MOJ
eISSN: 2374-6939


Research Article Volume 12 Issue 4
1Chief Consultant, Bari-Ilizarov Orthopaedic Centre, Visiting and Honored Prof, Russian Ilizarov Scientific Centre, Russia
2Professor, Bari-Ilizarov Orthopaedic Centre, Bangladesh
3Medical officer, Bari-Ilizarov Orthopaedic Centre, Bangladesh
Correspondence: Mofakhkharul Bari, Chief Consultant, Bari-Ilizarov Orthopaedic Centre, Visiting and Honored Professor, Russian Ilizarov Scientific Centre, Kurgan, Bari-Ilizarov Orthopaedic Centre, 1/1, Block#E, Suvastu Shirazi Square, Lalmatia, Dhaka-1207, Bangladesh, Tel +88 01819 211595
Received: July 20, 2020 | Published: August 6, 2020
Citation: Bari MM, Shahidul I, Shayan BAMR. Humeral lengthening by Ilizarov technique in patients with post septic shortening. MOJ Orthop Rheumatol. 2020;12(4):86-88. DOI: 10.15406/mojor.2020.12.00524
Purpose: Humeral lengthening in patients with post septic shortening is a challenging procedure for Orthopaedic surgeon. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of humeral lengthening using Ilizarov fixator. We reviewed the literature on humeral lengthening using different fixators with regard to indications, operative technique, results and complications. We also retrospectively reviewed 12 patients treated with humeral lengthening using Ilizarov external fixation. The etiology was epiphyseal injury (7 cases), infection (5 cases). The average age at surgery was 14,5 years (range 12,5-23,5) with post septic humeral shortening. The patients were assessed clinically and radio-graphically. Follow up ranged from 1-10-years.The magnitude of lengthening achieved ranged from 5-15cm with an average of 7, 5cm. Functionally all the patients returned to their preoperative jobs and daily activities including sports. Complications included pin track infection in 8 patients, radial nerve palsy which recovered completely in one patient. Conclusion; Humeral lengthening is a valid method that improves the outcome following arm shortening and deformity correction including angulation and rotation. Extensive lengthening up to 100% of the original length could be achieved without increasing the risk of complications.
Method: Twelve patients were included in this study with post septic shortening of the humerus. All patients underwent distraction osteogenesis with the use of an Ilizarov fixator.
Results: The mean lengthening in patients with post septic shortening was 7.5cm. The mean healing index was 24.8 days/cm in the patients with achondroplasia and 25.5 days/cm in the patients with post septic shortening.
Conclusion: Humeral lengthening with use of Ilizarov fixators in patients with post septic shortening is an efficient method.
Keywords: humeral lengthening, post septic shortening, Ilizarov fixator, upper extremity lengthening
Humeral lengthening is a challenge for Orthopaedic and Reconstructive surgeon.1–6 Our aim is to judge the safety and complications of humeral lengthening. Upper limb lengthening allows to perform perineal hygiene.6,7 Lengthening of the humerus is the easiest and well tolerated by the patients. Complication rate is low and results are gratifying. Distraction osteogenesis is a powerful technique. Ilizarov fixator is very stable for lengthening of humerus with less pain.
We included twelve patients with twelve treated humeri. We did humeral lengthening procedure between 1997 to 2018 at our BARI-ILIZAROV Orthopedic Centre. Out of twelve patients, eight males and four females. Their mean age was 14.5 years. Thorough clinical Orthopaedic evaluation of upper extremity was done for every case. We evaluated the range of motion of shoulder, elbow and wrist joints. We should also assess the function of all joints. Preoperative neurologic assessment of the hand is absolutely mandatory. Anteroposterior and lateral view of x-ray of shoulder to elbow was done.
Surgical technique
Under general anesthesia we did all the surgeries. With fluoroscopic guidance 1.8 olive wires were placed in the proximal humerus, two rings were introduced distally, rings were placed with the biocompatible 1.8 smooth wires. A 10 mm incision is made in the lateral side of the upper humerus for osteotomy distal to the deltoid tuberosity, another incision is made in the distal humerus with 10mm serrated osteotome osteotomy was done. The significance of using serrated osteotome is that it doesn’t slip during osteotomy.1,8
Parameters |
|
Average lengthening(cm) |
7.5±2.5 |
Lengthening percentence (%)±SD |
30±15 |
Distraction rate(mm/day)±SD(range) |
0.80±30 |
Healing index(days/cm)±SD(range) |
25.50±8.3 |
Table 1 Results of evaluated parameters of the patients with post septic shortening of the humerus
Post-operative protocol
We started physiotherapy on the next day. Distraction started on the 4th POD (Post Operative Day). We recommend follow up every 14 days during distraction phase. Clinical evaluation and x-ray are mandatory during every visit. During the end of distraction phase, we must see the axis of the bone. We must take the calculation of joint orientation angles on the x-ray to find out the axial deviation. If we see this then we adjust the Ilizarov fixator to correct the angles to normal. Postoperative active psychotherapy and social status of a patient are of great importance. It is connected with the fact that some patients have psychogenic disorders of different degree. That is why our recommendation is to use the following psychotherapeutic measures:
Kinesiotherapy is important for the increase of general tonus and improvement of functions of the vital organisms (cardiovascular and respiratory). Kinesiology provides early static and dynamic function of the operated limb as well as the increase of lost movements of adjacent joints.
Before dismounting the Ilizarov fixator we must see 3 cortices of good regenerate bone. A temporary plaster is applied for 2 weeks after removal of the Ilizarov apparatus. The X-ray evaluation of the lengthening process is shown in Figure 1.
Complications of humeral lengthening
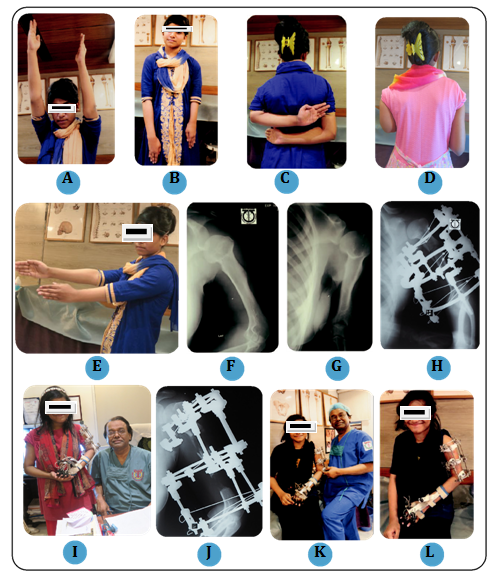
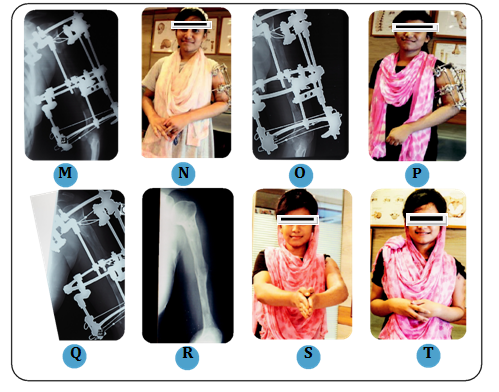
Figure 1 (A, B) Post septic 11cm shortening of left Humerus, 17 years old girl, front view before surgery
(C, D) Post septic 11cm shortening of left Humerus, 17 years old girl, back view before surgery
(E) Post septic 11cm shortening of left Humerus, side view position before surgery
(F,G) Radiograph of left Humerus, AP and Lateral view before surgery
(H) Radiograph of left Humerus, with the Ilizarov frame after surgery
(I) After 3 months follow-up smiling patient with Prof. M.M. Bari
(J) Radiograph of left Humerus during treatment procedure after 4 months
(K) Prof. M.M. Bari is ckecking the stability of the frame
(L) Smiling patient with the Ilizarov frame after 6 months follow-up
(M, N) Radiograph of left Humerus and patient during treatment procedure after 6 months
(O, P) Radiograph of left Humerus and patient during treatment procedure after 8 months
(Q) Radiograph of left Humerus during treatment procedure after 10 months
(R) Follow up after 11months, X-ray after treatment
(S,T) 11 months follow up, showing 11cm lengthening achieved, clinical result after treatment
We achieved 7.5cm lengthening on average. The distraction rate was 1mm/day. There were 2 axial deviations and one fixator loosening that was corrected accordingly. Pin-site infections were not a major problem; they were super facial and resolved with treatment. There were 2 axial deviations and that was corrected by changing the wires and rods. No neuropraxia of the radial nerve were occurred during the treatment time. Once we found the deformity, it was managed by closed manipulation.
Humeral lengthening is well tolerated by stable Ilizarov fixator. Neonatal osteomyelitis of the upper humerus and septic arthritis of the shoulder may cause severe shortening of the humerus. Humera vara is analogous to coxa vara in the hip. Lengthening of humerus improves function and cosmesis. Sometimes for simple lengthening uniaxial fixator can be used. For adults LRS system may be used. For angular deformity correction with length and rotation Ilizarov is the best option.9,10 In 8 patients we did bifocal lengthening. We considered both functional and cosmetic factors while planning the surgery. Lengthening of more than 20% of the primary length of bones in the lower extremity significantly increases the complication rate.11 Where as in the upper extremities even extensive elongation is relatively safe.12
Humeral lengthening in post- septic shortening with the application of Ilizarov fixator is an effective, safe, reliable method. Lengthening benefits the patient by giving him or her greater reach, while both sitting and standing.
None.
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
None.

©2020 Bari, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.