eISSN: 2576-4543


Review Article Volume 2 Issue 5
1Herschelstrasse 33, 90443 Nuernberg, Germany
2Head of Laboratory Biochemistry and Toxicology, Kiev Regional p/n Hospital, Kiev, Ukraine
Correspondence: Ponizovskiy MR, Head of Laboratory Biochemistry and Toxicology, Kiev Regional p/n Hospital, Kiev, Ukraine, Tel 4991 1653 7811
Received: December 21, 2017 | Published: October 3, 2018
Citation: Ponizovskiy MR. The role solar thermonuclear synthesis in forming earth living organisms and in influencing on human organism. Phys Astron Int J. 2018;2(5):425-437. DOI: 10.15406/paij.2018.02.00120
There were estimated Solar processes from the point of view of thermodynamics. The stable states of solar processes were considered from point of view of thermodynamics. Also the influences of Solar processes on both non living Nature and living organisms were considered as consequences of solar thermonuclear synthesis. There were described mutual influences between Environment and the existence of life on the Earth. Hence it was considered influences of solar thermonuclear synthesis on stability Internal Energy of open non equilibrium non linear thermodynamic systems of earth organisms, especially human organisms. The influences Solar rays on human skin induce biosynthesis Vitamin D in a human organism. Besides there was described interdependence between mechanisms maintenance stability both open thermodynamic systems of earth organisms including human organisms and open thermodynamic system of Atmosphere. Also there were described the role of solar processes in forming both non–living maters and living organisms. Furthermore there were described influences of solar radiation on germination living prokaryotic organisms which exert as germination different insects in spring as well as different viruses. Besides it was described the dependence eukaryotic organisms on lives of other organisms in condition Solar system influences.
Keywords: Solar thermonuclear synthesis, nuclear fusion energy, fission energy, carbon–nitrogen–oxygen cycle [CNO], proton–proton cycle
Influences of Environment on life activity and health of a human organism are observed as by medical practice as well as by each individual person. There are mutual influences between Environment and the existence of life on the Earth. These mutual influences cause as stability open non equilibrium non linear thermodynamic system of a human organism and other organisms as well as stability thermodynamic system of Atmosphere as an Environment of organisms.1,2 The processes in Environment of organisms how Ionosphere, Solar System, and even Galaxy are crucial productive factors for exertion of the dynamical interactions between Open non equilibrium non linear thermodynamic system of organisms and open thermodynamic system of Atmosphere.2 The mutual exchanges with energy and substances between open non equilibrium non linear thermodynamic systems of organisms including human organisms and thermodynamic system of Atmosphere cause as stability Internal Energy of human organisms and other organisms as well as stability Internal Energy of Atmosphere, corresponding to the first law of thermodynamics and been proved by famous Prigogine theorem.2 There were displayed the mechanisms of both stability Internal Energy of organisms and stability Internal Energy of Atmosphere in which organisms’ States link up with State of Atmosphere via flow energy and substances between Atmosphere and organisms exhibiting Stationary State of life on Earth.2 These mutual exchanges energy between open non equilibrium non linear thermodynamic system of organisms and thermodynamic system of Atmosphere are subjected to Sun influence via Solar System activity and even Galaxy influences. The exchanges of Energy between organisms including human organisms, Atmosphere and Sun of Solar System were displayed in the mechanisms of preservations stability Internal Energy of these thermodynamic systems. Besides there were exhibited dependence regulatory mechanism of maintenance stability Internal Energy and Internal Medium human organisms’ metabolisms upon these relationships.2 Also these relationships are the indicators of ineradicable flowing energy which cause stability Internal Energy of these systems. Just this ineradicable flowing energy give possibility to identify ineradicable flow energy with souls of living organisms which acknowledge the immortality of the earth alive souls between life and death of the organisms.2
The dissipation solar energy causes thermal energy with light ray. It is the formula of the second law thermodynamics: ; [ –entropy, –heat in calorie, –Kelvin temperature], i.e. increase of heat ( ) defines increase of Entropy ( ). Thus Entropy reflects measure dissipation energy to unit of Kelvin temperature in Solar System.
Therefore mechanism stability of Internal Energy thermodynamic system Sun must reflect balance between dissipation energy and absorption energy via accumulation energy into substance having certain mass, according Einstein formula: [E–energy,m–mass,c–the speed of light] and according the first law of thermodynamics.
Just there occurs reversible change of heat ( ) for prevention increase entropy (S) into Sun corresponding to following formulas of the second law of thermodynamics:
Thus the complete reversible change of heat ( ) leads to, but the non–complete reversible change of heat ( ) leads to .
The reversible change of heat ( ) occurs via solar thermonuclear synthesis. There occur processes of nuclear fusion and processes fission via dissipation solar energy. However balance between fission and fusion promotes stability of Internal Energy thermodynamic system Sun. Just both processes fusion and fission occur in core of Sun simultaneously. The proton–proton chain reaction starts at temperatures about , making initial dominant fusion smaller nucleus mechanism of Hydrogen and then Helium.3 Then it occurs nuclear fusion of larger nucleus in which two or more atomic nuclei come close enough to form one or more different atomic particles of nuclei and subatomic particles (neutrons and/or protons). The difference in mass between the products and reactants is manifested as the release of large amounts of energy. The difference in mass arises due to the difference in binding energy between the atomic particles of nuclei causing transmission energy into mass according to Einstein formula [ ]. Dissipation solar energy creates highest solar temperature about which displays increase Entropy (S) corresponding to data of second law of thermodynamics, i.e. increase fission versus nuclear fusion. However dissipation solar energy creates also light rays always simultaneously with highest solar temperature. Therefore we assume that nuclear fusion occurs due to either light rays separation operate or together with highest solar temperature. Just it’s known the role of light rays in growth plants and insects (beetles, fly etc.) at spring and even in artificial condition of greenhouse where light rays promote synthetic processes of cellular cycle with haploid and diploid genomes for growth plants and insects. Besides solar light ray influence on a human organism via synthesis of the necessary substances of an organism, e.g. vitamin D3 due to solar ultraviolet rays operation for prevention rickets. All of that occur in the complete reversible change of heat in Sun when leads to . But maybe the non–complete reversible change of heat happens more often when leads to . We suppose that Sun receives the energy for replenishment losing energy from accumulated energy in Solar Planets including Earth or maybe from Cosmic Dark Material.
The main reaction within the core of the Sun is the process of proton–proton cycle in which proton–proton chain fusion occur by very great pressures and enough high temperatures about .3–5 Just corresponding to the proton–proton chain reaction, hydrogen nuclei are converted to helium nuclei through number of intermediates. The mass–to–energy conversion is described by Einstein's famous equation: . The energy created by the fusion processes within the core of the Sun exerts an outward pressure. The outward pressure from the fusion reactions keeps Sun from collapsing. The inward pressure, that keeps Sun from exploding, is the gravitationalattraction of the gas mantle surrounding the core of Sun. Just combination outward pressure with inward pressure causes consumption energy in condition of enough high temperatures about for the fusion processes of thermonuclear synthesis versus the fission processes of dissipation solar energy.3–5 Besides proton–proton cycle also CNO cycle [carbon–nitrogen–oxygen cycle] provides reaction in which hydrogen is converted into helium.3–7 However CNO cycle is a catalytic cycle. In the CNO cycle, four fuse, using carbon, nitrogen and oxygen isotopes as catalysts, to produce one alpha particle, two positrons and two electron neutrinos.3–7 Although there are various pathways and catalysts involved in the CNO cycles, all these cycles have the same net result: The positrons will almost instantly annihilate with electrons, releasing energy in the form of gamma rays.3–8 The neutrinos escape from the star carrying away some energy. One nucleus goes to become carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen isotopes through a number of transformations in an endless loop. But as compared with proton–proton cycle, CNO chain starts at 15×106 ⁰Kapproximately, and its production of energy rises much more rapidly with increasing temperatures.3–10 At approximately 17×106 ⁰K, the CNO cycle starts becoming the dominant source of energy.3–10 Sun has a core temperature of around 15.7×106 ⁰K. Just the main production nuclei are born in the CNO cycle in Sun.3–10 Fusion reactions have an energy density many times greater than nuclear fission. These reactions produce far greater energy per unit of mass even though individual fission reactions are generally much more energetic than individual fusion ones, which are themselves millions of times more energetic than any chemical reactions. Only direct conversion of "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mass-energy_equivalence">mass into energy, such as that caused by the annihilation collision of matter and antimatter, is more energetic per unit of mass than nuclear fusion.3–10 The fusion processes release energy, which produces atoms in nucleus lighter than iron–56 or nickel–62. But elements with nucleus heavier than iron–56 or nickel–62 absorb energy and accumulate energy of solar processes. These elements have the smallest mass per nucleon and the largest binding energy per nucleon, respectively. Fusion of light elements toward these heavy elements releases energy via resulting of an exothermic process, while a fusion producing nuclei heavier than these elements, result in energy retained by the forming nucleons, and these resulting reaction is endothermic. The opposite is true for the reverse process,nuclear fission. This means that the lighter elements, such as hydrogen and helium, are in general more fusibility; while the heavier elements, such as uranium and plutonium, are more fissionable. Thus we suppose that most of elements with nucleus heavier than iron–56 or nickel–62 are gotten into creating Planet’s minerals. Besides there are the regular connections between solar energy processes and energy processes in core of Earth which cause as earthquakes, tsunami, volcanic explosion, hurricane etc. All of it maintains solar energy processes into core of Earth. Also solar thermonuclear synthesis via fusion processes in proton–proton cycle and CNO cycle forms Ionosphere and Atmosphere. Ionosphere consists of electrons and electrically charged atoms and molecules, i.e. ions, which transfer supplementary energy into Atmosphere and Earth causing exchanges with energy and substances between Atmosphere and Earth. Ultraviolet, X–ray and shorter wavelengths of solar radiation are ionizing, since photons at these frequencies contain sufficient energy to dislodge an electron from a neutral gas atommolecule upon absorption. In this process the light electrons obtain a high velocity so that the temperature of the created electronic gas is much higher of thousand ⁰K than the one of ions and neutral atoms. The reverse process to ionization is recombination, in which a free electron is "captured" by a positive ion. Recombination occurs spontaneously, and causes the emission of a photon carrying away the energy produced upon recombination. As gas density increases at lower altitudes, the recombination process prevails, since the electronic gas and ions are closer together.3–14 The balance between these two processes determines the quantity of ionization presentation. All of these phenomena occur simultaneously with disturbances such as solar flares and the associated release of charged particles into the solar windwhich reaches the Earth and interacts with its geomagnetic field.3–14
There occurs maintenance stability Internal Energy via balance fusion and fission processes in Sun causing balance thermonuclear synthesis in solar core and dissipation thermal energy into Environment. The pressures and temperatures in solar core are high enough in order to force fusion, which is nuclear reactions whereby some nuclei merge to make others which form units energy which are distributed via energy quanta corresponding to measure of Reduced Plank Constant [ ] value or also Planck quanta value [J–joule, s–seconds] (15, 16). Besides these particles of energy quanta are formed simultaneously as synthesized nuclear particles via concentration energy according known Einstein formula [ and ] as well as also dissipation radial thermal energy which both cause solar radial waves.15,16 This radial energy reflects as fusion processes of solar thermonuclear synthesis as well as fission processes of solar nuclear thermal energy.15,16 Just dissipation very high temperature of thermal energy into environment cause the waves of radial energy which consist of far higher than wavelength of infrared radiation and of far lower than wavelength of ultraviolet radiation which induce as positive particles due to positive quanta of energy as well as negative quanta of energy. The some waves of radial energy carry the mechanism of inducing synthesis positive particles in nuclei of atoms. The some waves of radial energy carry the mechanism of inducing synthesis negative particles in electron layers [K, L, M, N, O] and electron orbits [s, p, d, f] as main quantum numbers and orbital quantum numbers, filling orbital quantum number of synthesized atoms causing by corresponding to waves of radial negative energy. Just the waves of radial negative energy carry as high enough thermal energy (Q) due to energy of infrared radiation and far higher than infrared radiation as well as different negative wavelength energy due to ultraviolet radiation and far lower than ultraviolet radiation. Both of high enough thermal energy (Q) and different wavelength energy stimulate photochemical reactions forming simple inorganic ions and molecules as H2, O–2 and O2, N2, CO2 etc. in Ionosphere and Atmosphere.17 Besides the waves of radial negative photons knock out electrons from semiconducting photoelectric cell realizing photoelectric effect of electric current. Just differential of thermal energy is equaled differential of entropy multiply Kelvin temperature, corresponding to second law of thermodynamics: ; or [ –thermal reversible energy;Q – thermal energy;T –Kelvin temperature]. Boltzmann’s formula has tied Entropy ( ) with thermodynamic probability ( ): [Boltzmann constant ]. Thus Entropy determines that the each microstate of thermodynamic system (atom) is realized via great quantity microstates of thermodynamic systems (atoms). Therefore combination high enough thermal energy (Q) and different negative wavelength of radial energy forms different simple inorganic ions and molecules being subjected to thermodynamic probability of Boltzmann theory. The some elements are formed in Planet–Earth as Silicon (Si) existing via Silicon dioxide (SiO2) which creates terrestrial pressure and high temperature at the depth of the Earth which promote also forming minerals how coal anthracite, petroleum and so on. Earth core gravitation with pressure generates fluid of very high temperature causing sometimes volcanic explosion. Also solar gravitation influences on Planet–Earth especially on Earth core that exerts sometimes orogenesis. Being subjected to thermodynamic probability of Boltzmann theory, combination high enough thermal energy (Q) and D different negative wavelength energy of light waves radial negative energy forms different combinations covalent bonds and ionic bonds in organic molecules in living organisms. It is known the main role of Sunlights in synthesis vitamin (ergocalciferol). Just energy ultraviolet rays of wavelength 290–315nm promote transitions: 7–dehydrocholesterol into previtamin D1; previtamin D1 into previtamin D3; previtamin D3 into vitamin D2.18 Also the waves of radial energy ultraviolet rays especially exert biologic life at spring [different beetles, May bugs, fly and the other insects and even viruses which can not live outside of living organisms]. Furthermore it is known that ultraviolet rays of wavelength lower than 200nm can cause oncogenesis.18 It is meant, that ultraviolet rays promote proliferative processes of biologic life.
Being carriers of solar energy via reflecting solar balance fusion & fission, the solar radiation of positive and negative energy cause as complication of matters as well as reduction of matters corresponding to increase Entropy and decrease Entropy according second law of thermodynamics. Surely balance fusion & fission of radial energy induces forming balance positive particles & negative particles and balance positive ions & negative ions and so on. However also surely balance fusion & fission of radial energy induces balance decreased Entropy & increased Enropy. Distribution balance decreased Entropy & increased Entropy exert compound biochemical and biophysical processes which stimulate production compound inorganic molecules and organic molecules corresponding to quants of radial energy according Boltzmann theory and Einstein formula (see above). Thus these influences of solar radial energy generate forming solid Planet–Earth and gaseous medium of Atmosphere with produced maters. The maintenance stability Internal Energy and Internal Medium of Atmosphere and Planet–Earth promotes germination living organisms in order to make them the open thermodynamic systems. Just exchanges by energy and substances between thermodynamic systems of living organisms and thermodynamic system Atmosphere promote maintenance stability Internal Energy both open thermodynamic system Atmosphere and Open thermodynamic systems of living organisms on Planet–Earth according famous Prigogine theorem (see below). Thus it’s meant that balance fusion & fission of quantile radial energy induces processes germination living matters and influence also on processes reproduction as prokaryote as well as eukaryotic organisms. The processes of germination simple prokaryotic organisms as viruses and bacteria occur due to permanent influences of solar radiation’s energy. These influences solar radial energy, which cause oscillations balance decreased Entropy & increased Entropy, promote as anti–apoptotic processes in living organisms as well as apoptotic processes in living organisms. Just viruses are smallest infectious agents which replicate only inside the livingcells of other organisms. Viral particles, also known as virions, consist of two or three parts:19 1) The genetic material made from either DNA or RNA, long molecules which carry genetic information; 2) The protein coat, called the capsid, which surrounds and protects the genetic material; and 3) In some cases, an envelope of lipids that surrounds the protein coat when they are outside a cell. Just there are different opinions whether viruses are a form of life, or organic structures that interact with living organisms. Although they have genes, they do not have a cellular structure, which is often seen as the basic unit of life.19 Viruses do not have their own metabolism, and require a host cell to make new products. They therefore cannot naturally reproduce outside a host cell–although bacterial species such as and chlamydia are considered living organisms despite the same limitation.19 Accepted forms of viral life use cell division to reproduce, whereas viruses spontaneously assemble within cells.19 Virus self–assembly locates within host cells.19 Thus viruses can be defined as pathologic promotor of all living organisms which are produced by solar fusion radial energy permanently versus solar radial energy of balance fusion & fission carrying energy for development living organisms. Therefore viruses can infect all types of life forms, from human organisms, animals and plantsto microorganisms, including bacteria –bacteriophage. Taking into account developing viruses only within alive cells, it should consider that initial viruses generations occur due to broken cellular metabolic mechanism causing in weak point of cellular metabolism either by harmful factors of outer environment (human factors, technological factors, smoking, carcinogens etc.) or harmful influences some solar rays quanta (for example, wavelength lower than 200nm). The harmful factors carry dangerous energy causing infection disease in cells. Then after initial viruses infection disease it occurs infection of other persons. Hence there are occurred often influenzal epidemics as well as the other epidemics. Also there appear in the same mode HIV viruses and the other viral diseases, including v–oncogenes of oncologic diseases. Following simple organisms producing by corresponding quanta of solar radial energy are prokaryotes. The prokaryotes have single circular chromosome and their DNA is organized into structure called nucleoid which occupies whole region of bacterial cell, i.e haploid structure. The genes in prokaryotes are often organized in operons. However this structure is dynamic and is maintained by the actions of a range of histone–like proteins, which associate with the bacterial chromosome. The DNA in chromosomes is organized with the DNA packaged within structures similar to eukaryotic nucleosomes. Bacteria typically have a one–point from which replication starts. Just bacteria reproduce via asexual reproduction by binary fission. There occur exchanges and recombinations genetic matter as horizontal gene transfer, but it is not replication, i.e. transference DNA between two cells. In bacteria, gene transfer occurs by three processes. These are bacterial virus (bacteriophage)–mediated transduction, plasmid–mediated conjugation, and natural transformation.19,20 Transduction of bacterial genes by bacteriophage appears to reflect an occasional error during intracellular assembly of virus particles, rather than an adaptation of the host bacteria.19,20 The transfer of bacterial DNA is under the control of the bacteriophage’s genes rather than bacterial genes.21–24 Conjugation of bacteria is controlled by plasmid genes, and is an adaptation for distributing copies of a plasmid from one bacterial host to another. Infrequently during this process, a plasmid may integrate into the host bacterial chromosome, and subsequently transfer part of the host bacterial DNA to another bacterium. Plasmid mediated transfer adaptation. Natural bacterial transformationinvolves the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another through the intervening medium. Unlike transduction and conjugation, transformation is clearly a bacterial adaptation for DNA transfer, because it depends on numerous bacterial gene products that specifically interact to perform this complex process. For a bacterium to bind, take up and recombine donor DNA into its own chromosome, it must first enter a special physiological state called competence. About 40 genes are required in Bacillus subtilis for the development of competence. The length of DNA transferred during Bacillus subtilis transformation can be as much as a third to the whole chromosome. Transformation is a common mode of DNA transfer, and 67 prokaryotic species are thus far known to be naturally competent for transformation.25–29
Solar radiations influences on eukaryotic organisms
Different prokaryotes have either important useful function for an organism, e.g. producing Vitamin B12 in an organism, or harmful function causing pathologic processes. However development of eukaryotic organisms from its germination up to growth and down to death displays arising processes via decreasing Entropy and withering away processes via increasing Entropy. A eukaryotic organism is an open non equilibrium non linear thermodynamic system which is subjected to thermodynamic laws. The stability of an open non–equilibrium non–linear thermodynamic system of an able–bodied organism and also an open non–equilibrium non–linear thermodynamic system of a sick organism define stability of Internal Energy (∆U) an organism. Just according to first law of thermodynamics , Stationary State of open non–equilibrium non–linear thermodynamic system of an able–bodied organism and also Quasi–stationary State of open non–equilibrium non–linear thermodynamic system of a sick organism are characterized by stability of Internal Energy ( ) (stable temperature 36,0℃–36,9℃ by which all enzymes operate, stable PH=7,35 in blood etc.). The mechanism maintenance stability Internal Energy of an open non quilibrium thermodynamic system of a living organism is proved by outstanding Prigogine theorem.30
Here is the theorem Prigogine:
[The symbols: Entropy–S; Stream of Substances–Js; Stream of Energy–Je; Force of Substances–Fs; Force of Energy–Fe; Phenomenological Streams of Substances and Energy–Zss and Zee] dS = JsFs + JeFe > 0. Conjugated flows: Js = ZssFs + ZseFe and Je = ZeeFe + ZesFs. dS = (ZssFs + ZseFe)Fs + (ZeeFe + ZesFs)Fe = ZssFs²+ ZseFsFe + ZesFsFe + ZeeFe²= ZssFs²+ 2ZseFsFe + ZeeFe²> 0. Corresponding to the Onsager concept: Zse = Zes.
However there are Zss > 0; Zee > 0; Zse > 0. We can conceive that there is not change flow of Substances in stationary state Js = 0. Just after all, the concentrations of Substances in Internal Medium of an organism (in blood and in neurolymph) are constant, i.e. the quantity inflow of the Substances into Internal Medium of an organism is equal the quantity outflow of the Substances from Internal Medium of an organism. Hence there is the derivative dS from Fs, if it’s Fe = const (the constant production calories for maintenance temperature 36,0 °C –37,5°C by which all enzymes operate):
The second derivative (flexon) from S is peer:
It corresponds to extreme point. It means that . So the minimization increment of dissipation energy via minimization of gain entropy causes the stability of the open non equilibrium thermodynamic system of an organism.
The common mechanisms regulation maintenance stability Internal Energy (stable temperature 36,0°C–36,9°C etc.) and Internal Medium (stable concentration substances in blood and neurolymph) in high organised eukaryotic organisms consist of three level regulation: highest level regulation [Central Nervous System], high level regulation [“Basic Equilibrium Constants of all kinds of metabolisms] and low level regulation [“Equilibrium Constant of energy exchanges” and “Equilibrium Constant of metabolism”] (Figure 1).31,32 Also the common mechanism regulation maintenance stability Internal Energy and Internal Medium is supported by Hormonal system operations which influence as on metabolic processes via influencing through cellular receptors on some cellular functions. Besides an organism’s cells create supplemental mechanism maintenance stability Internal Energy and Internal Medium as in an organism’s cells as well as in an organism inducing autophagy and immune processes via remote reaction across distance on strange objects due to operation resonance waves of cellular capacitors.30 However the common mechanisms regulation maintenance stability Internal Energy and Internal Medium in eukaryotic organisms are subjected both positive influences and negative influences of solar radiations displaying balance increased Entropy & decreased Entropy in Environment. Just minimization gain increase Entropy in an open non equilibrium non lineal thermodynamic system of an organism, according famous Prigogine theorem,30 results in minimal shift balance increased Entropy & decreased Entropy into minimal decreased Entropy maintaining stable Internal Energy of an organism. Besides such oscillations of balance increased Entropy & decreased Entropy occur during the life of an organism reflecting states of an organism’s metabolism from its birth to death (Figure 2).32,33 Moreover these oscillations of balance increased Entropy & decreased Entropy correspond to thermodynamic propability of distribution Entropy according to outstanding Boltzmann formula. Just these solar radiation influences cause by direct actions and indirect actions on metabolic processes of the different organisms, e.g. plants, bacteria, animls, men and so on. The positive influence of solar radiation promotes life of the organisms via exerting as common mechanisms regulation maintenance stability Internal Energy and Internal Medium of an organism as well as the operation cellular mechanisms maintenance stability Internal Energy and Internal Medium of an organism. Just the mechanisms influences of solar rays on eukaryotic organisms are compared with the mechanisms photosynthetic processes. Although photosynthetic processes are occurred differently by different species, these processes always begin in plants when energy from light is absorbed by proteins calledreaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light–dependent reactions, some energy is used to release electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. The hydrogen freed by the splitting of water is used in the creation of two further compounds that act as an immediate energy storage means: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) andadenosine triphosphate(ATP), as the energy carrier of cells and extracellular medium.
Vitamins as cofactors are exerted by solar radiation energy in an operation
The producing by solar radiations photosynthesis direct acting Vitamin D2 is formed from natured ergosterol which is Provitamin D3 [7–dehydrocholesterol]. Just provitamin D3 or 7–dehydrocholesterol is located in a skin and in other tissues. Solar UV radiation transforms 7–dehydrocholesterol into Vitamin D3 or cholecalciferol. Then cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) is transformed into Vitamin D2 in liver. Vitamin D2 takes part in metabolism calcium [Ca2+] and phosphorus (HPO42–) increasing permeability across cellular membranes of calcium [Ca2+] and phosphorus (HPO42–) that influence on mineralization of osseous tissue making rearrangement between bivalent ions {calcium [Ca2+] / magnesium [Mg2+]} and univalent ions {natrium [Na+] / potassium [K+]}. The rearrangement bivalent ions and univalent ions induces interactions between mineralization of osseous tissue and demineralization connective tissue influencing on vessels’ muscular tissue and connective tissue due to ion pumps operations which exert cardiovascular function, intestinal function and function other organs. Just the plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase (PMCA) is a transport protein in theplasma membrane of cells and functions to remove calcium (Ca2+) from the cell. The plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase (PMCA) and the sodium calcium exchanger (NCX) are together the main regulators of intracellular Ca2+ concentrations.34–42 Since it transports Ca2+ into the extracellular space, the plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase (PMCA) is also an important regulator of the calcium concentration in the extracellular space.34–42 Also balance mineralization & demineralization is regulated by interactions between cortical hormones and mineralocorticoids which were produced from cholesterol too. Hence these are links between mechanisms of operation Vitamin D2 and mechanisms maintenance stability balance cortical hormones & mineralcorticoides, i.e. balance anti–inflammation hormones & pro–inflammation hormones. The direct actings solar radiation induce photosynthesis melanine in scin of an organism which defends against harmful actions solar energy ultraviolet rays of wavelength lower 200nm. Just UV solar radiations affect scin exerting tyrosinase that results in transforming tyrosine into DOPA (L–3,4–dihydroxyphenylalanine), then DOPA both into Eumelanine through processes polimerozation and into Pheomelanine through cysteine–cysteinildopa processes Oxidation and Polimerisation. The photosynthesis of solar radiation affecting eukaryotic organisms occurs in following mode: The living prokaryotic and some eukaryotic organisms subjecting by solar radiations photosynthesis cause indirect acting both positive influences and negative influences on eukaryotic high organized organisms. Thus solar radiation photosynthesis is a process which is used by plants and other organisms in order to convert solar radiation quants energy into chemical energy that can later be released to fuel the organisms' activities via energy transformation into substances. This chemical initial energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water. Here is this simple scheme of photosynthesis in plants: , i.e. . The photosynthetic process always begins when solar rays’ quants energy is absorbed by proteins of reaction centres which contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most of ones in leaf cells. In bacteria, these organelles called chloroplasts are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light–dependent reactions, some energy is used to tear away electrons from relevant substances, for exemle such as water for producing oxygen gas. The splitting water, caused by freed hydrogen, is used in the creation of two further compound structures as reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and denosine triphosphate (ATP) which operate in cells as energy storage means. Just this stored energy is used for biosynthesis of more compound substances in plants and bacteria as proteins, hydrocarbons, fats as well as microelement and vitamins some of which operate as coenzymes. Vitamins can serve as precursors to many organic cofactors (e.g., vitamins B1, B2, B6, B12, niacin, folic acid) or as coenzymes themselves (e.g., vitamin C). However, vitamins D have other functions in an organism.42,43 Symptoms of bone pain and muscle weakness can mean you have a vitamin D deficiency. However, for many people, the symptoms are subtle. Yet, even without symptoms, too little vitamin D can pose health risks. Low blood levels of the vitamin have been associated with the Vitamin D deficiency.44–48 Many organic cofactors also contain a nucleotide, such as the electron carriers NAD and FAD, and coenzyme A, which carries acyl groups. All vitamins exerted by appropriating quants of solar radiations energy are significant links in mechanism maintenance stability Internal energy of the open non equilibrium non linear thermodynamic system of eukaryotic organisms. Besides the operations of these vitamins reflect interactions between different mechanisms in metabolisms of different organisms causing common mechanism maintenance stability in Nature.
The liposoluble Vitamins [Vitamin D, Vitamin A, Vitamin K] are produced in animal organisms and in human organisms, being subjected to solar violet rays. Most of numbers of water–soluble Vitamins are produced in plants which cells are subjected to solar rays’ quanta. Vitamin B12 is produced by microbes in human intestine, which are formed due to influences solar rays in Environment.
Ascorbic acid is also known as Vitamin C which is associated with chloroplasts and apparently plays a role in ameliorating the oxidative stress of photosynthesis in plants.49 Just ascorbic acid is derived from glucose via uronic acid pathway. Ascorbic acid has no coenzyme form, but active form is ascorbic acid itself. The main function of ascorbic acid is as reducing reactants in a number of different reactions. Vitamin C reduces as cytochrome a and cytochrome c of a respiratory chain as well as molecular oxygen. The single important reaction requiring ascorbic acid as a cofactor is hydroxylation of proline residues in biosynthesis of collagen and metabolism of connective tissue. Eukaryotic high organized organism receives vitamin C from plants. In eukaryotic high organized organism vitamin C acts as an electron donor for eight different enzymes:49,50 Also vitamin C is found in high concentrations in immune cells and is consumed quickly from immune cells during infections.
Thiamin is also known as Vitamin B1 which is a derivate of substituted piramidine and thiamine, linked by a methylene. Its active form is thiamin pyrophosphate [TPP]. Thiamin pyrophosphate [TPP] is formed in brain and liver by the enzyme Thiamin diphosphotransferase. Also thiamin pyrophosphate [TPP] serves as a coenzyme for pyruvate and α–ketoglutarate dehydrogenase reaction as well as the transketolase catalyzed reaction of pentose phosphate pathway. Upon absorption into the body, thiamine is used to form thiamine pyrophosphate, which as noted in the Table 1 provided is an essential co–factor used by several cellular enzymes.52–54 Therefore a patient who consumes a thiamine deficient diet or has impaired absorption of thiamine from the intestines can easily become deficient. In fact, the most well known complications due to thiamine deficiency are Dry Beriberi, Wet Beriberi and Wernicke–Korsakoff Syndrome.54–56 Deficiency of vitamin B1 in an organism leads also to ataxia and mental confusion.
Riboflavin is also known as Vitamin B2. The riboflavin as coenzyme is creates two substances: flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). The enzymes that require flavin mononucleotide (FMN) or flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) as coenzymes are named Flavoproteins or Flavoenzymes.57 –60 The reduced flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and wizzflavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) form FMNH2 and FADH2 respectively.57–60 Riboflavins are key elements in cellular respiration which act as intermediate hydrogen acceptor in mitochondrial electron transport chain via accepting hydrogen, derived from foodstuffs, and transferring electrons to the cytochrome system.57–60 Riboflavin deficiency (also called ariboflavinosis) results in stomatitis including painful red tongue with sore throat, chapped and fissured lips (cheilosis), and inflammation of the corners of the mouth (angular stomatitis).
Biotin is known as vitamin H or B7 which is composed a tetrohydroimidazalone ring fused with a tetrohydrothiophene ring. Valeric acid substituents in catalysis of essential metabolic reactions of biosynthesis fatty acids, gluconeogenesis, metabolism of Leucine. Biotin is the cofactor which is required for enzymes that are involved in carboxylation reactions, e.g. Acetyl–CoA carboxylase and Pyruvate carboxylase.61–63 Thus Biotin is the link in “nodal point of bifurcation anabolic and catabolic processes in Acetyl–CoA [NPBac]” in causing anabolic pathways of biosynthesis fatty acids, gluconeogenesis and so on (Figure 3).64 Biotin is found in foods and also is synthesized by intestinal bacteria. Therefore deficiencies of Biotin are rare, only appears by long obtaining antibiotic therapy.
Vitamin B6 consists of Pyridoxine, Pyridoxal and Pyridoxamine. Pyridoxine, Pyridoxal and Pyridoxamine are the three components of Vitamin B6 which are converted in the body to the coenzyme form Pyridoxal–5–phosphate (PLP). This convertion is catalyzed by the ATP requiring enzyme Pyridoxal kinase. Pyridoxal–5–phosphate (PLP) functions as a cofactor for transamination and decarboxilation. These reactions involce in the formation of a Schiff’s linkage (–N=CH–). The phenyl ring with positive charge on nitrogen atom, delocalized over the ring, stabilizes the Schiff’s base linkage. Just active form, pyridoxal–5–phosphate, serves as a coenzyme in some 100 enzyme reactions in amino acid, glucose, and lipidmetabolism.65 Deficiencies of vitamin B6 are rare and depend on deficiencies all B–complex vitamins.
Niacin consists of nicotinic acid and nicotinamide and is also known as Vitamin B3. The enzymes forms of Niacin are connected with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and nicotiamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+). Both (NAD+) and (NADP+) function as cofactors for numerous dehydrogenases, e.g. lactate and malate dehydrogenases. There are nearly 40 different oxidoreductases which use either NAD+ or NADP+ as cofactors. NADH acts as carrier of Reducing equivalents (electrons) from metabolic intermediates and delivers them to ETC in mitochondria where they are oxidized to produce ATP.66,67,68–70 3 moles of ATP are produced per mole NADH oxidized.66,67,68–70 NADH is also involved in anabolic reactions like biosynthesis of fatty acids and some reactions of PPP synthesis.71–76 Deficiency of Niacin leads to disease pellagra with such symptoms: glossitis of tingue, dermatitis, weight loss, diarrhea, depression and demention.77
Pantothenic acid is also known as Vitamin B5. Pantothenic acid is formed from β–olanine and pantoic acid. Pantoic acid is part of coenzyme A (CoA) named also Pntothenate. Just coenzyme A (CoA) is formed from Pantothnic acid and 3–moles of ATP . Acyl groups of fatty acids are linked to coenzymes A (CoA) to give acyl CoA (Figure 3).78 Thus derived from Vitamin B5, Acetyl–CoA is “the nodal point of bifurcation anabolic processes and catabolic processes [NPBac]” which is the crusial point of mechanism maintenance stability of balance anabolic processes & catabolic processes of causing maintenance stability Internal Energy of an organism via low regulative level regulation (Figure 3).31,32,64,79
Vitamin A is a group of unsaturated nutritional organic compounds that includes retinol, retinal, retinoic acid, and several provitamin A carotenoids (most notably beta–carotene).80,81 Vitamin A has multiple functions: it is important for growth and development, for the maintenance of the immune system and good vision.82,83 Vitamin A is needed by the retina of the eye in the form of retinal, which combines with protein opsin to form rhodopsin, the light–absorbing molecule necessary for both low–light (scotopic vision) and color vision.84 Vitamin A also functions in a very different role as retinoic acid (an irreversibly oxidized form of retinol), which is an important hormone–like growth factor for epithelial and other cells.83,85 In foods of animal origin, the major form of vitamin A is an ester, primarily retinyl palmitate, which is converted to retinol (chemically an alcohol) in the small intestine. The retinol form functions as storage form of the vitamin, and can be converted to and from its visually active aldehyde form,retinal. All forms of vitamin A have a beta–ionone ring to which an isoprenoid chain is attached, called a retinyl group. Both structural features are essential for vitamin activity.86 The orange pigment of carrots (beta–carotene) can be represented as two connected retinyl groups, which are used in the body to contribute to vitamin A levels. Alpha–carotene and gamma–carotene also have a single retinyl group, which give them some vitamin activity. None of the other carotenes have vitamin activity. The carotenoid beta–cryptoxanthin possesses an ionone group and has vitamin activity in humans. The role of vitamin A in the visual cycle is specifically related to the retinal form. Within the eye, 11–cis–retinal is bound to the protein "opsin" to form rhodopsin in rods and iodopsin in cones at conserved lysine residues.84 As light enters the eye, the 11–cis–retinal is isomerized to the all–"trans" form. The all–"trans" retinal dissociates from the opsin in a series of steps called photo–bleaching. This isomerization induces a nervous signal along the optic nerve to the visual center of the brain. Rhodopsin is needed to see in low light (contrast) as well as for night vision. It is known that rhodopsin in the retina is only regenerated when the retina is attached to retinal pigmented epithelium, which provides retinal.84 It is for this reason that a deficiency in vitamin A will inhibit the reformation of rhodopsin and lead to one of the first symptoms, night blindness.87 Just wavelengths 380–780nm of solar electromagnetic radiation are visible spectrum lights for human eyes. However human eyes don’t take straight solar light but take either reflected solar rays from different matters or penetrated through some dark matter. The molecules of these matters reflect solar wavelengths rays via fission radiation corresponding to the Schroedinger equation of the method the molecular orbitals–a linear combination of atomic orbitals (MO LCAO).29,88 Just the wave function of any molecule is determined as the total wave functions of the nuclear orbitals, multiplied by the appropriating weight coefficients: .29,88
( –wave function of a molecule, –wave functions of the nuclear orbitals,– the weight coefficients). Human eyes due to rhodopsin in rods and iodopsin in cones take up the quants of the solar wavelengths rays via fusion radiation which were reflected from the molecules of the matters. Thus it is occurred human vision of the matters.
Also Vitamin A, in the retinoic acid form, plays an important role in gene transcription. The violation permeability of nuclear membranes due to insufficient Vitamin A leads to expression activity mitochondrial capacitors via resonance waves on chemical potential of nucleus ( ) that stimulates production supplementary quantity of ROS/H2O2/Free radicals in mitochondria. The complex ROS/H2O2 pass through mitochondrial membranes and cytoplasm into nucleus and generates superoxide [O2*] inducing free radicals (*OH). Free radicals (*OH) react on nDNA and induce process replication via realizing of 2nDNA:89,90
Vitamin B12 is also known as Cobalamin. Cobalamin is composed of complex tetrapyrrol ring structure (corrin ring) and Cobalt ion in center. Vitamin B12 is synthesized exclusively by microorganisms as bacteria in intestine of animals and men. Also Vitamin B12 is found in liver of animals and men which is bound to proteins. Vitamin B12 must be hydrolysed from protein in order to be active. Hydrolysis occurs in the stomach by gastric acids and in intestines by tripsin digestion. There are two coenzyme forms of Vitamin B12: a) 5–deoxyadenosyl cobalamine; b) Methylcobalamine:–CN is replaced by metyl group. Vitamin B12 and Folic acid are significant links in aerobic oxidative processes in mitochondria. The ATP is produced in mitochondria via the process of oxidative phosphorilation in which oxygen adds electron via transformings , It occurs in such pathway: Electrons are transferred through the reducing substances of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) to Complex I (NADH dehydrogenase) and flavine adenine dinucleotide (FADH2) to Complex II and further through Complex III (cytochrom bc complex) then Complex IV (cytichrom c oxidase) to Complex V (ATP synthase).91,92 Vitamin B12 deficiency is the medical condition of low blood levels of vitamin B12 which leads to diseases Pernicious Anemia. Just a type of blast red blood cells known as megaloblastic anemia is often but not always present at Pernicious Anemia.
Folic acid is known as Vitamin B9. Folic acid is abundantly found in green leaves. It is conjugated molecule consisting of a pterine ring structure linked to para–aminobenzoic acid (PABA) that forms pteroic acid which is conjugated to glutamic acid residue forming Folic acid.93 Folic acid is obtained from yeasts and leafy vegetables. Besides Folic acids are found in animal liver and human liver. Thus a human organism and an animal organism require folate intake in the diet from leafy vegetables in which Folc acid is synthesized due to influences of appropriating quats energy of solar radiation on leaves of plants. Folic acid and Vitamin B12 are significant links in aerobic oxidative processes in mitochondria. The ATP is produced in mitochondria via the process of oxidative phosphorilation. It occurs in such pathway: Electrons are transferred through the reducing substances of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) to Complex I (NADH dehydrogenase) and flavine adenine dinucleotide (FADH2) to Complex II and further through Complex III (cytochrom bc complex) then Complex IV (cytichrom c oxidase) to Complex V (ATP synthase).91,92 Folate deficiency results in symptoms nearly identical to B12 deficiency.94,95 Just the most pronounced effect of folate deficiency on cellular processes is upon DNA synthesis.94,95
Vitamin K is known as Phylloquinone. Phylloquinone is needed synthesis Prothrombin [Factor II of blood coagulation] and the other Factors of blood coagulation [VII, IX, X]. These Factors function as cofactors for –Carboxylation of amino–terminal Glutamine sequence of corresponding enzyme. The mechanism of blood coagulation occurs through activation corresponding phospholipids and Calcium ions due to operation these blood coagulation cofactors. Just vitamin K is a group of structurally similar fat–soluble vitamins in a human organism. Vitamin K includes two natural vitamers: vitamin K1 and vitamin K2. Vitamin K2 consists of a number of related chemical subtypes which have different lengths of carbon side chains made of isoprenoid groups of atoms. Vitamin K1, also known as phylloquinone, is made by plants, and is found in highest amounts in green leafy vegetables because it is directly involved in photosynthesis by appropriating quants of solar radiation. Thus Vitamin K1 can be considered as the plant form of vitamin K. It is active as a vitamin in animals and performs the classic functions of vitamin K, including its activity in the production of blood–clotting proteins. Animals may also convert it to vitamin K2.96–100 Bacteria in the flora can also convert K1 into vitamin K2 (menaquinone). Preliminary clinical research indicates that deficiency of vitamin K may weaken bones, potentially leading to osteoporosis, and may promote calcification of arteries and other soft tissues.101–106 Theus the certain energy quantums of solar rays induce biosynthetic metabolic processes in plants via producing Vitamin K.107 Human organism receive Vitamin K from plants, and Vitamin K play role in mechanisms metabolism Ca2– ions which influence as on blood coagulation as well as on ionic metabolism of Ca/Mg pump, K/Na pump etc., i.e. influences on “Equilibrium Constant of ionic metabolism” and “Equilibrium Constant of blood coagulating system” of high level regulation stability Internal Energy and Tnternal Medium an orgaganism (Figure 1).30,31,107,108 Vitamin K deficiency leads to impairing Internal Energy and Internal Medium of an orgabism causing violation osseous metabolism with bone fracture, cardiovascular diseases and so on.101–103
Vitamin E is known as Tocopherol. The biologically active forms of vitamin E constitute a family of four related compounds called tocopherols.109 –113 The most abundant tocopherol in non–hepatic tissues in humans is the α–tocopherol form. Vitamin E is a mixture of several related compounds known as tocopherols and tocotrienols. The tocopherols are the major sources of vitamin E in the diet. The different tocopherols are designated α–, β–, γ–, and δ–tocopherols. All four tocopherols are able to act as free radical scavengers thus they all have potent antioxidant properties.114–122 Vitamin E is absorbed from the intestines packaged in chylomicrons. Absorbed Vitamin E is delivered to the tissues via chylomicron transport and then to the liver through chylomicron remnant uptake.114,115 The major site of vitamin E storage is in adipose tissue. The major function of vitamin E is to act as a natural antioxidant by scavenging free radicals and molecular oxygen. In particular vitamin E is important for preventing peroxidation of polyunsaturated membrane fatty acids.116,119,120 The vitamins E and C are interrelated in their antioxidant capabilities.115 Most vitamin E in diets is in the form of γ–tocopherol from soybean, canola, corn, and other vegetable oils.123–126 The conditions that result from vitamin E deficiency are related to disturbances in nerve cell membrane lipid homeostasis.120,121,127

Metabolic and Energy “Equilibrium Constants” regulate interactions of intracellular and extracellular chemical potentials ( ) for maintenance stability of Internal Energy and Internal Medium an organism. The intracellular and extracellular chemical potentials ( and ) cause the formations of the positive/negative charges on internal and external membranes of cellular wall, promoting operation of remote cellular reactions via cellular capacitors operation.
Figure 1 Maintenance stability of internal energy and internal medium an organism.
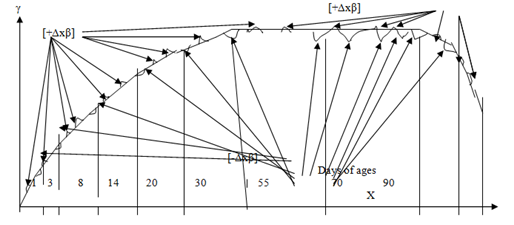
The organism’s ages: from 0 till 3years–babyhood; from 3 till 14 years–young age; from 14 till 20–juvenile age; from 20 till 30 years–middle age; from 30 till 55 years–full age; from 55 till 70 years–elderly age; after 70 years–old age.
Figure 2 The changes of metabolism during a life of an organism.
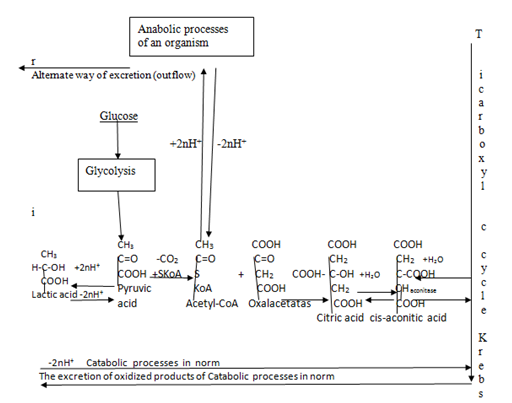
Figure 3 The point of bifurcation anabolic processes and catabolic processes in metabolism of an organism.
1. Nodal point of bifurcation anabolic and catabolic processes in “Nodal point of bifurcation anabolic and catabolic processes” [NPBac].
2. Moderate metabolic processes displaying balance anabolic and catabolic processes in able-bodied tissue.
3. Accumulation of energy into lactic acid for anabolic processes. 4. Normal excretion substances via catabolic oxidative processes in able-bodied tissue.
Vitamins |
Chemical names |
Coenzymes names or consist |
Additional component or enzymes |
Chemical group(s) transferred |
Distribution |
Vitamin C |
Ascorbic acid |
an electron donor for eight enzymes |
None |
Electrons |
Bacteria, plants and eukaryotes |
Vitamin B1 |
Tiamin |
Coenzyme: thiamin pyrophosphate |
Pyruvate and α–ketoglutarate dehydrogenase |
2–carbon groups, α–cleavage |
Bacteria, plants and eukaryotes |
Vitamin B2 |
Riboflavin |
Coenzymes: FMN, FAD, Coenz. F420 |
Enzymes: Flavoenzymes and ADP |
Electrons |
Bacteria, plants and eukaryotes |
Vitamin B6 |
Pyridoxine |
Coenzyme: Pyridoxal phosphate |
Enzynes: Transaminase, Decarboxilase |
Amino and Carboxyl groups |
Bacteria, plants and eukaryotes |
Vitamin H or B7 |
Biotin |
Biotin |
Acetyl–CoA carboxylase and Pyruvate carboxylase |
CO2 |
Bacteria into intestine. |
Vitamin B3 |
Niacin |
Coenzymes: NAD+ and NADP+ |
lactate and malate dehydrogenases as well as ADP |
Electrons |
Bacteria, plants and eukaryotes |
Vitamin B5 |
Pantothenic acid |
Coenzyme A (CoA) |
70 enzymes require coenzyme A (CoA) |
Acetyl group and some acyl groups |
Bacteria, plants and eukaryotes |
Vitamin B12 |
Cobalamine |
5–deoxyadenosyl cobalamine and Methylcobalamine |
Methionine synthetase transfers Methyl group |
Acil groups, hydrogen, alkyl groups |
Bacteria in intestine. |
Vitamin B9 |
Folic acid |
NADPH coenzyme and Tetrahydrofolic acid |
Dehydrofolate reductase (DHFR) |
Methyl, formyl, methylene, formimino groups |
Bacteria, plants and eukaryotes |
Vitamin K |
Phylloquinone |
Menaquinone, Vitamine K1, K2, MK7, MK11 |
Proteine Synthetases |
Carbonyl group and electrons |
Bacteria, plants and eukaryotes |
Vitamin E |
Tocopherol |
α–, β–, γ–, and δ–tocopherols |
Proteine Synthesis for coagulative processes |
α–tocopherol us carrier proteins |
Bacteria, plants and eukaryotes |
Vitamin A |
Coenzyme A Carotenoids |
retinol, retinal, retinoic acid |
α–carotene, β–carotene, |
retinol, retinal, retinoic acid
|
Bacteria, plants and eukaryotes |
Table 1 The characteristic vitamins of indirect production by solar radiation energy.
This article is dedicated to the memory of my daughter T.M. Ponizovska.
Author declares that there is no conflict of interest.

©2018 Ponizovskiy. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.