We received the structural diagram of the multilayer electromagnetoelastic actuator of adaptive optics for composite telescope and astrophysics equipment in difference from Cady's and Mason's electrical equivalent circuits of the piezotransducer and the vibration piezomotor. In this work we used the method of the mathematical physics with Laplace transform for the structural-parametric model and the structural diagram of the multilayer electromagnetoelastic actuator for the adaptive optics of the composite telescope in astronomy.8,14,19,29,30 We have the equation8,9,11,24,29,31 of the electromagnetoelasticity in the form
where
is the relative displacement,
is the coefficient of electromagnetoelasticity in the form
piezomodule or magnetostrictive coefficient,
is control parameter in variables: electric
, magnetic
field strengths or electric
induction,
is the elastic compliance with
,
is the mechanical stress, i, j, m are the indexes.
For the multilayer electromagnetoelastic actuator we received the equation of the causes force in the form
where
is the cross sectional area of the multilayer electromagnetoelastic actuator. The matrix the equivalent quadripole of the multilayer piezoactuator29,31 has the form
where l is the length for longitudinal
for transverse
and for shift piezoeffect
for the piezolayer
are the thickness, the height, the width,
is the coefficient propagation.
We obtained the structural-parametric model and the structural diagram of the multilayer electromagnetoelastic actuator of adaptive optics for composite telescope and astrophysics equipment on Figure 1 from the equation of the force that causes deformation, the equivalent quadripole and the boundary conditions with the forces on faces of the actuator in the following form
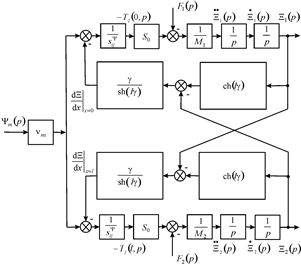
Figure 1 Structural diagram of multilayer electromagnetoelastic actuator for adaptive optics.
where
,
We have the matrix transfer function of the multilayer electromagnetoelastic actuator of adaptive optics for composite telescope and astrophysics equipment from the generalized structural-parametric model in the form
where
,
,
are the matrixes of the displacements the faces, the transfer functions, the control parameters.
In the static we obtained displacements for
the faces of the voltage-controlled multilayer piezoactuator for the longitudinal piezoeffect and the inertial load at
,
, where m is the mass of the multilayer piezoactuator,
are the load masses, and the forces on faces
in the following form
where U is the voltage.
For the multilayer piezoactuator at
= 4∙10-10 m/V, n=16,
=100 V,
=1 kg and
=4 kg we obtained the static displacements of the faces the multilayer piezoactuator
=512 nm,
=128 nm,
=640 nm.
We received transfer function of the multilayer piezoactuator at longitudinal piezoeffect with one fixed face and voltage control for the elastic-inertial load at
in the following form
,
where
,
are the Laplace transforms the displacement face and the voltage,
,
are the time constant and the damping coefficient,
is the rigidity of the multilayer piezoactuator for
.
At the elastic-inertial load for
=4∙10-10 m/V, n=12, U=200 V,
=4 kg,
= 2∙107 N/m,
=0.4∙107 N/m we received the steady-state value of the displacement of the multilayer piezoactuator
=800 nm and the time constant
=0.4∙10-3 s.


