eISSN: 2473-0815


Perspective Volume 6 Issue 3
GPwSI Diabetes CCG Board Member, UK
Correspondence: Sami Ozturk, GPwSI Diabetes CCG Board Member, Southend, UK
Received: April 11, 2018 | Published: June 25, 2018
Citation: Ozturk S. Safe and effective prescription of metformin in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Endocrinol Metab Int J. 2018;6(3):246-247. DOI: 10.15406/emij.2018.06.00184
We live in an aging world, 8.5% of population around the world are aged 65 and over according to National Institute of Health1 and this is expected to be around 17% by the year 2050. Expectedly, as Abdelhafiz & Sinclair2 explain, diabetes incidence is increasing all over the world too due to aging, longer living population and higher rates of obesity. Especially in the developed countries, it is becoming more evident that diabetes is no longer a disease of the middle aged people but more of a disease of older people as result of higher life expectancy. This brings with it special issues and adds specific complications of “geriatric syndromes” such as decline in the physical status, cognitive functional decline, higher risk of falls and polypharmacy on top of the well-known vascular and other complications of diabetes seen in younger age groups.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence3 in the UK recommends metformin as initial drug treatment of choice in patients with T2DM. Similarly American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) (2015) (Appendix 1) published a position statement on the management of T2DM putting metformin as first line drug of choice. Florez43 describes metformin as the “undisputed queen” of all type 2 diabetes drugs which tops all the professional society algorithms as first-line drug to be given as soon as patient is diagnosed with T2DM.
Scheen & Paquot5 however mention that elderly patients especially with diabetes prone to accumulate multiple comorbidities which are considered contraindications to the use of metformin, hence special consideration should be given when it is prescribed in this group.
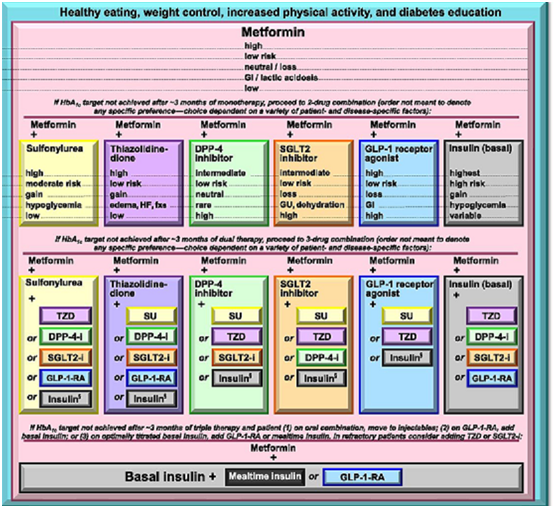
Appendix 1 American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) (2015).
Following considerations should be given when prescribing metformin in elderly patients with diabetes:
None.
The author declares there is no conflict of interest

©2018 Ozturk. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.