eISSN: 2572-8474


Introduction: The quality and safety of the patient are two essential lines to provide care with quality and warmth, through interventions, actions and care performed by the nursing professional contributing to the protection of the rights of users and particularly in the nursing process, strengthened by supervision to consolidate continuous improvement methods. The issue of supervision is addressed according to various fundamental bases of the administrative process which are broken down into various aspects, such as the characteristics of the leader, strategic planning, quality for continuous improvement, reengineering, teamwork, coaching among others, in this work we give total credit that without a good performance of this personage within the nursing headquarters, many of the care processes, when not supervised, are easily lost in distracted care.
Methodology: This is a quantitative, nominally dichotomous, documentary type research standardizing the evaluation process, being the global variable compliance with each of the standards in the records of the Nursing sheets according to the clinical history, progress notes and inter consultations, medical orders, preoperative note, surveillance and anesthetic record, post-operative note, application and results of laboratory study, cabinet, pathology and others, references and / or transfers and discharge note of the points requested in the "Certificate of standards for the comprehensive analysis of nursing care, through of the medical complaint file "corresponding to the Nursing care process (PAE) that are classified from 1 to 35, those referring to the structure that could contribute to the malpractice of nursing and that are related to the availability of personnel, of medicines and healing material, are specified in PAE 36, 37 and 38 and finally referring to the results of the PAE 39 to 40 care.
Results: With the implementation of the project "Supervision and strengthening of the shift link: strategy to improve the practice of Nursing", a 97.5% compliance was achieved in all of the 40 standards in the 11 hospital units, in general it had an increase above of 60% considering that 27 standards were found with figures below 50% and only 13 above it.
Conclusions: The prelude to a substantial change must be promoted basically by Nursing Headquarters, which for these purposes we will define as the group of members that make up the leaders who lead the group of nurses who work in a hospital unit, and who, when supervised daily and constant interventions and care provided by the health care personnel not only ensures a considerable increase in the numbers of the appropriate clinical records of nursing to complete, correct, timely, legible, without erasures or amendments but also the safety of attention, dimensioning the quality of care.
Keywords: Standard, training, supervision, progress and results
The National Commission of Medical Arbitration (CONAMED) giving continuity to the results of the investigation " Identification of the bad practice of nursing from the medical complaint " carried out in 20121 and after a thorough analysis of the final data that I throw such research, It was evident that standards that apply to nursing responsibilities and more specifically to monitoring, are documented downward trend, theorizing that this is an area of opportunity that can boost the work of the sick, motivating her to proactive leadership and that for application purposes, certainly it is better to give who directs tool, visualizing the empowerment of charge, ensuring that the application of knowledge to reinforce current rough and continuing education and care enabling on of human capital that later will be subject to supervision.
Addressing another point of similar interest for the proper execution of good practices in nursing and the performance of the professional who performs the role of supervising among its functions, it was determined that a moment of impact is during the shift delivery, an ad hoc moment for what implement this action by adopting, and strengthening new measures in the delivery - reception of patients, from service to service and even from unit to unit, allowing the understanding of the general condition and evolution of the patient, to give continuity, update and /or start with the appropriate development timely and effective nursing process, thus ensuring the reduction of adverse events, sentinels and / or quasi-failure, which leads to increased patient safety, since the breakdown of the communication process has been the main cause of these mistakes.2
The quality and the safety of the patient are fundamental pillars to offer attention with quality and warmth, contributing to the protection of the rights of the users, through the interventions, actions and cares carried out by the nursing professional particularly in the nursing process, reinforcing continuous improvement strategies that strengthen the consolidation of the supervisory figure. The CONAMED considered this transcendental idea, in order to raise the security and quality of the services and thus be able to influence the decrease of the complaint, therefore I generate a Course - Workshop that through an educational intervention the structure was trained general of the nursing headquarters and all personnel who have under their charge the action of verifying the good practice of nursing interventions, making reference to the understanding that supervision is the process, in which an experienced and qualified person offers a person the learning opportunities through guidance, instruction or control3 this with a view of improving care in care giving quality warmth, based on "40 standards of nursing care" queue para purposes of this research were divided into eight sections:
The project called "Monitoring and strengthening of the shift link: strategy to improve the practice of Nursing will be considered by the Permanent Commission of Nursing". It should be noted that CONAMED has no direct relationship with the service areas, presenting the opportunity to work in conjunction with the Mexico City Secretariat (SEDESA CDMX), initially starting with 11 of its hospital units. In general terms one of the fundamental objectives that was raised in the execution of the project, is the training and implementation in the shift link of the instrument "Schedule of standards for comprehensive analysis of nursing care, through of the medical complaint file",4 that is nothing more than the transformation of the capture sheet for the analysis of clinical records of these already mentioned 40 standards in a checklist with precise instructions for their execution, integrating as a manual, which for its construction is took into account the existing bibliography with the quality of patient care and safety, the NOM-004-SSA3-20125 d the clinical file, the institutional regulations of the health sector and the content of the clinical records of the nursing sheets of the different institutions1 .
This is a quantitative, nominally dichotomous, documentary type research standardizing the evaluation process, being the global variable compliance with each of the standards in the clinical records of Nursing sheets according to the Clinical History, evolution notes and inter consultations, medical orders, preoperative note, anesthetic surveillance and record, post-operative note, request and lab study results, cabinet, pathology, references and / or transfers and discharge note, as well as the points requested in the "Certificate of standards for the comprehensive analysis of nursing care, through of the medical complaint file"4
The existing records in the clinical files of the participating hospital units in this project are considered as the unit of analysis of this investigation; in which the attachment of each one of the items of the aforementioned Identification Card was analyzed, verifying if there is documentary evidence of compliance with the standard or not, qualifying the value of 0 "or" 100 based on its results.
For the purposes of this investigation, a non-probabilistic and intentional sampling of 3096 records was considered. The inclusion criterion was the existence of clinical nursing records. The study was carried out in the months of August 2015 to February 2017 within the participating hospital units. Given programming operation scheme in implementing this strategy, l to implement the project began in 2015, participated in the first stage units 5 and second 6. Each stage is divided into 4 moments and these in multiple activities among them:
Course - workshop (1st moment) consisted of providing training to the total structure of the nursing headquarters in relation to the "40 standards", analyzing the instrument "Certificate of standards for the comprehensive analysis of nursing care, through of the medical complaint file " 4 and applying in file files of the same units, generating the situational diagnosis of the participating hospitals, determining the documentary status of the nursing actions (baseline data) , verification of the registry and the actual execution of the intervention during the shift link with an application exercise using the instrument as a checklist, performing an analysis of results.
Based on the initial data and the training of good practices in relation to lex artis ad hoc the nursing body determined a line of work based on a strategic, tactical and operational plan called commitments where the first challenge was to give the information to all the care staff to improve the practice and consequently raise the quality and the security not only of the users but also of the multidisciplinary team.
First visit (2nd time) two weeks after the start of the project, this follow-up visit was carried out, showing supervisory personnel training activities for the health care personnel, after this He made an oversight in turn link directly with hospitalized patients, using the "Certificate standard instrument for comprehensive analysis of nursing care, through of the medical complaint file "4 to be able to have data and thus evaluate the improvement in nursing care and clinical records.
Second visit (3rd time) six weeks after the start of the project, visiting the participating units, continuing with the evaluation of the care through the ID card in order to continue obtaining data.
Third visit (4th time) to finalize the documentation for this investigation, twelve weeks after the start of the project , a visit was made having the same dynamic as in the previous visit. It is worth mentioning that this last visit is surprising in order to evaluate the real impact of the project within the participating medical units.
With the implementation of the project "Monitoring and strengthening the link shift: strategy to improve nursing practice", a performance of 97.5% was achieved in all the 40 standards within the 11 hospital units, generally it is obtained an increase above 60% considering that 27 standards were found at the beginning with figures below 50% and only 13 above it . In general terms, the evidence derived from the reviews carried out in the 4 moments we can determine that the total result of compliance of the 40 standards in the baseline data is only 40.70%, when executing the project "Supervision and strengthening of the link shift: strategy to improve the practice of Nursing " increases 29.11 points, the highest increase in the entire process, reaching the first follow-up visit (two weeks after the project started) at 69.81%, at six weeks After the project was completed in the second visit, 9.51 progress points were achieved, increasing to 79.30% compliance in all the standards, evidencing an advance of 38.61 points of the baseline data to this second revision, for the third visit an advance was obtained from 43.37 points of the baseline data to this evaluation that was carried out twelve weeks after implementing the project and between visit two and the last one, there was an eve of 4.75 points achieving the final figure of 84.07% compliance in the 40 standards, all this represented in Figure 1. The specific results of each section were the following

Figure 1 Impact of the progress from the baseline data and in each of the visits, and all the standards in the 11 participating units.
General data: In the initial data (baseline data) obtained from standard 1: patient identification, was of 30.13% compliance, that in implementing the project was achieved, up to 79.1%, emphasizing the strengthening f of Essential Actions for the safety of the patient of the Council of General Health, being an area of opportunity this action since the omission of the correct identification of the patients can mean increase in the cause of adverse events. For standard 2: medical diagnosis.- a baseline figure of 29.63% was obtained, reaching 60.6% by reinforcing NOM-004-SSA3-2012, 5 from the clinical file to the interior of the units evaluated, following up on the update of the medical diagnosis according to the evolution of the patient.
Vital signs: The percentage of compliance in the standards related to vital signs were, 3: heart rate and temperature. - baseline data corresponded to 29.96% 99.3% managing to reach compliance, 4: Pressure arterial.- a 51.85% improved to 90.9%, PAE 5: venous pressure of 84.34% central.- reached 100% taking into account that only in 47 of the patients this care was indicated in the baseline data and in 4 in the final data, PAE 6: blood pressure. - The first data was met with 40.40%, optimizing to 97.6% PAE 7: alteration of the vital constants.- of 39.56% is evaluated at the end in a 72.4% compliance, demonstrating that the return to the importance of records of vital signs must be done in the right place, in an appropriate, readable, complete and correct they allow the staff to know and intercommunicate the patient's health status by performing it according to the medical indication and/or at least once every 8 hours.
Compliance with general care: Of the standards related to the taking of height, weight and perimeters: PAE 8, 9 and 10, the baseline data were 44.78%, 42.08%, 67.50%, respectively, having significant advances up to 92.6%. % for 8, 94.3% for 9 and 10 for 100%. The standard 11, 12 and 13 proper to 11: Formula / Diet / oral fluids. - The baseline data is 29.63%, increasing to 92.6% with the awareness of the staff to record on the nursing sheet properly and correctly the medical indication regarding diet; 12: Patient intake. - 27.61% was the compliance in the baseline data, increasing to 77.4% with the recording of the detailed description of the food ingested by the user, allowing a better control of the income. 13: fasting.- the initial figure of 50.50% extending the compliance record to 96%.
Administration of parenteral fluids: parenteral fluids began with a 38.89% compliance amplifying the appropriate record in the nursing sheet regarding the consistency between the type of solution provided, dose, frequency, quantity and schedule with the prescription medical examination 94.3%; in 15: blood elements. - for the baseline data, only 60 cases were found, of which 77.27% had compliance, adequately registering the medical indication for the final data. Only 12 cases were detected, of which compliance was detected. of 94.6% , Standard 16: OPPORTUNITY.- requesting compliance with regulations for disposal of human blood and blood components for therapeutic purposes NOM-253-SSA1-2012 5 by reinforcing the registry in an adequate way, we achieved a 100% growth of 79.45% which was considered as data at the beginning of the project. Standard 17: Total parenteral income - starting with 25.42%, it is improved to 87.5% by highlighting and making the timely and complete registration, correct and with a unit of measurement of the sum of the total parenteral income per shift.6-10
Control of liquids: Standard 18: Control of liquids (Income).- increases from 30.64% to 92.6% by recording the sum of all elements of income (VO, parenteral, drugs, blood elements) per shift. The first values obtained in the PAE 19: control of liquids (outflows) uresis PAE 20: control of liquids (discharges) evacuation were at levels of 14.65%, 13.64% achieving a significant improvement with the disposition obtained when emphasizing around performing correctly the records reaching compliance of 97.6%, 94.3%. Standard 21: control of liquids (discharges) bleeding, vomiting, suction and drainage. - marking the baseline data in 30.97% when making the records of these eliminations correctly, with unit of measurement and facilitating the summation of the total of discharges by shift and in the balance of 24 hours achieve a 90.2% compliance. The results obtained by standards 22: total revenue.- and 23: total expenditures.- by not losing sight of the fact that strict liquid controls must be precise, quantifying the total of expenses and expenditures with the calculation and record of insensitive losses and metabolic water, obtaining a 19.36% and 21.04% improvement of 82.5% in both standards.11
Compliance with the medical prescription: 24 request and taking of laboratory studies, 25 taking of reagents, 26 programming of surgical intervention, 27 administration of medicines and 28 realization of treatments;
For own standards to 24: Request to take laboratory studies. - and 25: Reagents taking .- are 41.24% and 63.46% of compliance prior to the implementation of the educational strategy where emphasis was placed on good nursing practice in the adequate and timely collection and recording of these standards, increasing compliance to 82.5% and 90.9% respectively. 26: programming of surgical intervention. - The data in the first review were only 77.94% compliance, where the standard requests the congruence between the records contained in the nursing sheet related to the date and type of request programming of surgical intervention with the type and date recorded in the medical prescription reaching 100% after the educational strategy.12–14
27: Administration of medicines: There was an advance of the initial data 61.11% of compliance increasing only to 85.9%, the record that was detected in the first measurements with respect to 28. Performance of treatment.- is 42.25% that later on the educational strategy improved the registration obtaining a compliance of 84.2%,
Detection of nursing care and independent care needs: 29: Signs and symptoms referring to the assessment, in the baseline data 21.72% improving to 80.8% in the final data, 30: Nursing Care.- registering in the baseline data 17.51% and for the final data 77.4% percentage that showed the lack of documentary evidence in the granting of nursing care. 31: Identification of needs.- basal data sample 38.55% final data 75.8%, 32: Nursing Interventions.- basal data 19.63% final data 69% evaluating in the registry with the congruence in relation to the nursing diagnosis made to the patient . El 33: Response and evolution. - 11.28 % compliance and reaching only 23.6% progress. In the complete record of the person in charge of standard care 34, a percentage of 13.64% was obtained and when implementing the educational strategy, only 69% of compliance was achieved, 35. Responsible for supervising the service: 2.19% performed the registration according to the baseline data, increasing only to 23.6%.15
Structure and results: 36: sufficient staff.- showed us in the initial evaluation that 48.65% of the cases did not comply with this standard after orientation when implementing the educational strategy, an increase of 84.2% was obtained in the improvement of the staff distribution. 37: trained personnel. - Evaluates if the personnel has the competences to provide quality care and insurance according to the academic profile, obtaining a 61.78% compliance achieving the final optimization of 85.9%. The standard 38: material .- assesses whether there is congruence, sufficiency and opportunity in the provision and availability of supplies to provide care such as medicines, equipment, healing material and clothing was identified that in the initial data alone, 56.22% of records reported insufficiency, achieving an improvement of 77.4% in the final estimate. In relation to standard 39: complaint - related to the results in society, which investigates the presence of complaints and / or claims filed by patient / family, related to incidents derived from the provision of services; in 177 67.17% complied with the registration of these complaints after orienting the personnel, an evolution of the record of 79.1% of 15 cases was obtained. Standard 40 : results.- absence of patients suffering adverse events related to nursing care, it was identified that in the initial evaluation only 64.64% of 149 cases were detected, at the end the process obtained an advance to 80.8% of registration of 18 cases. Figure 2–5

Figure 2 Impact of the progress after the educational strategy at 12 weeks from the start of the project standards from 1 to 10.
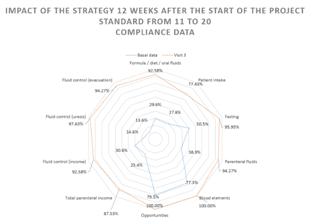
Figure 3 Impact of the advance after the educational strategy at 12 weeks from the start of the project standards from 1 1 to 20.

Figure 4 Impact of the progress after the educational strategy at 12 weeks from the start of the project standards from 21 to 30.
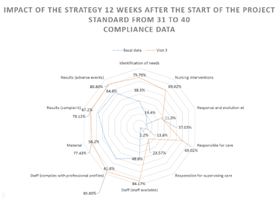
Figure 5 Impact of the progress after the educational strategy at 12 weeks from the start of the project standards from 3 1 to 40.
Analysis
Today it is emphatically speaks of the quality of care and patient safety and the big question is: Does the nurse is really giving quality care and patient safety? Although it is true the standardization of procedures, current regulations, clinical practice guidelines, essential actions for patient safety, among others they indicate the lines to follow to give adequate attention to the users, however by not having complete and correct proper records of these activities put on disadvantage all actions performed attached to the lex artist ad hoc performed by the nurse. With a compliance of less than 40% in the baseline of all the standards, and these being only the request for registration of basic actions of the nurse's day- to- day activities, it reveals that there are important flaws of knowledge or of implementation proper record of the care of patient before by staff of nursing to and even this is questioned whether it was or not executed properly care.
Analyzing the 5 standards with the greatest opportunity for improvement that were found in the conjunction of the evaluated units, by order of appearance on the card the medical diagnosis record that is defined as the process that requires the existence and/or absence of any disease performed by a doctor, based on information accumulated in different sources 7; is you without doubt is a support element for a good tour valuation and thereby be able to perform diagnostics Nursing more appropriate, however baseline data reveal that meets less than 30% of a good record, complete, correct and legible of this important section of the clinical file, which according to NOM-004- SSA3-2012 5 It must be present in all the pages that integrate this document, in addition to the fact that the medical diagnosis must be progressed in line with the evolution of the patient or modified if a pathology is added or the patient's state of health changes. We observed that it is not done properly, so it is emphatically suggested that the responsible physician be asked to change this information according to the patient's evolution and, on the part of the nursing team, record the information in a timely manner. On the other hand, NOM-019-SSA3-2013 6, for the practice of nursing in the National Health System, refers in section 4.17 that the process of nursing care: is the methodological tool that allows for the granting of care to healthy or sick people through a systematized and comprehensive care, whose main objective is to address individual or group, real or potential human responses; It is composed of five interrelated stages: assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, execution and evaluation. In relation to the above, the standards from 29 to 33 evaluate compliance with the registry related to independent nursing care resulting in linking the 5 points a baseline figure of 21.73% managed to 'm reaching only 65.2% after implementation of the education strategy being 32: Nursing Interventions and 33: Response and evolution, those found most affected since they initially meet 19.63% and 11.28% achieving 69% and 23.6% respectively after the improvement intervention. The non-documentation in the clinical records of nursing, repeatedly wants to justify with the supposed overwork, which was observed to be rather lack of planning and organization of times, in the distribution of patients and in the execution of the same care, being that this lack of written evidence does not exempt the person who executes the intervention from responsibility, to this must be added that as such the intervention is "All treatment, based on the knowledge and clinical judgment, that a nursing professional performs to favor the patient's expected outcome" and what is requested in this standard is to fully comply with the registration. Around the need to emphasize the area of opportunity for 33: Response and evolution we can comment that this is the number 3 standard of the most unfulfilled and is where we put to the table some questions Why not register this point? Is it due to lack of knowledge? Why lack of interest in monitoring patients? What is observed is that the lack of supervision coupled with the non-existence in some units of the shift link causes the breach of this standard where the assessment must be recorded performed at the end of the shift, change of service, discharge and / or voluntary discharge must be consistent with the patient's condition.
In relation to the 34 Responsible for the care, which requests the existence of the registration in the corresponding space of: name and surname of the mother and father signing and registration of the nurse responsible for the care, a percentage of 13.64% was obtained, achieving a change to 69 % compliance with the registry after the supervision observations were made, observing the improvement in the care and care given to the patient by the healthcare personnel.
Compared to standard 35 responsible for overseeing the care is important to emphasize that e l initial or baseline data corresponds to an alarming 2.18 % increase only to 23.6% after implementation of the project "Monitoring and strengthening the link shift: a strategy for improving practice of Nursing ", without a doubt we are completely convinced that if we work in compliance with this standard, the totality of the standards would be raised and maintained, based on the fact that the empowerment of the Nursing should be based on greater knowledge and ability to manage human capital and based on the NOM-019-SSA3-2013 6, For the practice of nursing in the National Health System, determines in paragraph 5.7 that the authorities of establishments for medical care that provide nursing services must: Give the induction to the position to all new staff to an institution or subject to movement, in a specific area, according to the needs detected, in terms of the provisions applicable legal systems, and therefore should carry out constant supervision of the appropriate compliance with the procedures provided, as well as the correct nursing records.
In the application and implementation of this educational strategy, as already mentioned, 11 hospital units were included where we could verify that it is not enough to only determine the problems and incidents, nor to understand the causes, but to find solutions that address the fundamental causes of the little attention safe.
Based on this evidence, we can point out that the baseline data obtained in this research referring to the nursing practice records are alarming, worrisome and totally impacting, the improvement proposal with the implementation of the project "Supervision and strengthening of the shift link: strategy to improve Nursing practice "and the adoption of new measures are important contributions that ensure a change in the increasing compliance with the appropriate clinical records , as well as the substantial improvement of safe care and, therefore, the quality of patients and the reduction of adverse events and nonconformities of users and / or their relatives. This being a problem not only in form but in the background of which the care units should be occupied as well as the educational ones, since the totality of the standards evaluated in this intervention are part of the daily work of nursing when giving care, such as patient identification, record vital signs, anthropometric, dietary compliance and description of this, control log liquids in their income and expenses as well as the nursing process related to the practice itself and independent of nursing.
The concern generated by getting l to evidence of poor compliance in the units evaluated, startle gender and prompt reaction by the set of integrant is the headquarters of Nursing to undoubtedly the institutional approach, played an important role in the results were obtained after the implementation of the educational strategy by modifying in the evidence not only the correct registration but the improvement in care to more than 80% of favorability of showing with this the change, which facilitates the impulse of proactivity in the good practices and with this the safety of the patient. The prelude to a substantial change must be promoted basically by the heads that for these purposes we will define as the group of members that make up the leaders that lead the group of nurses that work in a hospital unit , and that by performing daily and constant supervision of The interventions and care carried out by the health care personnel not only ensures the increase of a considerable amount of the figures of adequate clinical records, correct, timely, legible, without erasures or amendments but also the safety of the care dimensioning the quality in the watch out.
The training and constant updating in the operational processes is becoming increasingly important , however continuous action plans must be made for the personnel that in their function is to supervise, as this ensures correcting possible deviations, avoiding failures, achieving one proper supervision in the implementation of care and l as good practices and nursing to turn on the link.
None.
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.

© . This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.