Journal of
eISSN: 2471-1381


Review Article Volume 3 Issue 4
Department of Pharmacology, India
Correspondence: Arif A Faruqui, Department of Pharmacology, Clinical Pharmacologist, D-2, 16th Road, Midc Area Andheri East, Mumbai-93, Maharashtra, India, Tel 9193 2242 9615
Received: June 12, 2017 | Published: September 8, 2017
Citation: Faruqui AA. Anxiety induced refractory gastrointestinal disorders. J Liver Res Disord Ther. 2017;3(4):90-93. DOI: 10.15406/jlrdt.2017.03.00062
Million suffer from acid related disorders with little respite without treatment. Today progress made has given us a quantum leap in understanding the disease and this has translated into the development of effective treatment. Right from the use of antacids which dominated the treatment arena in the last century to the discovery of Histamine-2-receptor antagonists towards the second half of the last century, progress has been constant over the decades. Today the benefits of the PPIs (proton pump inhibitors) have percolated to countless people across the globe. At no point in history were acid disorders this effectively managed. Furthermore, the relationship between anxiety and heartburn is not an obvious one. Many of the patients that suffer from heartburn when they have anxiety already had GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disorder). However, GERD patients with psychological comorbidity tend to seek medical assistance for their acid reflux earlier than patients without comorbidity, probably due to anxiety, concern over painful symptoms and depression, prompting scientist to dwell on the approach forward. Lead by observations that are based on recent data about the contribution of psychological comorbidity to the PPI failure phenomenon, GERD patients who are not responsive to treatment should be evaluated for psychological comorbidity.
Keywords: histamine-2-receptor, GERD patients, PPI, inflammatory reactions, clinical condition
GI, gastrointestinal; IBS, irritable bowel syndrome; FD, functional dyspepsia; GERD, gastro esophageal reflux disorder; BE, barrett’s esophagus; EE, erosive esophagitis; NERD, non-erosive reflux disease; NCCP, non-cardiac chest pain; TCAs, tricyclic antidepressants
Functional gastrointestinal (GI) disorders are clinical syndromes characterized by chronic or relapsing GI symptoms in the absence of structural or biochemical abnormalities that can be identified following a standard diagnostic work-up. The irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and functional dyspepsia (FD) are the best recognized functional bowel disorders and both these disorders are highly prevalent. FD is a very common clinical condition affecting one-third of the population. Neurotransmitters produced in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract regulate GI motility, blood flow, secretion and absorption. The enteric nervous system and central nervous system have direct effects on each other. The brain-gut connection (axis) seems to be a mechanism that links the psycho emotional state with GI dysfunction. In the majority of FD patients, treatment is symptom based (Figure 1). Depending on the most dominant symptom, acid inhibitory or prokinetic compounds are given but the results remain often unsatisfactory. There remains a substantial group of patients that do not respond to therapy. It is believed that psychosocial factors and abnormalities of gut function play a role in the manifestation and severity of symptoms.1-3
GERD and its refractoriness to PPI treatment
GERD or gastroesophageal reflux disease is a condition that develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications. PPIs have profoundly revolutionized the treatment of GERD. Most patients with GERD fall into one of 3 categories: Non-erosive reflux disease (NERD), erosive Esophagitis (EE) and Barrett’s Esophagus (BE). The 2 main phenotypes of GERD (NERD and EE) appear to have different pathophysiological and clinical features and, most importantly, differ in their response to antireflux treatment. Patients with NERD often fail to respond adequately to PPI treatment. Refractory GERD is defined as partial response or lack of response in GERD patients taking PPI twice daily over a period of at least 3 months. It has been estimated that between 10% and 40% of GERD patients fail to respond symptomatically, either partially or completely, to a standard-dose PPI1 (Figure 2). Currently, this disorder is the most common presentation of GERD in gastroenterology practice.
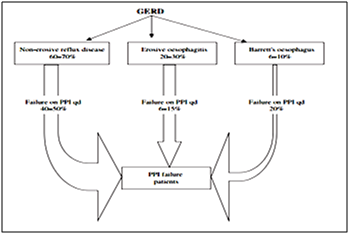
Figure 2 The proportion of patients that fail symptomatically PPI once daily in each of the GERD groups.1
Partial response to PPI therapy for GERD is associated with
Possible causes for failure of PPI therapy
Compliance, Improper dosing time, weakly acidic reflux, visceral hypersensitivity, Psychologic comorbidities, Concomitant functional bowel disease, Delayed gastric emptying, and Eosinophilic esophagitis.3
Non cardiac chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that we feel between neck and upper abdomen. Non-cardiac chest pain (NCCP) is defined as recurring retrosternal chest pain of non-cardiac origin. NCCP affects almost one-third of the general population. Among various underlying mechanisms for this condition, GERD is by far the most common cause.4 Other important etiological factors that were proposed for NCCP include esophageal dysmotility, visceral hyperalgesia, and psychological comorbidity. Psychological comorbidity is common in patients with NCCP and affects up to 75% patients.5
Mechanisms of NCCP includes
Esophageal hypersensitivity
Regardless of the reflux contents, it should be emphasized that esophageal hypersensitivity may play a critical role in the development of heartburn. In patients with GER (gastro esophageal reflux) symptoms, visceral hypersensitivity may occur as a consequence of long-term exposure to acid or nonacid reflux, or may even be present without exposure to erosive substances. This involves dilated intercellular spaces and exposure of sub-epithelial nerves to acid leading to sensitisation of peripheral afferent nerves and spinal dorsal horn neurons. Once central sensitisation is established, it can continue to potentiate pain after the initiating peripheral stimulus is discontinued. Increased esophageal sensitivity to chemical, mechanical and electrical stimuli in functional heartburn patients is one of the commonest causes of PPI failures.6
GERD and psychological comorbidity
Patients with GERD demonstrate significantly higher anxiety and depression scores as compared with normal subjects. It has been shown that subjects who have been exposed to prolonged life stressors are more likely to complain of symptoms of GERD. Additionally, psychological comorbidity may contribute to patients’ failure to respond to PPI treatment. Patients with stress-related symptoms display a higher intensity and frequency of GERD symptoms than stress-unrelated patients. During acute stress, patients report increased severity and/or frequency of GERD-related symptoms in the presence or even in the absence of an alteration in oesophageal acid exposure. Kamolz et al.7 demonstrated that psychological intervention significantly improved subjective outcome in GERD patients with stress-related symptoms, which was comparable to the outcome of patients with stress-unrelated GERD undergoing laparoscopic antireflux surgery (Figure 3).

Figure 3 Frequency of heartburn in cases of specific psychiatric disorders.7
Up to 60% of patients with GERD reported worsening of their symptoms in times of stress. GERD affects a wide range of aspects of quality of Life. GERD patients demonstrate higher levels of anxiety, depression, obsessionality, pessimism, and gastrointestinal susceptibility and are more likely to have psychiatric diagnoses. Thus, a clear synergy exists between GERD and psychological disorders. These patients require a multimodality approach to include antidepressants.6 A synergy exists between the psychological and physiological aspects of esophageal and other gastrointestinal symptoms. Patients with GERD demonstrate significantly higher anxiety and depression scores as compared with normal subjects.8
Clinical evidence: Population-based studies reported positive association between anxiety, depression with increased reflux symptoms and patients with poor correlation of symptoms with acid reflux events display a high level of anxiety and hysteria. Refractory patients are more likely to experience psychological distress that exacerbates esophageal pain hypersensitivity. Psychological stress contributes to esophageal hypersensitivity by central neural mechanisms and by a contributing effect of stress-induced impairment of esophageal mucosal integrity. Thus, both hypersensitivity and psychological factors can lead to enhanced perception and contribute to refractoriness.6
In population-based, cross-sectional, case-control study, reflux symptoms were assessed in 65333 participants. Subjects reporting anxiety without depression had a 3.2-fold increased risk of reflux, subjects with depression without anxiety had a 1.7-fold increased risk and subjects with both anxiety and depression had a 2.8-fold increased risk, compared to subjects without anxiety or depression, suggesting anxiety and depression are strongly associated with reflux symptoms9,10 (Figure 4). Furthermore, clinical trials have demonstrated that, adding Tricyclic antidepressant to a PPI was more effective than a double-dose of PPI in patients with FCP refractory to a conventional dose of PPI.

Figure 4 Prevalence of
Need of psychological intervention
Psychological comorbidity among GERD patients appears to play an important role in response or failure of response to PPI treatment. Psychological intervention can improve the general well-being and quality of life of patients with GI symptoms and also influence the outcome of medical and surgical treatment.11 Tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors have shown to improve visceral analgesic effect in esophageal pain in patients with non-cardiac chest pain.12 Antidepressants reduce or relieve psychological and mental factors, which are known to be capable of inducing FD, GERD, NERD symptoms. Reduce cortex excitability, thus reducing cortical interference on the enteric nervous system and helping the recovery of gastrointestinal function, including motility, secretion and sensation. Reduce stress responses and coordinate the function of T-helper cells and inhibitory T cells, thus reducing the inflammatory reactions of the gastrointestinal mucosa. Affect the modulatory effect of neurotransmitters on gastrointestinal function (motor, sensory and secretion).13
Emotional stress is one of the risk factors for GERD and continuous reflux symptoms and other discomfort may lead to emotional disorders. Furthermore, anxiety or depression of the patient reduces the effectiveness of treatment with a PPI.14In patients with non GERD-related NCCP (especially those refractory to conventional doses of PPI), treatment should be targeted to alternative drugs, such as pain modulating agents. Recent studies have focused on modulating nociception and visceral pain sensation pathways for decreasing chest pain using antidepressants. Symptomatic response to PPIs in patients with NERD is as low as 37% compared to 56% in patients with EE. PPIs account for a significant cost expenditure and expose the patients to potential risks associated with long term PPI therapy. Low response rate to PPI is likely to be due to other disorders such as psychological comorbidities.14Stress has been demonstrated to exacerbate symptoms in 64% of GERD patients & stress, anxiety, and psychological conditions are important determinants of heartburn perception.15Hypersensitivity and psychological problems have an important role in the pathogenesis of FCP. It is believed that TCAs (Tricyclic Antidepressants) confer their visceral analgesic effect by acting at the CNS and/or sensory afferents level. A commonly held hypothesis is that TCAs, which indirectly stimulate Norepinephrine and serotonin receptors by blocking the reuptake of Norepinephrine and serotonin, work as neuromodulators, affecting the brain-gut axis by altering neurotransmitter systems within the limbic system and other pain centres of the brain (e.g., anterior cingulate cortex). FCP respond favourably to low-dose Amitriptyline in combination with a PPI. PPIs decreases acid production and have high healing rates and enhance the rates of resolution of dyspeptic symptoms.
NERD patients demonstrate higher prevalence of psychological disorders which is postulated as underlying reasons for their lower response rate to PPIs. Stress, anxiety, and psychological conditions are important determinants of heartburn perception. Low-dose tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline), work as a neuromodulators by altering visceral sensation and increasing the pain threshold in patients with reduced gastric sensitivity. Norepinephrine and serotonin are the endogenous analgesic mechanisms in the descending pain pathways. TCAs stimulate norepinephrine and serotonin receptors by blocking the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin. PPIs (Pantoprazole) decrease acid production and have high healing rates and enhance the rates of resolution of dyspeptic symptoms. The synergistic effects of tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline) in combination with a conventional dose of PPI (Pantoprazole) could have an important role in improving quality of life of patients with reflux disorders associated with psychological comorbidities.
None.
Author declares that there is no conflict of interest.

©2017 Faruqui. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.