MOJ
eISSN: 2471-139X


Research Article Volume 5 Issue 6
1Department of Biology, Medical University of Varna, Bulgaria
2Vita Multidisciplinary Hospital for Active Treatment, Sofia, Bulgaria
Correspondence: Yaneva Galina, Department of Biology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Medical University of Varna, Varna 9003, 55 Marin Drinov Street, Bulgaria
Received: October 11, 2018 | Published: November 16, 2018
Citation: Galina Y, Ingilizova G. Main line patterns of palmar dermatoglyphics in female breast cancer patients. MOJ Anat & Physiol. 2018;5(6):347-349. DOI: 10.15406/mojap.2018.05.00223
Aim: Breast cancer incidence and mortality rates represent a serious socio-medical challenge worldwide. The present study illustrates some dermatoglyphic differences between breast cancer females and healthy controls.
Material and methods: We examined 82 females with clinically, histologically and mammographically proved breast cancer and 60 healthy controls. Conventional palmoscopic features including the four main palmar lines A, B, C, and D were examined by the method described by Cummins & Midlo.1
Results: We established statistically significant differences between both groups concerning the frequencies of main palm line A (χ2=14,96; p=0,0001), A 3(+4) (р<0,001), А 5(5‘+5“+6) (р<0,001), main palm line D (χ2=32,86; p=0,0001), D 9(+10) (р<0,0001) and D 11(+12+13) (р<0,0001) of the left hand. There were statistically reliable differences between these groups in terms of the frequencies of main palm line A (χ2=22,51; p=0,0001), A 3(+4) (р<0,001), А 5(5‘+5“+6) (р<0,001), main palm line D (χ2=15,65; p=0,0001), D 9(+10) (р<0,001), D 11(+12+13) (р<0,001), main line B (absence) (р<0,05) as well as of main line C (absence) (р<0,02) of the right hand.
Conclusion: We concluded that dermatoglyphic investigations of the main palmar lines could serve as an additional valuable prognostic tool for risk stratification in women suspected for breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer, dermatoglyphics, main palmar lines A, B, C, D, risk prognostication
In the recent decades, several articles deal with dermatoglyphic investigations in breast cancer patients.2–6 Fingerprint research prevails over palmar dermatoglyphics. However, specific palmar patterns such as ridge count, ATD angles and A, B, C and D main lines represent an integral component of diagnostic and prognostic armamentarium in female breast cancer patients.
Our purpose was to examine the differences between breast cancer females and healthy controls in terms of the A, B, C, and D main line palmar characteristics as a possible prognostic tool for breast cancer risk evaluation.
Our study covered 82 females with clinically, histologically and mammographically proved breast cancer and 60 healthy controls of Bulgarian ethic origin. Their age distributions in 10-year intervals were juxtaposed in Figure 1. The patients were hospitalized and operated on in the Clinic of Thoracic Surgery, St. Marina University Hospital of Varna, during the period between January 1, 2014 and December 31, 2017.
Conventional palmoscopic features including the four main palmar lines A, B, C, and D were examined by the method described by Cummins & Midlo.1 Data were processed by means of variation analysis (Student t-test) and χ2 test using SPSS software, version 19.
The results from χ2 test demonstrated statistically significant differences between both groups concerning the frequencies of main palm line A (χ2=14,96; p=0,0001), A 3(+4) (t=4,005; р<0,001), А 5(5‘+5“+6) (t=4,005; р<0,001) (Figure 2), main palm line D (χ2=32,86; p=0,0001), D 9(+10) (t=6,286; р<0,0001) and D 11(+12+13) (t=6,298; р<0,0001) (Figure 3) of the left hand.
The frequencies of the main lines B and C of the left hand did not differ statistically reliably between breast cancer females and healthy controls (χ2=2,00; p=0,156 and χ2=2,21; p=0,137, respectively).
The results from χ2 test demonstrated statistically reliable differences between both groups in terms of the frequencies of main palm line A (χ2=22,51; p=0,0001), A 3(+4) (t=4,922; р<0,001), А 5(5‘+5“+6) (t=4,922; р<0,001) (Figure 4), main palm line D (χ2=15,65; p=0,0001), D 9(+10) (t=4,185; р<0,001), D 11(+12+13) (t=4,326; р<0,001), main line B (absence) (t=2,056; р<0,05) as well as of main line C (absence) (t=2,42; р<0,02) (Figure 5) of the right hand.
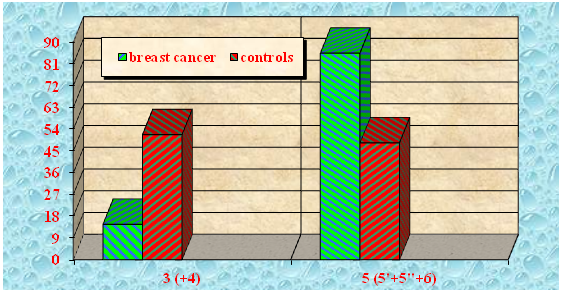
Figure 4 Main palm line A frequency of the right hand in breast cancer females and healthy controls.

Figure 5 Main palm line D frequency of the right hand in breast cancer females and healthy controls.
The results from a palmoscopic investigation of 48 bilateral palmar prints of breast cancer patients from different hospitals of Madhya Pradesh, India, demonstrated that the main line formula of 11.9.7 was less frequent (23,95%; 33,33% in the right and 14,58% in the left hand) than that in healthy controls (27,08%; 25,00% and 29,16%, respectively).7 This difference was, however, statistically insignificant.
The comparative study of palmar traits of 25 breast cancer female patients and 25 healthy controls of the same ethnic origin in India showed more aberrations of main palmar line C in the patients than in the controls.8 A scale for dermatoglyphic assessment was suggested that could be applied in the preliminary mass screening for identification of women bearing a high breast cancer risk.
A template-based image preprocessing as a functional plug-in of the dermatoglyphics analysis and detection system was developed.9 It included histogram redistribution, ridge orientation, and skeletonization for automatic identification of ridges and triradiuses. This system could be applied as an auxiliary diagnostic tool for mammary cancer and other hereditary diseases.
Based on our own data demonstrating statistically significant differences between breast cancer patients and healthy women concerning the frequencies of main palmar lines A and D as well as on scanty literature data available we could draw the conclusion that dermatoglyphic research dealing with these main palmar lines deserves a particular attention as an additional valuable prognostic tool for risk stratification in women suspected for breast cancer.
None.
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.

©2018 Galina, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.