International Journal of
eISSN: 2475-5559


Review Article Volume 3 Issue 3
Department of Mathematics, Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology, Bangladesh
Correspondence: Ishrat Zahan, Department of Mathematics, Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology, Bangladesh
Received: January 05, 2018 | Published: June 29, 2018
Citation: Nasrin IZR, Alim MA. MHD effect on conjugate heat transfer in a nanofluid filled rectangular enclosure. Int J Petrochem Sci Eng. 2018;3(3):114-123. DOI: 10.15406/ipcse.2018.03.00085
In the present research a numerical solution has been carried out to investigate the problem of magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) conjugate natural convection flow in a rectangular enclosure filled with copper water nanofluid. The relevant governing equations have been solved numerically by using finite element method of Galerkin weighted residual approach. The investigation uses a two dimensional rectangular enclosure with heat conducting vertical wall and uniform heat flux. The effect of Hartmann number on the parameter Rayleigh number, divider position and solid volume fraction of nano particles on the flow and temperature fields are examined for the range of Hartmann number (Ha) of 0 to 60. Parametric studies of the fluid flow and heat transfer performance of the enclosure for the pertinent parameters have also been performed. The numerical results have been provided in graphical form of streamlines and isotherms for various dimensionless parameters. It is found that the heat transfer rate increases with an increase of Rayleigh number and divider position but it decreases with an increase of the Hartmann number. It is also obtained that an increase of the solid volume fraction enhances the heat transfer performance. Finally, the implications of the above parameters have been depicted on the average Nusselt number of the fluid.
Keywords: MHD flow, conduction-convection heat transfer, nanofluid, finite element method
Conjugate heat transfer corresponds with the combination of heat transfer in solids and fluids. In solids, conduction often dominates whereas in fluids, convection usually dominates. Conjugate heat transfer is observed in many situations. For example, heat sinks are optimized to combine heat transfer by conduction in the heat sink with the convection in the surrounding fluid. The classical problem of natural convection in an enclosure has many engineering applications. In some practical cases such as the crystal growth in fluid, the metal casting, the fusion reactors and the geothermal energy extractions, the natural convection is under the influence of a magnetic field.
Nasrin and Alim1–7 investigated MHD effect on different shapes of geometries with natural, free and forced convection using water, air and water based different nanofluids. All these investigations showed there has been an increasing interest to understand the flow behavior and the heat transfer mechanism of enclosure that are filled with electrically conducting fluids and are in the influence of a magnetic field. The general finding of these studies is that the fluid within the enclosure, which is under the magnetic effects, experiences a Lorentz force. This force affects the buoyancy flow field and the heat transfer rate. Nanofluids which enhanced thermal characteristics have widely been examined to improve the heat transfer performance of many engineering applications.
Sarris et al.,8 presented a numerical study of unsteady two dimensional natural convection of an electrically conducting fluid in a laterally and volumetrically heated square cavity under the influence of a magnetic field. Ece & Byuk9examined the steady and laminar natural convection flow in the presence of a magnetic field in an inclined rectangular enclosure heated and cooled on adjacent walls. Dulikravich & Colaca10 they found that the convection heat transfer can be controlled by the magnetic field. A numerical investigation on the double-diffusion convective flow in a rectangular enclosure by Teamah11 also concluded that the heat and mass transfer mechanism and the flow characteristics inside the enclosure strongly depend on the strength of the magnetic field and the heat generation.
Sivasankaran & Ho12 numerically studied the effect of temperature dependent properties on the natural convection of water in a cavity under the influence of a magnetic field. They conclude that the heat transfer rate is influenced by the direction of the external magnetic field and decrease with an increase of the magnetic field. Mamun et al.,13 investigated MHD –conjugate heat transfer analysis for a vertical plate in presence of viscous dissipation and heat generation. Kahveci & Oztuna14 numerically simulated the natural convection flow in a laterally heated partitioned enclosure and concluded that the magnetic field and its direction affect the heat transfer performance of the enclosure. Mansour et al.,15 numerically investigated the unsteady magneto- hydrodynamic free convection in an inclined square cavity filled with a fluid-saturated porous medium and with internal heat generation.
Finite element analysis on the conjugate effect of joule heating and magnetohydrodynamics on double diffusion mixed convection in a horizontal channel with an open cavity was performed by Rahman et al.,16 Ghasemi et al.,17 studied magnetic field effect on natural convection in a nanofluid filled square enclosure. Nemati et al.18 studied magnetic field effects on natural convection flow of nanofluid in a rectangular cavity using the Lattice Boltzmann model. Effect of joule heating on natural convection in non-linearly heated square enclosure from right vertical wall was investigated by Oztop & Salem.19 They found that flow becomes weaker near the right corner of the cavity due to non-isothermal boundary condition. They also showed that both Hartmann number and joule parameter have significant effects on heat transfer and fluid flow. After this benchmark study, in present of magnetic field with heat flux boundary conditions in a nanofluid filled enclosure was studied by Sheikholeslami et al.20 Effect of wall conductivity and magnetic field on conjugate natural convection in a square enclosure was studied by Abdennacer Belazizia et al.21 In another study Seremet et al.,22 investigated MHD natural convection in an inclined wavy enclosure with corner heater. They focus on the effect of Hartmann number on the flow pattern and heat transfer inside the enclosure.
In addition, Sivaroj & Sheremet23 investigate MHD natural convection in an inclined porous cavity with a heat conducting solid body at the centre of the enclosure. They investigate the inclination angle of the magnetic field and the effect of Hartmann number on the flow and the thermal field in detail; they also concluded magnetic field reduces the convective heat transfer rate in the cavity. In recent time, Son & Park24 examined MHD natural convection in a rectangular enclosure with an insulated square block. They also found that heat transfer decrease with the increase of Hartmann number, they also conclude that insulated block contributes to enhance heat transfer rate for a certain range of the block size. Water based different types of naofluid have been used in both numerical as well as experimental research of25–27 in order to enhance heat transfer mechanism considering different types of numerical model and practical equipments.
As discussed earlier, the magnetic field results in the decrease of convective circulating flows within the enclosure filled with electrically conducting fluid, this in turn, results the reduction of heat transfer. The addition of nanoparticles to the fluid can improve its thermal performance and enhance the heat transfer mechanism in the enclosure. Up until now, no significant studies include MHD effect on conjugate heat transfer flow on the natural convection in nanofluid filled enclosure having finite thick wall. Hence the presence study numerically examines the effect of conjugate heat transfer on flow of nanofluid under the influence of horizontally applied magnetic field.
A two dimensional rectangular enclosure which is filled with copper water nanofluid is displayed in Figure 1. The nanofluid used in the study is assumed to be Newtonian, incompressible and laminar .The side of the enclosure is considered of width L and height H. On the left side of the enclosure a constant heat flux q is applied whereas a constant low temperature Tc applied on the right side of the cavity. The top and bottom walls are regarded as adiabatic. On the enclosure the left wall has a thickness of width , while the thickness of other walls are assumed zero. A magnetic field B0 applied horizontally normal to the side wall. A heat conducting divider is attached on the bottom wall of the cavity. The divider also supposed to be movable. It is also considered that both the base fluid and nanofluid are in thermal equilibrium and no slip condition is maintained among the walls.
The prevailing continuity, momentum and energy equations for the problem of viscous incompressible flow and the temperature distribution with the Boussinesq approximations inside the enclosure can be the present as follows:
For Fluid
Continuity Equation:
∂u∂x+∂v∂y= 0 ……. (1)
Momentum Equation
u ∂u∂x+v ∂u∂y= 1ρnf[−∂P∂x+μnf(∂2u∂x2+∂2u∂y2)] ………….(2)
u∂v∂x+v∂v∂y=1ρnf[−∂P∂y+μnf(∂2v∂x2+∂2v∂y2)+(ρβ)nf(T−Tc)− σnfB2°v] ………. (3)
Energy Equation:
u ∂T∂x+v ∂T∂y= αnf(∂2T∂x2+∂2T∂y2) hellip;………. (4)
For Solid:
∂2Tw∂x2+∂2Tw∂y2= 0 …………. (5)
Where,ρnf= (1−ϕ)ρf+ ϕρp is the effective density of the nanofluid
The thermal diffusivity of the nanofluid is,αnf= knf(ρCp)nf
The heat capacity of the nanofluid is,(ρCp)nf= (1−ϕ)(ρCp)f+ϕ(ρCp)p
The thermal expansion coefficient is,(ρβ)nf= (1−ϕ)(ρβ)f+ϕ(ρβ)p
the viscosity of the nanofluid is considered by Brinkmann model28μnf= μf(1−ϕ)2.5
The thermal conductivity is taken by Maxwell model 29 is,knf= kf[(kp+2kf)−2ϕ (kf−kp)(kp+2kf)+ϕ (kf−kp)]
The non-dimensional boundary conditions for the current problem are precise as follows:
T=Tc at x= L,0 ≤ y ≤ H
∂T∂y = 0 at y = 0, H,0≤ x ≤L
At the left side of thick wall:q = − kw ∂T∂X|w+h∞(TW−T∞)
At the fluid solid wall interfaces:kw ∂T∂x|w= knf∂T∂x|nf
u = v = 0, at x = 0, L, 0 ≤ y ≤ H
u = v= 0, at y=0, H,0≤x≤L
At the divider surface: u = v = 0
Nul=− knfkfH(Tw−Tc)∂T∂X|x=0.1 The average Nusselt number can be used in process for engineering design calculations to estimate the heat transfer from the heated surface. In order to estimate heat transfer enhancement, we have calculated the local Nusselt number and average Nusselt number at the thick wall (hot wall) as
. The average Nusselt number is given by,Nuav=H∫0Nul dy
In the present study the following dimensionless parameters are introduced to obtain the governing equation (1-5) in non-dimensional forms as follows:
X=xL,Y=yL, U= uLαf,V=vLαf,P=ˉpL2ρnfα2f,θ = T−TCΔT and ΔT=q''Lkf
Later than substituting these dimensionless variables into the equations the non-dimensional continuity, momentum and energy equations are written as follows:
For Fluid:
Continuity Equation:
∂U∂X + ∂V∂Y = 0 …………. (6)
Momentum Equations:
U∂U∂X +V ∂U∂Y= − ∂P∂X+μnfρnfαf(∂2U∂X2+∂2U∂Y2)………….. (7)
U∂V∂X+V ∂V∂y=−∂P∂Y+μnfρnfαf(∂2V∂X2+∂2V∂Y2)+(ρβ)nfρnfβfRaPrθ−Ha2Prv ………. (8)
Energy Equation:
U∂θ∂X +V ∂θ∂Y= αnfαf(∂2θ∂X2+∂2θ∂Y2)…………. (9)
For Solid:
∂2θw∂X2+∂2θw∂Y2 = 0 ………… (10)
The dimensionless parameter appearing in the Esq. (7)-(10) are as follows:
Hartmann number Ha = B°L√σnfρnfνf, B° is the magnitude of the magnetic field and σ is the electrical conductivity, Rayleigh numberRa = gβfL3ΔTνfαf , and Prandlt number,Pr = νfαf
The non dimensional boundary conditions under contemplation can be written as:
θ=0 at X= L, 0 ≤ Y ≤ H
∂θ∂Y=0 at Y=0, H,0 ≤ X ≤ L
q= − kwknf∂θ∂X|w+Hknfh∞θw=1 , At the left side of thick wall
At the fluid solid wall interfaces:∂θnf∂X=Kr ∂θw∂X,
U = V = 0, at X = 0, L,0 ≤ Y≤ H
U = V= 0, at Y = 0, H,0 ≤ X ≤ L
At the divider surface: U = V = 0. The local Nusselt number at the thick wall on the enclosure base on the non dimensional variable can be expressed as,Nul= −knfkf∂θ∂X|x=0.1 and the average Nusselt number at the left thick wall asNuav=−knfkfH∫0∂θ∂X dy
The set of non-dimensional governing equations along with boundary conditions for the considered problem solved numerically by the Galerkin finite element method.30,31 The explanation procedure is sustained until the steady state solution is reached. The finite element method is used to solve the Eqns. (2-5). The continuity equation is automatically fulfilled for large values of this constraint. Then the velocity components (U, V) and temperature (θ) are prolonged using a basis set. Three points Gaussian quadrature is used to evaluate the integrals in these equations. Then the non-linear residual equations are solved using Newton-Raphson method to determine the coefficients of the expansions. The convergence criterion for the solution procedure is defined as ,|ψn+1−ψn|≤10−4 where n is the number of iteration and ψ is a function of U, V and θ.
Grid generation
Meshing the complicated geometry make the finite element method a powerful technique to solve boundary value problems occurring in a range of engineering applications. Figure 2 shows the mesh configuration of present physical domain with triangular finite elements.
Grid independent test
To facilitate the proper grid size for this study, a grid independence test is conducted with five types of mesh Ra =106, Ha=30,ϕ = 0.05 ,l1= 0.4 ,Pr= 6.2,h∞= 100W/m2K , Kr =10 and W1= 0.1 through an rectangular enclosure.
In the present work, five different non-uniform grid systems with the following number of elements within the resolution field: 394, 533, 1058, 3258 and 13020 are examined. Figure 3 depicts the meshing information and grid refinement check of this computational domain. Table 1 shows the Nusselt quantities on the grid size. The scale of the average Nusselt number for 3258 elements shows a little difference with the results obtained for the other elements. Hence, considering the non-uniform grid system of 3258 elements is preferred for the computation. Since, it is noticed that no further improvement is found for higher values.
Thermo-physical properties
The thermo-physical properties of the nanofluid are taken from Aminossadati & Ghasemi32 and given in Table 2.
Model validation
The model validation is an essential part of a numerical investigation. The outcome of the present numerical procedure is benchmarked against the numerical results of Aminossadati & Ghasemi32 which are reported for natural convective cooling of a localized heat source at bottom of a nanofluid filled enclosure in a cavity having relatively low temperature at the top and vertical walls and Rahman & Alim33 which are reported for conjugate heat transfer in a lid-driven square enclosure having heat conducting circular cylinder placed at the center. The model validations have been depicted in the Figure 4(a)-(b). Excellent agreement is achieved, as illustrated in Figure 4(a) & Figure 4(b), between present results and the numerical results of Aminossadati & Ghasemi32 and Rahman & Alim33 respectively for both the streamlines and isotherms inside the cavity. These validations boost the confidence for the numerical procedure to carry on with the above stated objectives of the current investigation. So the accuracy and reliability of the present numerical solution could be justified by these Figures. So we do not need to incorporate any other validation.
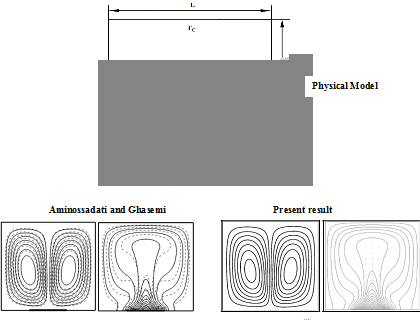
Figure 4A Model generation of Aminossadati and Ghasemi32
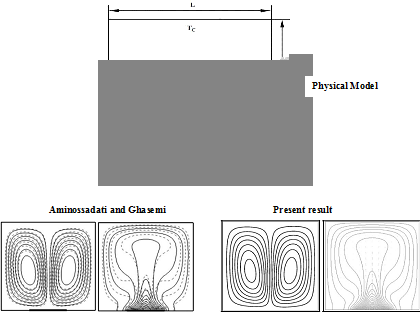
Figure 4B Model generation of Rahman and Alim33
Nodes |
6181 |
10062 |
13922 |
16181 |
28926 |
(elements) |
(394) |
(533) |
(1058) |
(3258) |
(13020) |
Nu (nanofluid) |
2.81063 |
2.81877 |
2.92582 |
3.01603 |
3.01899 |
Nu (base fluid) |
2.71233 |
2.72012 |
2.8481 |
2.95562 |
2.95577 |
Time [s] |
96.265 |
106.594 |
192.157 |
256.328 |
390.377 |
Table 1 Grid test at Ra =106, Ha=30 ϕ = 0.05 l1= 0.4 , Pr= 6.2,h∞= 100 W/m2K , Kr =10 and W1= 0.1
Physical properties |
Fluid phase (Water) |
Solid phase Copper (Cu) |
Cp(J/kgK) |
4179 |
385 |
r(kgm3) |
997.1 |
8933 |
k (W/mK) |
0.613 |
401 |
βx105 (k−1) |
21 |
1.67 |
Table 2 Thermo physical properties
In this section, the effects of MHD on conjugate natural convection heat transfer in a rectangular enclosure with heat conducting vertical wall and uniform heat flux are explored with solid volume fraction ϕ = 5% . Numerical results in terms of streamlines, isotherms for various Rayleigh number (Ra), position of divider(l1) and solid volume fraction (ϕ) of the nanoparticles on heat transfer and fluid flow inside the cavity have been studied for the range of Hartmann number (Ha) of 0 to 60. The ranges of Ra (l1) ,and,(ϕ) for this investigation vary from 104 to 106, 0.1 to 0.7 and 0 to 0.05 respectively. In addition, the values of the average Nusselt number (Nu) in the domain have been calculated for the above mentioned parameters. The working fluid is assigned a Prandtl number 6.2 throughout this investigation. The outcomes for the different cases are presented in the following sections.
Effect of Hartmann number on Rayleigh number
The effect of Hartmann number (Ha) on the streamlines and isotherms for the present configuration atϕ= 0.05, l1= 0.4 , Pr= 6.2,h∞= 100W/m2K , Kr =10 and W1= 0.1 are presented in Figures 5(a) & 5(b) respectively for three values of the Rayleigh number (Ra = 104,105,106) . The enclosure is filled with nanofluid, which has the solid volume fraction (ϕ= 0.05) . We here notice that the buoyancy driven clockwise circulating flows are evident for all values of the Rayleigh number (Ra ) and Hartmann number (Ha).We see that the strength of these circulating increases as the Rayleigh number (Ra) increases and decreases as the Hartmann number (Ha) increase. The result also shows a conducting dominating regime at low Rayleigh number with vertical isotherms and convective dominating regime at high Rayleigh number with horizontal isotherms. We also observe here that the strength of the flow circulation and the streamlines are affected by different values of Hartmann number. This effect is more prominent at Ra= 105 , where a rising in Hartmann number (Ha), the isotherm goes from horizontal to vertical trend. Since at Ra= 105 , wherever the convective flow field is not very strong and can be manipulate by the magnetic field. This is a sign of weaker convection flows at higher Hartmann number (Ha) owing to influence of magnetic field on the convective flows.
Effect of Hartmann number on divider position
The flow and temperature field due to various values of Hartmann number (Ha) on different divider positions is shown in Figures 6(a) & 6(b) on taking for Pr=6.2, Ra=106,h∞ =100 W/m2K, Kr =10 and W1= 0.1 with ϕ = 0.05 . It is observed that an increasing in divider position (l1) from the solid wall leads to increase the flow strength, but it retards the flow strength with the higher values of Hartmann number (Ha) due to the effect of magnetic field. When the distance between the solid wall and the divider increase the isotherms demonstrate more convective dominating mode, and its go to horizontal from vertical position. It is an indication of higher convection flow. But it reduces with the raise of Hartmann number at Ha=30, 60 due to the influence of higher effect of magnetic field.
Effect of Hartmann number on solid volume fractions
The effect of Hartmann number (Ha) on stream lines and isotherms for various values of solid volume fraction is depicted in Figures 7(a) & 7(b) with, Pr= 6.2, Kr =10 and. The addition of nanoparticles results in an increasing of the utmost stream function. The basis for this is that the accumulation of solid nanoparticles with higher thermal conductivity enhances the conduction heat transfer process at low Rayleigh number (Ra) and with the increase in Rayleigh number (Ra) due to mounting the strength of the buoyancy driven flow within the enclosure, we see stronger flow pattern. But in present of the Hartmann number (Ha) due to magnetic field the power of convective circulation decreases.
The mechanism is that the cavity that are filled with electrically conducting fluid, are in the influence of magnetic field. The judgment of these studies is that the fluid within the enclosure, which is under the magnetic effects, creates a Lorentz force, which affects the buoyancy flow field and reduces the flow velocities, which revolve affects in the heat transfer. The addition of nanoparticles results in an increasing of the maximum stream function in the absence of the magnetic field has been examined; however the strength of the convective circulation decreases when the magnetic field is applied. It is because the adding up of nano particle in the presence of the magnetic field, produce a weaker buoyancy driven circulation and make lower value of the stream functions. On the other hand it is notice that the enhance of the solid volume fraction (ϕ) the temperature gradient in the thick wall increases, and due to the restraint of the convection circulation flows by the influence of stronger magnetic field, it decreases as a Hartmann number (Ha) increases, which is noticed in the isotherm line, as it is found more clustered near the thick wall for the lower value of Hartmann number, this is an indication of higher convection flow at lower Hartmann number.
Average nusselt number
Figure 8(a), displays the effect of Hartmann number (Ha) on the average Nusselt number (Nu) along the hot wall at four different values of Rayleigh number,Ra= 104,105,106,107 , with ϕ= 0.05 . The result shows that due to the strong buoyancy flow the average Nusselt number (Nu) increases as the Rayleigh number increases and due to the suppression of the convective circulating flows by the magnetic fields, it decreases as the Hartmann number (Ha) increases. We also notice that for lower Rayleigh number (Ra) where the heat transfer is only due to conduction and in this case magnetic field does not have a considerable effect on the heat transfer performance, we see the change of average Nusselt number (Nu) remains same, but the average Nusselt number decreases faster when the Hartmann number (Ha) increase for higher value of Rayleigh number (Ra), where heat transfer occurs mainly for convection and the magnetic field can suppress the convective flow.
From Figure 8(b) it is found that the average Nusselt number (Nu) decreases mildly with increasing values of Hartmann number (Ha) at various position of divider (l1) .We see that in absence of Hartmann number (Ha=0), the heat transfer rate increases as the increase of distance between the solid wall and the divider but it reduces as the value of the Hartmann number (Ha) increase.
Finally, Figure 8(c) shows the effect of Hartmann number (Ha)on the average Nusselt number (Nu) along the hot wall of the enclosure at five different values of solid volume fraction ϕ = 0.0,0.01,0.02,0.03,0.04,0.05 withPr= 6.2, ,Ra = 106 ,l1 = 0.4 h∞= 100W/m2K Kr =10 and W1= 0.1 .This shows that the Hartmann number (Ha) plays a critical role in the study of the heat transfer performance of the enclosure at various value of solid volume fraction(ϕ) of nanoparticles. We see that the strength of the buoyancy flow and heat transfer rate increases as the solid volume fraction (ϕ) increases, however an increasing in Hartmann number (Ha) reduces the heat transfer rate. So we can control convective heat transfer by the manipulate magnetic field.
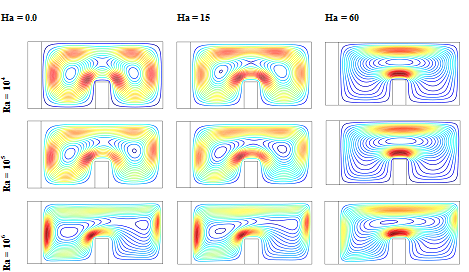
Figure 5AEffect of Hartmann number (Ha=0.0,15,60) on streamlines at various Rayleigh number for Pr=6.2, ϕ=0.05 , Ra = 106 , l1= 0.4 h∞= 100 W/m2K , Kr = 10 and W1 = 0.1 .
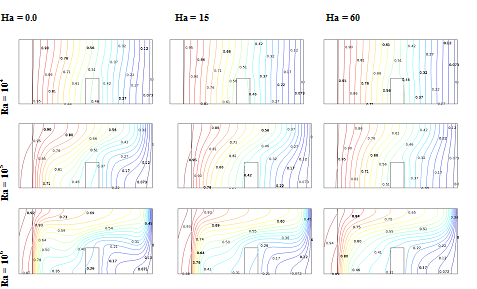
Figure 5B
Effect of Hartmann number (Ha=0.0,15,60) on isotherms at various Rayleigh number for Pr=6.2, ϕ=0.05 , Ra = 106 , l1= 0.4 h∞= 100 W/m2K , Kr = 10 and W1 = 0.1 .
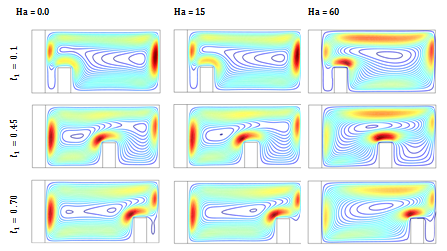
Figure 6AEffect of Hartmann number (Ha=0.0,15,60) on on streamlines at various divider position at various divider position for Pr=6.2, ϕ=0.05 , Ra = 106 , h∞= 100 W/m2K , Kr = 10 and W1 = 0.1 .
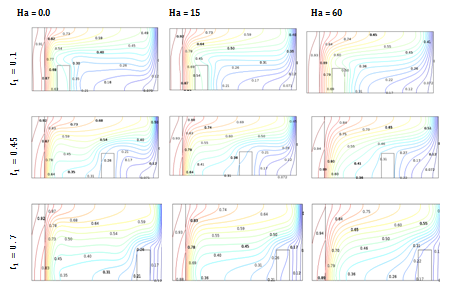
Figure 6B
Effect of Hartmann number (Ha=0.0,15,60) on isotherms at various divider position for Pr=6.2, ϕ=0.05 , Ra = 106 , h∞= 100 W/m2K , Kr = 10 and W1 = 0.1 .
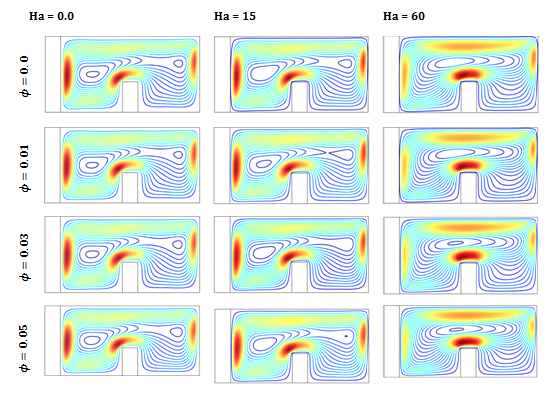
Figure 7A
Effect of Hartmann number (Ha=0.0,15,60) on on streamlines at various divider position at various Solid volume fraction for Pr = 6.2 , Ra = 106 , l1= 0.4 h∞= 100 W/m2K , Kr = 10 and W1 = 0.1 .
Numerical investigation on the effect of conjugate heat transfer in a thick walled cavity filled with copper-water nanofluid has been performed for heat transfer and fluid flow by solving steady state two dimensional Naviers-Stokes equations, energy equation and continuity equation. Based on the outcome of the numerical investigation, precise conclusions released some vital point such as:
None.
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.

©2018 Nasrin, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.