eISSN: 2574-9838


Introduction: A higher incidence of swallowing and developmental disorders has been reported in term infants with gastroesophageal reflux (GER) and no other apparent disorders when compared to healthy. No physiological explanation for this has been suggested and none of this evidence is considered when infants with GER are assessed. Brainstem is involved in deglutition and other automatism regulation especially early in life and has been proposed to participate, in a vertical-integrative hierarchical system, with higher nervous structures in the regulation of functional status, attention, and emotional reactivity.
Objective: Report the follow-up during the first year of life of three term infants born under low risk conditions apparently healthy except for GER. Search for a relation between GER, swallowing disorders and development in which nervous system could be involved.
Methods: Three infants born under low risk conditions and diagnosed with GER within the first three months of life were followed for a year. Radiological study of swallowing, and brainstem auditory-evoked potentials (BAEP) were performed at involvement and at six months of age. Patients where monthly assessed with Bayley II infant developmental scale and a neurological evaluation.
Results: The three patients showed deglutition, development and self-regulation alterations that may not be explained by GER itself. Alterations on BAEP were reported.
Conclusion: Further research should be done to establish if GER in infancy could be an early indicator of brainstem and neurological disorganization that could be associated to other complications that could be prevented with early intervention.
Keywords: gastroesophageal reflux, development, brain stem, self-regulation, swallowing disorders, deglutition
Almost 60% of infants younger than three months old regurgitate daily.1 It is known that 13.4% of term infants with gastro esophageal reflux (GER) or respiratory symptoms without any other apparent disorders show significantly higher frequencies of sucking and swallowing disorders than healthy infants.2,3 Isolated reports of lower developmental scores in healthy children except for GER have been made.4 No physiological explanation for this has been proposed, and none of this evidence is considered when infants with GER are assessed, especially if they do not have any neurological or concomitant diseases.
Sucking, swallowing, and breathing is a complex process that requires different central and peripheral nervous structures to mature in order to be performed successfully. Brain stem and higher central nervous system structures participate in regulating sucking-swallowing sequences and their coordination with breathing.5–7 Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) control develops gradually and is regulated by brain stem nuclei.8
We searched for a possible association of GER with other swallowing disorders, and development, where central nervous system and brainstem regulation could be involved. Three term infants were randomly selected from a cohort of patients born under low risk conditions with normal APGAR score, without perinatal complications or neurological disorders, clinically diagnosed with GER within the first three months of life by a certified pediatric gastroenterologist at the Neurodevelopment Monitoring Laboratory of the National Institute of Pediatrics, Mexico City, Mexico and were followed until one year of age. Radiological study of swallowing, and brainstem auditory-evoked potentials (BAEP) were performed at involvement and at six months of age. Patients were monthly assessed with Bayley II infant development scale and a neurological evaluation. The three children were included in an early intervention program.
Case 1
Swallowing study at diagnosis showed a slow oropharyngeal phase, minimum nasopharyngeal reflux, retention of the contrast medium on the floor of the mouth, abnormal anterior/posterior lingual movements, and medium laryngeal penetration (Figure 1). Two spontaneous GER events to the middle third of the esophagus were observed. BAEP reported as normal showing latency of the wave V and of the interval I-V at the upper limits for the left ear.9 several alterations were found throughout the development and neurological examinations during follow up (summarized in Table 1).
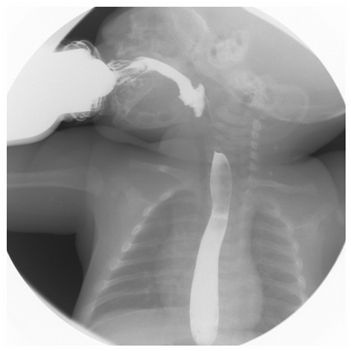
Figure 1 Swallowing study at one month of age shows mild pharyngonasal reflux and laryngeal penetration of the barium solution.
Age |
IFS |
Automatisms |
Active tone |
Passive tone |
Movement |
Reflexes |
Development (Bayley II) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
mental scale |
Psychomotor scale |
Behavior scale |
|||||||
3 m. |
5 |
Choking |
Axial hypertonia |
Asymmetries |
Clonus |
Exalted tonic labyrinthine extensor (TLE) and asymmetric tonic neck (ATNR) reflexes |
89 |
82 |
40 |
|
|||||||||
6m. |
4-5 |
Choking |
Axial hypertonia |
Asymmetries |
|
Spontaneous plantar grasp reflex |
82 |
67 |
20 |
No growling nor babbling |
|||||||||
9m. |
5 |
Does not accept pureed food |
Axial hypertonia |
Asymmetries |
Increased in lower limbs |
Primitive reflexes exalted when crying Spontaneous plantar grasp reflex |
68 |
52 |
6 |
Frustration intolerance |
|||||||||
12m. |
5 |
Irritability+++ |
|
Asymmetries |
Tremors |
Primitive reflexes exalted when crying Spontaneous plantar grasp reflex |
72 |
69 |
3 |
Lack of persistence. |
|||||||||
Table 1 Alterations found in the neuro-development follow up of case 1
*IFS: Infant Functional Status: 1. Closed eyes, regular breathing, no gross movements. 2. Closed eyes, irregular breathing, no gross movements. 3. Opened eyes, no gross movements. 4. Opened eyes, gross movements, no crying- 5. Crying. (Prechtl 1965).
At six months of age, the swallow study showed tongue mobility disorders, delayed onset of swallowing, and barium laryngeal penetration, which was spontaneously removed from the airway. BAEP showed increased latencies of the I-III interval of the right ear and III-V of the left ear. Latency of the I-V interval was within the upper normality range for both ears.9
Case 2
At the first month of age, the swallowing study showed 3 events of spontaneous GER to the middle third of the esophagus. BAEP showed increased latencies of the I-III and I-V intervals of the left ear.9 Alterations observed throughout the development and neurological examinations during follow up are summarized in Table 2.
Age |
IFS |
Automatisms |
Active |
Passive |
Movement |
Reflexes |
DEVELOPMENT (Bayley II) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Mental scale |
Psychomotor scale |
Behavior scale |
|||||||
3 m. |
4 |
Sucks aggregated into 'runs' alternated with breathing |
|
Fluctuating Asymmetries |
Tremors Starts |
Persistent right TANR |
85 |
70 |
37 |
No social smile |
|||||||||
6 m. |
5 |
Irritability. |
Hypotonia |
Hypotonia |
Tremors |
Spontaneous plantar grasp reflex |
90 |
88 |
22 |
Weak attention |
|||||||||
12 m. |
4 |
Wakes up several times during night. |
Hypotonia |
Hypotonia |
|
Exalted osteotendinous reflexes |
83 |
93 |
99 |
No da-da or equivalent vocalization |
|||||||||
Table 2 Alterations found in the neuro-development follow up of case 2
*IFS: Infant Functional Status: 1. Closed eyes, regular breathing, no gross movements. 2. Closed eyes, irregular breathing, no gross movements. 3. Opened eyes, no gross movements. 4. Opened eyes, gross movements, no crying- 5. Crying. (Prechtl 1965).
At six months of age, the swallowing study showed tongue motility disorders, slow oral transit, delayed onset of swallowing, barium laryngeal penetration, and 5 events of GER to the upper third of the esophagus (Figure 2). BAEP at 11 months of age showed I-III and I-V intervals latencies within the upper normality limits on the right ear, increased absolute latency of wave V and increased latency of intervals I-III and I-V of the left ear.9
Case 3
The swallowing study at diagnosis showed slow oral transit, abnormal anterior/posterior tongue movements, 5 events of pharyngonasal reflux, alteration of the epiglottic fold, bolus laryngeal penetration, barium aspiration to the upper third of the trachea, at least in the upper 2 cm, and leakage through the tracheal walls to carina, which was almost completely expelled by the cough reflex (Figure 3). BAEP were within normal limits.9 Neurological and developmental findings during follow up are summarized in Table 3.
Age |
IFS |
Automatisms |
Active tone |
Passive tone |
Mobility |
Reflexes |
Development (Bayley II) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
mental scale |
Psychomotor scale |
Behavior scale |
|||||||
3 m. |
4 |
Regurgitation |
Axial hypertonia Hands tightly closed
|
Asymmetries |
Increased basal activity |
Exalteded primitive reflexes |
101 |
73 |
44 |
Brief visual tracking |
|||||||||
6 m. |
4-5 |
Regurgitation Choking |
Stands on tiptoes |
Asymmetries |
Constant activity |
Spontaneous plantar grasp reflex |
96 |
104 |
39 |
Disorganization |
|||||||||
9 m. |
4-5 |
Choking Wakes up |
Fluctuating Stands on its tiptoes |
Asymmetries |
Very active |
Exaggerated LTE reflex Spontaneous plantar grasp reflex |
72 |
101 |
25 |
Weak attention |
|||||||||
10 m. |
4 |
Wakes up several times at night to eat |
|
|
Hyperkinesia |
|
94 |
105 |
66 |
Does not mimic vocalizations |
|||||||||
Table 3 Alterations found in the neuro-development follow up of case 3
*IFS: Infant Functional Status: 1. Closed eyes, regular breathing, no gross movements. 2. Closed eyes, irregular breathing, no gross movements. 3. Opened eyes, no gross movements. 4. Opened eyes, gross movements, no crying- 5. Crying. (Prechtl 1965).
At six months of age, the swallowing study showed reduced tongue base retraction, barium laryngeal penetration, and 4 events of spontaneous GER to the oropharynx. BAEP showed increased absolute latency of wave V, and increased latency of the III-V and I-V intervals of the right ear. Latencies, intervals, and amplitudes were within normality for the left ear.9
The brainstem has already been directly related to the pathogenesis of GER in children with neurological damage.10,11 The brain stem matures quickly between 33 to 38 weeks of gestation,12 earlier than limbic and cortical structures, and significant functions for survival depend on it. Over time and from experience, the sucking-swallowing process is partially subordinated to voluntary control by the modulation exerted by upper brain levels. In children suffering from neonatal brain stem dysfunction, slow or absent sucking, poor swallowing with gastroesophageal and/or nasopharyngeal reflux, as well as respiratory and heart rate disorders have been reported in early stages; the overall evolution of these children in their first year of life is deemed to be good, but they often have shown mild psychomotor developmental disorders.13 Considering that the nervous system takes part in the pathogenesis of GER in infants, requires an integral examination, in order to rule out other alterations. In these cases, data from sucking-swallowing disorders such as choking and milk leakage from the corner of the mouth (cases 1 and 3) or sucks aggregated in "runs", alternating with breathing (case 2) were reported from interrogation, and later documented in the fluoroscopic study, which showed additional oral management difficulties, laryngeal penetration, and even, tracheal aspiration (case 3). These alterations were partially modified, but not normalized, by 6 months of age, when they still showed contrast medium penetration to the larynx.
Neurobiological models on the development of behavior and emotion regulation in infants propose a vertical-integrative hierarchical system in which brainstem, limbic and cortical systems are involved. Brainstem-related systems provide the physiological foundation for the regulation required for high-order processes.14 Disorders may be reflected in the autonomic nervous system, sleep-wake cycles, and modulation of visceral homeostasis of internal states such as hunger and satiety, functions that are also necessary for the later development of more complex self-control and socio-cognitive processes.14
All three cases presented herein showed self-regulation difficulties. Case 1 showed irritability as the most important sign, which was reflected in the Bayley II behavior scale since six months of age. The self-regulation difficulties in case 2 were, intolerance to physical contact, irritability at the first two examinations, and a non-optimal score on the Bayley II behavior scale at six months of age. In case 3, these difficulties were observed since the first months of life with increased basal activity, and subsequent hyperkinesia which located him within percentiles considered questionable on Bayley II conduct scale. Parents also reported difficulties in regulating sleep-wake cycles that became more evident towards the end of the first year of life, when they continued to awaken up to three times during night. Additionally, the infants had difficulties on weaning characterized by the rejection of solid foods and new flavors, consistent with previous reports.15,16
Asymmetries, tone disorders, and isolated neurological signs were noticed in the neurological examinations of all three cases. Results from the Bayley II behavior rating scale showed some developmental indexes with delays tending to be in the normal range, except for case 1, whose delay was significant in both the psychomotor and mental areas since the ninth month of life. This delay was associated to the infant´s lack of cooperation on examinations characterized by irritability and deficient self-control. Case 3 had a low developmental index at nine months of age related to his high activity and lack of response to the test’s requirements; this was also reflected in the behavior rating scale on that same examination. These signs that suggest regulatory disorders could represent, as proposed by the referred model,14 obstacles to the development of subsequent cognitive processes, contributing to explain the low developmental indexes obtained by these patients. This evolution is in accordance with those delays reported in follow-up patients with neonatal brain stem dysfunction,13 and in infants with GER with no neurological damage in other reports which lacked support for some potential etiology.4,15 Another example of this, is the delay to acquire some behaviors related to language. Despite the lack of controlled studies on the development of language in children with GER, these data are consistent with isolated reports by other groups.15,16
BEAP showed increased latencies at some time during follow-up in the three cases, latencies within higher limits of the normal range for age and asymmetries, which could be interpreted as disorganization. The alterations reported in the BEAP, on the first stages of swallowing, and the delay of psychomotor development and language behaviors observed in these three cases, cannot be explained by GER itself.
All three cases were included in an integral breeding orientation program, where the parents received instructions aimed to achieve the establishment of routines, organize sleep-wake cycles, decrease irritability, and promote attention and tolerance spans through regulation of mother-child interactions. This may have favored a beneficial evolution
Although not conclusive, our results suggest that further research on this topic should be done in order to establish if GER as a frequent and easily diagnosed ailment, could be an indicator of early brain stem and neurological disorganization related to other disorders of swallowing or development. Taking these into consideration would allow the physician to alert mothers about the risk of bronchial aspiration, and provide them with instructions aimed to prevent it, and design strategies to promote self-regulation and normal development from early life stages.
The first author received a scholarship awarded by "Mexican Council of Science and Technology" to doctorate in biological and health Sciences.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.

© . This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.