MOJ
eISSN: 2374-6939


Research Article Volume 2 Issue 4
1Department of Orthopaedics, Bari-Ilizarov Orthopaedic Centre, Bangladesh
2Visiting and Honored Prof., Russian Ilizarov Scientific Centre, Russia
Correspondence: Mofakhkharul Bari, Bari-Ilizarov Orthopaedic Centre, 72, Satmasjid Road, Nizams Shankar Plaza, Dhanmondi, Dhaka, Bangladesh, Tel +8801819211595
Received: April 12, 2015 | Published: April 18, 2015
Citation: Bari MM, Islam S, Rahman M, et al. Treatment of chronic osteomyelitis in children by Ilizarov technique. MOJ Orthop Rheumatol. 2015;2(4):123-125. DOI: 10.15406/mojor.2015.02.00054
Chronic osteomyelitis in children is very difficult to eradicate completely. The patient with chronic osteomyelitis has a new hope of cure by recent advances in the management of chronic osteomyelitis. Systemic manifestations may subside, but one or more foci in the bone may contain purulent material, infected granulation tissue or a sequestrum. Treatment of this condition is to irradiate the infection and to restore the functional activity of the patient. Our objective is to highlight the various causes of recurrence, relevant classification, pathophysiology and modern treatment of chronic osteomyelitis with Ilizarov technique.1–3
Keywords: Chronic osteomyelitis, Radical resection, Ilizarov
Recent advances in the management of chronic osteomyelitis in children includes
Chronic osteomyelitis is often associated with
What are the causes of chronic osteomyelitis?
In children sometimes you don't need to perform radical resection, even if you find pandiaphyseal osteomyelitis with pathological fracture, and persistent discharging sinus. It is a waste of money to advice intravenous antibiotic for a long time.
Anatomic classification or adult chronic osteomyelitis is of 4 types
Study places
Duration: January 1993 to January 2013
Number of Children: 165 (85 were severe)
Age range: 3-15 years
Follow-up period: 2-19 years.
The cases were treated as follows
In adult we must identify the organisms. Clinical staging can be done according to Cierny-Mader classification. This classification has developed an anatomical situation of chronic osteomyelitis and physiologic response of the host are taken into consideration.
Radical resections
The treatment of chronic osteomyelitis should be similar to treatment of giant cell tumor of bone. Surgical debridement is the main th9ing of treatment in chronic osteomyelitis
Noramal saline is used for cleaning and when oozing Haversian systems are visualized, we stop here.
Treatment of cavity
With the liizarov method a well off bone above or below the cavity can be transported across the cavity which can be completely closed.
Bone gap and bone transport
In chronic osteomyelitis: Academician professor llizarov introduced the method of bone transport in a large gap (Figure 1). For bone transport the orthopaedic surgeon can now resect the entire avascular bone and create a large gap. Resection followed by bone transport has revolutionized the better management of chronic Osteomyelitis in children and adult. The Ilizarov method simultaneously addresses the deformity, limb length discrepancy and joint mobility (Figure 2).
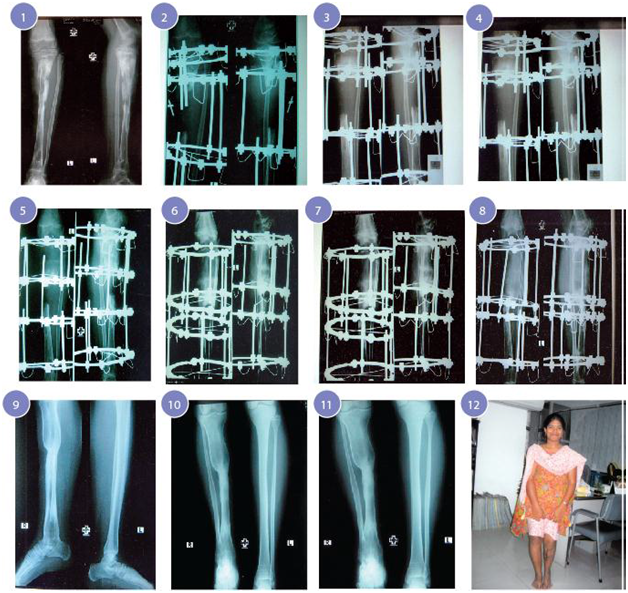
Figure 1 Case 1 1. Pandiaphyseal osteomyelitis of left tibia.
2. Excision of avascular dead bone to create gap non-union 2nd post OP.
3. Corticotomy & lengthening performed after 10 days follow up.
4. After 3 weeks follow up.
5. After 1 month follow up.
6. After 1 and half months follow up.
7. After 2 months follow up.
8. After 2 and half months follow up.
9,10,11. Radiographic result after 3 months follow up.
12. Clinical appearance of the patient after 6 months.
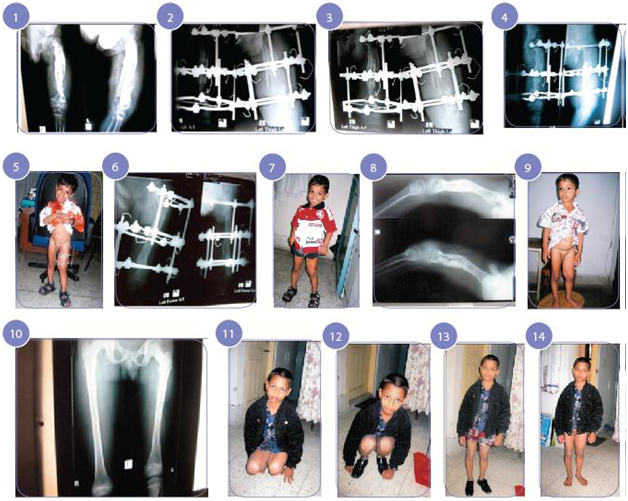
Figure 2 Case 2 1. Pandiaphyseal osteomyelitis with pathological fracture of left femur.
2. 5 days after application of Ilizarov.
3. 2 months after application of Ilizarov.
4. 3 months after application of Ilizarov.
5. Smiling baby with Ilizarov in situ.
6. 4 months follow up after application of Ilizarov.
7. Patient is happy.
8. Radiograph result after 5 months.
9. Clinical appearance of the patient after 5 months.
10. Radiograph after 6 years follow up.
11. Baby can squat.
12. Full range of movements.
13. Clinical appearance of the patient after 6 years.
14. After 6 years of follow up.
Surgical procedure
Preoperative planning and assessment is very important in treating the chronic osteomyelitis in children. 1. We must palpate arteria dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial artery. 2. Local temperature and color of the foot must be seen. 3. We must assess with preoperative pulse- Occimeter. If the Ilizarov fixator is stable then the Corticotomy is performed at the proximal metaphyseal or distal metaphyseal region. To eliminate infection vascularization of the osteomyelitic centre is increased by the biological stimulation of corticotomy. Professor Ilizarov said – infection burns in the fire of regeneration and that is absolutely true in case of children osteomyelitis. The gap is closed by gradual controlled coordinated stretching by transporting the segment. 1mm per day till the distal end locks the proximal end of the distal fragment. Then the two fragments are compressed together. If the gap is too large, we should introduce a guide wire in between the fragments to keep the bone in anatomical position and to prevent any kind of angulation and rotation which can cause malunion and deformity of the limb. The Ilizarov fixator is kept till the new corticotomy site the fragments are distracted till the limb length is restored.8–10
Nutritional status
In Bangladesh, poor nutrition is also a major factor. Complications are a fact of life that every orthopaedic surgeon has to face. Poor nutrition in orthopaedic surgery can make its complications more obvious. We can decrease complication by maintaining appropriate patient nutritional status.7
Antibiotics
First generation cephalosporin are appropriate for prophylactic uses: these drugs are more affective against gram positive cocci. Ciprofloxacin is bactericidal against most gram negative aerobic organisms, including P. Peruginose.7
Ilizarov technique serves four purposes:
Chronic osteomyelitis in children with pandiaphyseal osteomyelitis with pathological fracture, including discharging sinus can be treated by stable fixation of Ilizarov apparatus. Sometime radical resection can also be done to create a gap which can be filled up by bone transportation with excellent results.
None.
None.

©2015 Bari, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.