International Journal of
eISSN: 2574-9889


Clinical Paper Volume 2 Issue 3
Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Royal Brisbane and Women's Hospital, Australia
Correspondence: HC Cheng, Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Royal Brisbane and Women's Hospital, Queensland, Australia
Received: April 20, 2017 | Published: May 4, 2017
Citation: Cheng HC. Expect the unexpected - a case of traumatic right sided diaphragmatic hernia in third trimester and literature review. Int J Pregn & Chi Birth. 2017;2(3):67-69. DOI: 10.15406/ipcb.2017.02.00021
Diaphragmatic hernia (DH) during pregnancy is rare with only 30 cases reported worldwide in the last 50years. The mortality rate is as high as 50%. Low level of suspicion is required to make the diagnosis. This is the first documented case report of a third trimester maternal DH in Queensland, Australia. DH diagnosis and decision of treatment in the obstetric population can be difficult and challenging. A multidisciplinary team is required to optimise maternal and fetal outcome.
DH, diaphragmatic hernia; AXR, a plain abdominal radiograph; CXR, chest radiograph; NGT, nasogastric tube; CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging
We encountered a low risk antennae presented with an incarcerated and non-strangulated diaphragmatic hernia (DH) in our institution in 2017. Case reports of DH published in the English medium were identified via Medline and evaluated. This article described the statistics, presentation, investigation and recommended treatment of DH from current literature.
The case patient was a 41-year-old primigravida who was at 38 weeks plus 4 days of gestation. She presented to the obstetric assessment unit in the evening with one hour history of severe epigastria pain which was associated with nausea and vomiting after food intake. On further questioning, she tripped and fell off a 15cm stair two hours prior to the onset of epigastria pain. She landed on her buttocks and denied any abdominal contact with the ground or head injury. Her husband was also at the scene, confirmed her mode of injury. The epigastria pain which started only two hours after the fall was described as constant in nature with no radiation to the back. No chest pain or dyspnea was reported. Normal fetal movement was felt and there was no lower abdominal pain or vaginal bleeding throughout the event.
Case patienthadan uncomplicated antenatal course until a normally grown frank breech fetus was formally diagnosed at 36 weeks with ultrasound. External cephalic version was offered by her obstetric team but was declined. An elective caesarean section was scheduled at 39 weeks. She sustained a Weber a right ankle fracture nine years ago on an aversion injury; otherwise her medical and surgical history is largely insignificant. In particular, no congenital diaphragmatic defect or abdominal surgery was evident. A BMI of 19 was recorded.
On examination, her vital signs were stable (blood pressure: 108/84, heart rate 95, respiratory rate: 16bpm, oxygen saturation: 98% on room air, a febrile). She did not appear to be jaundiced. Epigastria tenderness was localised and reproducible on deep palpation. The abdomen was otherwise soft and unremarkable. In particular, the fundal height was 38cm and the uterus was non-tender on palpation. The fetus was in breech presentation. Murphy’s sign, McBurney’s point tenderness and renal angle tenderness could not be elicited. Chest examination was normal with equal and adequate bilateral air entry. Fetal wellbeing was confirmed by cardiotocography which showed a baseline of 125 with good variability and accelerations throughout the entire duration of the recording. Her full blood count was normal with a white cell count of 14x109/L and a normal lipase, liver functions and CRP. Urine analysis showed no sign of urinary tract infection. Bedside ultrasound performed by senior obstetrician confirmed fetal wellbeing and no placental abruption or separation.
The epigastria pain was only temporarily relieved with two repeat doses of 10mg of intramuscular morphine and nausea was treated by multiple doses of intravenous metoclopramide. The cause of the pain was unclear at this stage despite being reviewed by another senior obstetrician the next morning. A decision was made to deliver the baby via caesarean section two days earlier than the elective date. The operation was successful and a 3.5kg live female baby was born in good condition. No anatomical or intestinal abnormality was noted by the operating obstetrician.
Case patient developed two episodes of large (200ml) green vomit 24hours after the caesarean section. On review, her epigastria pain improved after the delivery but nausea remained. The vomit was brought on by food. Bowel sound was absent on abdominal examination. The abdomen was generally soft and appropriately tender to what one would expect soon after a caesarean operation. A plain abdominal radiograph (AXR) revealed dilated loops of small bowel indicating post-operative ileus. Input from the general surgeons was sought on day two post-op which recommended nasogastric tube (NGT) decompression with free drainage. Chest radiograph (CXR) was ordered to confirm correct position of the NGT. Interestingly, the NGT still remained coiled in the oesophagus on the second CXR see Figure 1 after being repositioned. Despite of this, the NGT was draining stomach content freely and a decision was made not to subject the functional NGT from further repositioning. Case patient’s symptoms did not improve after 24 hours of drainage, therefore a repeat AXR with gastrograffin study see Figure 2 was organised which suggested the possibility of a small bowel obstruction. An abdominal computed tomography (CT) was arranged to confirm and locate the small bowel obstruction. It showed the presence of abdominal content in the right sided chest through a diaphragmatic defect see Figure 3. A right sided non-strangulated diagrammatic hernia was diagnosed. The general surgeons performed an emergency laparoscopic right sided diaphragmatic hernia repair and returned the incarcerated bowel to the abdomen. Upon direct visualisation, 20cm of terminal ileum was herniated through a 6cm defect on the right diaphragm. The defect was approximated and sutured with four interrupted size 0 monofilament nylon sutures. The case patient recovered well after the operation and was discharged home 5 days after with a healthy baby girl.
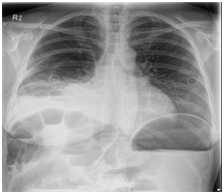
Figure 1 repeat CXR which showed coiling of NGT in the oesophagus despite reposition was attempted. Pleural effusion is also seen in the right lung base.
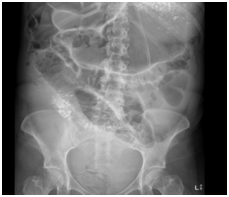
Figure 2 AXR with Gastrograffin study - The stomach which is significantly distended. Small amounts of ingested contrast are seen in proximal small bowel loops. No contrast is seen in the colon. The features suggest a mechanical mid to distal small bowel obstruction.
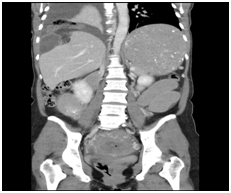
Figure 3 CT abdomen - There is a diaphragmatic hernia on the right containing loops of small bowel and associated with a right pleural effusion. It is associated with a small bowel obstruction. The colon is not distended. The stomach is grossly distended. Features are consistent with a right sided diaphragmatic hernia with small bowel obstruction.
Rarity
Diagrammatic hernia (DH) is a rare clinical complication during pregnancy. A literature search showed that only 36 documented cases of DH was reported between 1959 and 2016 worldwide. Only one case of DH was recorded in Australia.1 Despite its rarity, this condition can be highly lethal due to common misdiagnosis which leads to the delayed administration of treatment. A maternal and fetal mortality rate is reported to be as high as 35-50%.2 {Chen, 2011 #2}{Chen, 2011 #2} DH can be divided into three types3 congenital, acquired and traumatic. Congenital DH results from faulty embryologic development causing a weakness on the diaphragm. Acquired DH occurs when there is an anatomical weakness (i.e. oesophageal hiatus, aortic openings, caval openings) allowing displacement of abdominal content.2 Traumatic DH develops when there is a direct or indirect mechanical trauma to the diaphragm as in our case. We believe that the patient in our case sustained a traumatic DH during the fall, with the breech baby’s head impacting firmly on the diaphragm. From the available literature, we derived that the occurrence of these three types of DH are: congenital (30%), traumatic (30%) and acquired (40%).
Presentation
The most common symptoms of DH are nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain and dyspnoea. However, it can also be asymptomatic when the incarcerated bowel is small and not obstructed. The manifestation of DH is non-specific and they can also occur in other more common conditions in pregnancy highlighting a diagnostic challenge. 60% of patient with DH experienced nausea and vomiting which is commonly confused with hyper emesis gravidum2,4 Severe abdominal pain is encountered in 57% of patient with DH during pregnancy alongside with nausea consistent with signs of intestinal obstruction.2 The abdominal pain caused by a DH can be described as colicky in nature and ranges from mild to severe and constant or intermittent pain. DH usually protruded into the left thoracic cavity since the right diaphragm is protected by the liver. This causes the pain to usually manifest in the epigastrium or left upper quadrant. Pancreatitis, biliary colic and appendicitis during pregnancy can also produce pain of similar description confounding the clinical picture.5,6 Dyspnea was also experienced in 57% of patients with DH due to the reduction of lung capacity by herniated bowel content.2 In particular, 50% of patients who’s DH became symptomatic in the postpartum period developed respiratory distress.2 Fortunately, this did not happen in out patient’s case. Pneumonia, asthma, amniotic embolism and heart failure can also cause dyspnea during pregnancy. Other reported non-specific symptoms include shoulder pain (30%), heart palpation (23%) and chest pain (13%).2
Investigation
Diagnosis of DH requires radiological imaging combined with thorough history taking and physical examinations. In our case, there was less concern of radiation exposure as the fetus was already born at the time of performing the radiological studies. It can be an issue in women who are still pregnant, especially during the early gestation. Plain chest and abdominal radiography is the preferred modality with low dose of radiation (0.12mSv) and is generally regarded as safe for pregnancy.7 However, Radiography may not lead the right diagnosis as in our case, due to the limited view of abdominal organs unless the hernia volume is significant in the thoracic cavity. Although CT and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provide a better and more detailed study, CT’s radiation exposure is considered higher than plain radiography. MRI is expensive and may not be immediately available in some facilities. Full blood count, liver and renal function tests are usually unremarkable until a ruptured necrotic intestinal obstruction is manifested.
Treatment
Surgical repositioning of herniated intestinal content and repair of diaphragmatic defect is necessary and is the only effective treatment. Abdominal, thoracic and combined approach had been performed and documented in literature with equal results.1 Anaesthesia during the repair needs particular consideration and adjustment due to reduced lung capacity.8,9
Among the pregnant population with DH, the time to operate is dependent on the gestation and the severity of the symptoms. If the hernia is diagnosed during first and second trimester, it is recommended the defect to be repaired in the second trimester when organogenesis is complete. Also, this can prevent further displacement of bowel content into the thoracic cavity, as a result of an enlarging gravid uterus, causing hernia strangulation or rupture.3 Current literature suggested that pregnant women with a repaired DH can undergo labour spontaneously as uterine contractions alone are not likely to break the repair.10 Instrumental second stage, however, is advised to prevent women from active pushing and thereby increasing intra-abdominal pressure which may break the repair subsequently.10 DH repair should not be attempted after the third trimester as the abdominal viscera are displaced from their normal location making the hernia closure more challenging and more likely to fail.3 Women with a DH detected in the third trimester should therefore avoid labour and be offered a caesarean section at term followed by a surgical DH repair when fetal lung maturation is achieved. However, when the women develop signs of obstruction or strangulation, surgical repair should be performed urgently regardless of gestation to prevent further lethal complications.3,10 The major cause of mortality from DH, as demonstrated in literature, are intestinal perforations, cardiogenic shock and respiratory distress.11
Although DH is a rare complication in pregnancy, it has a high mortality rate. Low index of suspicion is required to detect its presence. Diagnosis is challenging due to its non-specific symptoms which overlap with other diseases in pregnancy. Fetal wellbeing and uterine displacement of abdominal organs pose considerable challenges to the management. A multidisciplinary team consisting of obstetricians, general surgeons, anaesthetists and nursing staff is definitely required in the management of DH.
None.
Author declares that there is no conflict of interest.

©2017 Cheng. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.