging" of the soft tissues of the upper airways in horses and apparently of not well understood importance in cattle, where these processes reduce airflow in the respiratory tract. In horses, we can explain that this loss of palatal and oropharyngeal tone, in general, the regional lymph nodes are in contact with the pharyngeal branches of the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves and retropharyngeal lymphadenopathy (increased volume and infra-auricular tumoration, Figure 1,2) could result in compression and irritation,11 a very important fact for equine athletes but apparently not so important in cattle, as they, with the presence of large tumors, did not show signs of dyspnea, respiratory discomfort or even any form of postural compensation to improve breathing.
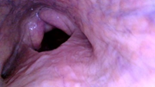
Figure 7 A collapse of the palatal arch, chondritis of the right cuneiform recess, epiglottic entrapment.
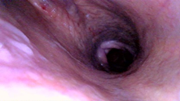
Figure 10 Bovine soft palatal collapse. These images show the similarity of problems in two species - cattle and horses.
With these endoscopic findings from these experiments in cattle, with tumors in the infra-auricular region mainly, we can say that the cranial nerves VI, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI and XII are not directly affected, but rather their very specific branches, based in the findings by videoendoscopy, which leads us to ask in horses what would be the causes of these probable injuries in these specific branches, causing specific injuries, altering the oropharynx in a very particular way, hindering the flow of air in the upper respiratory tract, decreasing athletic capacity, often irrecoverably.
What we can conclude is that endoscopy of the upper respiratory tract of cattle is rarely or practically not performed, given the cost of the device, given findings that often still represent injuries such as those found without clinical manifestations that deserve greater attention and treatment, but that in horses, in particular athletic horses, it is a very effective way of diagnosing, treating and predicting the main diseases of the respiratory tract and that in this specific case the use of cattle with ocular tumors or not and tumors in the infra-auricular region helps us to understand , at least in part, through anatomical comparison, some of the pathophysiology of diseases in the equine oropharynx.
None.
None.
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.

©2024 Vasconcellos. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.