
Proceeding Volume 7 Issue 3
Post Dural Punct: Headache
Lt Col Faiz Lt Col Faiz
Regret for the inconvenience: we are taking measures to prevent fraudulent form submissions by extractors and page crawlers. Please type the correct Captcha word to see email ID.

Department of Medicine, India
Correspondence: Lt Col Faiz Ahmed, Department of Medicine, Armed Forces Medical College, Pune, India, Tel 9988677867
Received: October 21, 2016 | Published: March 1, 2017
Citation: Ahmed LCF (2017) Post Dural Punct: Headache. J Anesth Crit Care Open Access 7(3): 00261. DOI: 10.15406/jaccoa.2017.07.00261
Download PDF
Proceeding
PDPH can occur both in spinal and epidural due to CSF leakage.
Pathio Physiology of PDPH
- CSF leakage.
PDPH occurs when CSF leakage > CSF Production
- Cerebrovasodilation.
Body attempts to maintain homepstasis within cranium.
- CSF lead to compensatory Cerebrovasodilation and headache.
- Menigeal Irritation.
- Pnemocephalus.
Accidental intrathecal injection of air during epidural may cause relatively sudden onset of headache.
Risk factors of PDPH
- Patient factors:
- Gender__females at higher risk.
- Age__younger pts at higher risk.
- Needle characteristics:
- Size larger needle size increases loss of CSF and incidence of PDPH.
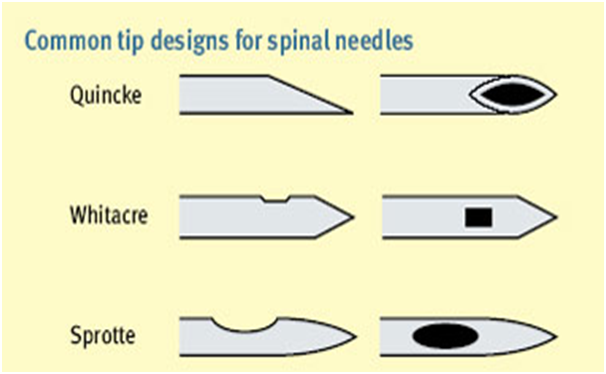
- Shape sharp cutting-edge beveled needle has increased
- Incidence of PDPH when compared with pencil-point needles.
Control risk factors of PDPH
- Procedure factors:
- Needle should be inserted “parallel” to dural fibers. Usually, dural fibers run longitudinally.
- Paramedian versus midline approach: paramedian may have decreased incidence of PDPH (“flap” rather than a “tin-lid” opening).
- Mulitiple punctures increase risk of PDPH because of increased loss of CSF.
Clinical assessment of PDPH
- Occipto frontal headache.
- Aggravate sitting position.
- Patient comfortable supine position.
- PDPH usually appears 1 to 2 days after dural puncture and lasts (if untreated) for upto 7 days in most cases.
- Other associated symptoms (not reliable).
- Photphobia, nausea, vomiting, auditory disturbances.
- Cranial nerve involvement (diplopia).
Treatment of PDPH
- Conservative
- Analgesic + Rehydration and caffine (i/v or oral)
- Soft diet.
- Caffenie provides transient relief via vasoconstriction.
- Invasive.
- Epidural blood patch (gold standard).
- Success rate is 70% to 90%.
- Two operators required.
- One takes 15-20 ml of blood from patient.
- Other injects this blood in epidural space at same level or one level below after starile technique.1–3

Acknowledgments
Conflicts of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Funding
References
- Johns Hopkins Anesthesiology Book.
- MorganText Book.
- Aitkenheads Text Book.

©2017 Ahmed. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the,
which
permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.




