eISSN: 2572-8474


Mini Review Volume 8 Issue 3
Department of Epidemiology COSTAMED, Benemérita Universidad Autónoma de Puebla, Mexico
Correspondence: Israel Shomar Galicia, Department of Epidemiology COSTAMED, Hospital Epidemiological Surveillance Network, Benemérita Universidad Autónoma de Puebla, México
Received: October 15, 2022 | Published: October 26, 2022
Citation: Galicia IS. Frequency of cutaneous leishmaniasis with population characteristics and treatment behavior in second level hospital care in the Mexican caribbean in 2020 and 2021. Nurse Care Open Acces J. 2022;8(3):82-83. DOI: 10.15406/ncoaj.2022.08.00243
The epidemiology of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the Americas is very complex, with variations in transmission cycles, reservoirs, sandfly vectors, clinical manifestations, and response to treatment. In addition, there are several species of Leishmania in the same geographical area. In 2018, Brazil concentrated 97% of the cases of visceral leishmaniasis in the region. But in Mexico it is still difficult to diagnose cutaneous leishmaniasis, being a problem for public health in the Caribbean region.1,2
With the frequency of attention to cutaneous leishmaniasis in attention in the emergency service and epidemiology as well as the main causal agents, measuring the state of health, accompanying comorbidities, unnecessary antibiotics given by a misdiagnosis and determining the frequency of cure with the different treatment alternatives with respect to the bibliography used.
(Figure 1–6).
Geolocation of cases by postal code
WOMEN
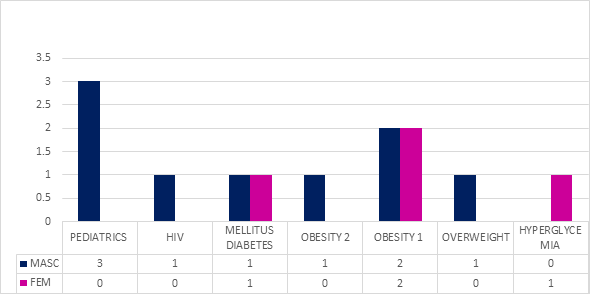
Figure 4 69% treated with itraconazole (1 tablet every 8 hrs for 14 days)/ketonoazole (twice a day for 14 days) and the pediatrics only ketonazole (twice a day for 7 days).
In the present investigation it was found that 30.7% are female and 69.3% belong to the male group, 100% of patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis were given antibiotics indiscriminately, being 61% third generation cephalosporins without need it. Adding comorbidities such as Diabetes Mellitus in 15.3% and HIV in 8%. Being the attentions with the highest frequency of use of the medication Glucantime with Itraconazole/ketonoazole for monitoring and treatment, having a higher frequency of use of intralesional treatment of 16 doses (with comorbidities of HIV and DM2) and having cases of rapid response to treatment with 4 applications in 2 weeks without recurrence in a follow-up period of 6 months.3–6
The prevention of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis is based on three fundamental strategies:
3 analysis strategies of all clinical care physicians:
The treatment of leishmaniasis depends on several factors, such as the form of the disease, concurrent conditions, the species of the parasite, and the geographic location. It is a disease that can be treated and cured, but for this a competent immune system is necessary, since the medicines, by themselves, are not capable of eliminating the parasite from the body. Hence the risk of recurrence in case of immunosuppression.
None.
None.

©2022 Galicia. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.