Journal of
eISSN: 2379-6359


Short Communication Volume 11 Issue 1
Consultant ENT Surgeon at Leicester University Hospitals, Currently at Al Zahra Private Hospital,UAE
Correspondence: Abdul Juratli, DLO-RCS Eng. FRCS (ORL-HNS) England, Consultant ENT Surgeon at Leicester UniversityHospitals 2004-2016. Currently at Al Zahra Private Hospital, Cosmesug, Sharjah, UAE
Received: November 04, 2018 | Published: January 4, 2019
Citation: Juratli ARS. Classification of nasal deviation a short review. J Otolaryngol ENT Res. 2019;11(1):11-13. DOI: 10.15406/joentr.2019.11.00400
Due to its central location, the nose plays a prominent role in addressing the central facial axis which helps at camouflaging a large proportion of facial asymmetry. It gives the standard norm to the facial expressions, any little nasal deviation results in conspicuous facial disharmony and is often attended by nasal airway dysfunction. The nasal deviation causes a cosmetic deformity that is often disconcerting for patients. Nasal deviation carries considerable risk at the nasal airflow by increasing the nasal valve resistance at the level of midvault and/or lower alar structures.
The lack of objective measurement of the external nasal deviation puts the professions at risk of standardizing the severity of the deviation. It deprives the nasal plastic surgeons of having a common thought about the most likely convenient and available techniques for correcting the deviation in upper, middle, and lower thirds and nasal root as the grade of deviation is indicated.
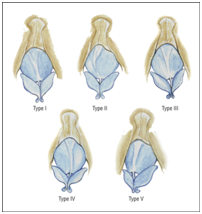
History and classification: The only classification of nasal deviation in the English publishes was published by"Yong Ju Jang, MD; Jong Hwan Wang, MD; Bong-Jae Lee, MD" in 2008. on reference "Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;134(3):311-315. doi:10.1001/archoto. 2007.46". They classified the nasal deviation into 5 types: I, a straight tilted bony pyramid with a straight tilted cartilaginous vault in the opposite direction; II, a straight tilted bony pyramid with a concavely or convexly bent cartilaginous vault; III, a straight bony pyramid with a tilted cartilaginous vault; IV, a straight bony pyramid with a bent cartilaginous vault, and V, a straight tilted bony pyramid and a tilted cartilaginous dorsum in the same direction. The classification has never been used in facial plastic references due to its complexity and the lack of its clinical implication and it is an observation of seventy-five sample size with twisted noses. The classification talked about the nose as two horizontal subunits (the bony pyramid and the cartilaginous vault) concerning the facial midline which isn’t identified Figure 1.
My study divides the external nose, for correction purposes, into three parts; upper, middle and lower. Each could be straight (Grade 0) or deviated first, second or third degree. It presents the nasal root separately because it is either not deviated (Grade 0), or deviated (Grade 1). The classification takes the axial facial midline and its equal distances from the brow-tip lines as the norm.1,2
The Classification helps at drawing a more precise picture of the outlining of the nasal deviation, helps at quan-tifying the improvement or the clearance of the deviation after surgery, it gives the surgeon an idea about the expected surgical time and could help at standardizing the number of the available techniques for correcting each grade of each third of the nasal deviation.
The external nose is divided into 3 parts; upper, middle and lower thirds. The upper is a bony structure made from the nasal spine of the frontal bone, two nasal bones, and the ascending or frontal process of the maxilla on both sides. The Middle third is a cartilaginous extension of the nasal dorsum consisting of a combination of triangular septal cartilage on the middle, the upper alar cartilages on each side and little sesamoid cartilages on the basal connection with the nasal bony pyriform aperture and the lower attachment of the alar base.3–7 The lower third is a fibrofatty cartilaginous structure with condensation of retaining ligaments; it is structured by the lower alar cartilages, caudal part of the nasal septum and the anterior maxillary nasal spine.
Alar base stabilization and the anterior nasal spine suture technique are essential for achieving a stable midline anchor for ensuring long-term straight nasal alignment.
The dorsal aesthetic line (DAL), provides a thoroughfare between the radix and nasal tip, it is in the middle between the two brow-tip aesthetic lines (BTAL) (Figure 2).
Each line follows a slight curve from the medial aspect of the superior orbital rim at the medial brow, passing through the lateral radix and extending to the nasal tip defining points. Brow-tip aesthetic lines are expected to follow an unbroken path.
The BTALs form a subtle and fluid hourglass appearance, slightly wider at the radix and tip, with the narrow most portions in the middle third (Figure 3).
During rhinoplasty, the facial plastic surgeon must carefully recreate a smooth brow-tip contour for a natural and aesthetically pleasing result.
Assessment of the dorsal aesthetic lines is helpful for identifying dorsal irregularities that will need to be corrected. These include asymmetry, excessive width, excessive narrowness or poor definition, likewise inverted V deformity, which results from a disruption of the brow-tip aesthetic lines secondary to prominent caudal edges of the nasal bones and loss of mid vault support and could hide a nasal dorsal aesthetic asymmetry.8–12
For the purpose of clinical implication, the nose is divided into three parts as I mentioned above. When the Nasal Root at the level of radix is not on the midline, it needs to be separately mentioned.
Ro: Nasal root.
U: Upper bony third.
M: Middle inner nasal valve cartilaginous third.
L: Lower external nasal valve and alar third.
Midline of the nose is identified as the vertical or sagittal line which connects between the mid-brow glabellar point and a mid-filtrum point on no-congenitally deformed upper lip.
|
Nasal root |
Upper third |
Middle third |
Lower third |
Grade 0 |
Ro |
U 0 R/L |
M 0 R/L |
L 0 R/L |
Grade I |
Ro I |
U 1 R/L |
M 1 R/L |
L 1 R/L |
Grade II |
N/A |
U 2 R/L |
M 2 R/L |
L 2 R/L |
Grade III |
N/A |
U 3 R/L |
M 3 R/L |
L 3 R/L |
Brow-Tip Aesthetic line: There are two lines, each one is a curvilinear line which extends from the medial aspect of the brow at the level of the medial border of the upper orbital margin extending down the lateral aspect of the radix and the dorsal projection of lateral nasal sidewall to the tip defining point at the side of the line.13
Grade (0) nasal deviation: each BTAL is 50% away from the midline (Figure 3).
Grade (1) nasal deviation: the BTALs are unequally away from the midline but none of them touching the midline. (Figure 4)
Grade (2) nasal deviation: One of the BTALs touching the axial facial midline (Figure 5).
Grade (3) nasal deviation: One of the BTALs is passing over and crossing the axial facial midline (Figure 6).
The classification is applied for pre and post op assessment and for the nose which has a history of any surgery. We need to mention any irregularity alongside the brow-tip lines separately.
The classification is applied when both BTLs touch each other in such case of having a sharp, edgy nasal dorsum, but there will be either Grade 0 when the midline meets the effused BTLs or Grade 3 when the midline does not touch the area of effusion.14
Ro 1 R: The BTALs at the level of the root of the nose of the nose are at the unequal distance from the axial midline, but none are touching the midline, and the deviation is on the right, Figure 4.
U 2 R: One of the BTALs is touching the midline in the upper third, and the deviation is on the right, Figure 5.
M 3 R: One of the BTALs is crossing over the midline in the middle third, and the deviation is on the right, Figure 6.
L 3 R: One of the BTALs is crossing over the midline in the lower third, and the deviation is on the right
Finally: The nose is out of the midline Ro1R, U2R, M3R, L3R. Such deformity is common in Developmentally Deviated Nose (DDN) which often comes with congenital facial asymmetry, asymmetrical sidewall’s length and asymmetrical alar base horizontal and axial levels Figure 6–8.
General considerations
Root deviation (Ro): Consider root transverse osteotomy and fracturing of the frontal nasal spine.
Upper third deviation: Consider tilted hump reduction and central ethmoidal block deviation. Medial, medial oblique, lateral, intermedial and transverse osteotomies are required depending on the severity of the deviation. Camouflage nasal dorsum and/or the short concaved side-wall could be necessarily required.
Middle third deviation: Consider thick, thin, unilateral, bilateral or extended spreader graft. Spreader flap is often applied when there is a hump reduction for 3 mm hight or more. Clocking suture helps in some cases, and crisscross with or without camouflaging the key-stone junction with diced cartilage and platelets poor plasma (PPP) or Tisseel glue or fascia or perichondrium grafts should be accounted to avoid a gap depression at the bony-cartilaginous junction. Extracorporeal septoplasty could be the only option to correct a severe deviation in the bony-cartilaginous junction and mid vault of the nose.
Lower third deviation: Consider stabilizing the caudal part of the septum on the midline. There are few techniques to secure the caudal septum on the anterior nasal spine. Creating straight caudal septal cartilage usually proceed the stabilization, by getting a firm L-Strut, extended septal graft, extended spreader graft or deploying 0.15 mm thickness, perforated PDS foil plate for temporary support. 15–20
Each of the lower alar cartilage domal angle and interdomal angle should be optimized and stabilized with the support of columellar strut, tongue-in-groove or anterior septal angle suspension suture on the midline. The lateral alar crurae should be wide enough, well supported and symmetrical before the final closure.
Quantification of nasal deviation by giving ascending numbers for each third of external nasal alignment will draw a clear picture for the listener to understand the description of nasal deviation. Specific shapes raise a risk on keystone area and suspicion about Lateral Wall Insufficiency "LWI" and nasal valve deficiency.
How the classifications help in managing cases and planning for the most convenient approach?
Ro1R or L: Transverse root osteotomy and facial asymmetry in case of non-traumatic history, are thought about, and the theory of Developmental nasal deviation become more to consider.
U1R or L: Asymmetrical hump reduction and lateral osteotomies, are considered as sufficient.
U3R or L: Raises the plan for an on-lay camouflage graft on the concave part of the bony sidewall as well as the osteotomies as per U1 including median and medial oblique osteotomy.
M1: On its own, unilateral spreader graft is usually adequate when a valve function issue is involved.
M3: Consider unilateral spreader graft, camouflage graft, asymmetrical auto spreader flap, and Clock suture at the same time. Keystone area is at significant risk, and extracorporeal septoplasty or Anterior Septal Reconstruction ASR is a technique which is, thought about in case of dorsal and caudal septal deformity. We could often find ourselves dealing with Zone 1 lateral wall insufficiency LWI.
L1: With straight and robust caudal septum, consider symmetrical intradermal followed by tip suspension on the anterior septal angle or Tongue-in-groove.
L3: with tip ptosis, asymmetrical lateral crural steal sutures and tip suspension with or without columellar strut and Shield graft or diced cartilage in glue and fascial graft should be considered dependant on the skin thickness and the severity of the ptotic tip. In case of over projected tip and tip ptosis, consider asymmetrical lateral crura overlap and vertical cut.
Finally: When the situation is Grade 2 in any of the thirds, address something in between as per the third neighbor deformity.
The anterior nasal valve integrity is often at risk, supporting the boundaries of the internal and external parts of the valve will give proper extended lasting nasal function. Most of the techniques as mentioned above will certainly help.
The Developmental Deviated Nose (DDN) often carries alar base level asymmetry which could require grafting the alar base-pyriform fossa junction with allogenous, homogenous or autogenous grafts at the receded side of the alar base.

©2019 Juratli. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.