eISSN: 2641-936X


Editorial Volume 1 Issue 1
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Bits Pilani, India
Correspondence: Mahesh Angira, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Bits Pilani-333031, India
Received: June 19, 2017 | Published: June 29, 2017
Citation: Angira M. RF-MEMS: a promising technology for future reconfigurable wireless systems. Electric Electron Tech Open Acc J. 2017;1(1):13-14. DOI: 10.15406/eetoaj.2017.01.00003
In recent years, RF-MEMS have been identified as the most significant enabling technology in developing the reconfigurable wireless systems. New wireless standards are coming up which require replacement of bulky, expensive and off-chip passive RF components with RF-MEMS technology based devices having small size, high linearity, low power consumption and multi-band tunability.1,2 In general, the outstanding performance of the RF-MEMS is due to the air gap between the active elements and lossy substrate, use of high conductivity metals and integration compatibility with existing IC fabrication technologies. Figure 1 shows the schematic diagram of a multi-band wireless transceiver.3 The block diagram contains a good number of off-chip, High-Q components such as RF filters, including image rejection filters, tunable capacitors, High-Q inductors, resonators, tunable filters, oscillators, and switches for transmitter/receiver selection. Despite many years of research, RFIC technologies were not able to deliver the high performance and on chip solution for the above cited devices. RF-MEMS technology has paved the way for the development of these devices. In addition, RF-MEMS devices can be reconfigurable to the different wireless standards to be used and thus would be suitable for the multi-band operation.
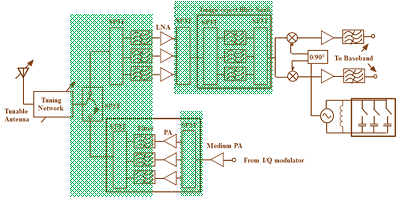
Figure 1 Block diagram of a multi-band wireless transceiver. The components in the colored blocks can be implemented through RF-MEMS Technology.
One of the most important components in any wireless transceiver is a switch. It consumes a significant part of the power budget. Switches are used to select the electrical signal, e.g. the incoming and the outgoing signal of an antenna, or to reconfigure a sub-system. Typical applications include the switching of filter banks, tuning of filters, switching of delay lines in phase-shifters, impedance matching, switch matrix and in reconfigurable antenna. RF MEMS SPST switches consume virtually zero dc power consumption and have excellent RF performance. RF-MEMS SPST also serves as the building block for SPDT and more complex SPNTs. The multi-band reconfigurable SPST, SPDT and SPNTs has been presented in the literature.4-7 Furthermore, reconfigurable phase shifters, true time delay lines for electronically steered antennas, High-Q variable inductors and capacitors, tunable filters have also been demonstrated through the RF-MEMS technology.1,3,8,9 In future, integration of RF-MEMS technology with solid state technology can lead to develop a high performance single chip reconfigurable wireless transceiver.
None.
The author declares no conflict of interest.

©2017 Angira. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.