eISSN: 2473-0815


Research Article Volume 7 Issue 6
1Chairman, National Institute of Health and Research, India
2Bihar State Health Services, India
3Director, Centre for Indigenous Medicine and Research, India
Correspondence: Avinash Shankar, Chairman, National Institute of Health and Research, Bihar, India
Received: October 21, 2019 | Published: November 15, 2019
Citation: Shankar A, Shankar A, Shankar A. Diabetes mellitus, challenges & hopes. Endocrinol Metab Int J. 2019;7(6):160-169. DOI: 10.15406/emij.2019.07.00264
India, a world capital of diabetes mellitus and Bihar to be considered a first state in the world with 30% population suffering with diabetes mellitus as per 2019 report, a consequent t of changed dietary status, emergence of non nutrients in diet, altered life style and increasing stress, poses a challenge in spite of continuing anti diabetics and insulin supplementation due to increasing insulin resistance, thus an study to evaluate the regime dietary restriction, limited initial diet, modified life style and an adjuvant herbal composite been done.
Material: 3770 diabetic patients attending RA. Hospital & Research Centre, Warisaliganj (Nawada) Bihar and Aarogyam punarjeevan Bihar Patna during Jan 2017 to December 2017 been selected for the study.
Method: Selected patients were interrogated for the history of disease how it is detected, treatment taken and their result, clinically examined and, investigated for diabetic, lipid, haematological, hepatic and renal profile pre and post therapy. Each patients after 10days of restriction, changed life style, limited initial diet, been supplemented with herbal composite Cap META Reg 1 cap 30minutes before breakfast, lunch and dinner. Patients were followed up every 15days for 1year to adjudge the efficacy, safety profile and quality of life.
Result: All patients show marked decline in blood sugar and HbA1C, lipid profile and continuing dose of antidiabetics with complete withdrawal of insulin in 6months of therapy, marked improvement in haematological, hepatic and renal profile. No patients had any blood sugar surge or any consequent sequel during 1 year of follow up with minimal dose of OHA, adjuvant and modified dietary schedule, and life style.
Conclusion: Though growing incidence of diabetes mellitus in India affecting even hard worker, remain a challenge but modified life style, dietary plan and adjuvant Herbal composite remain a hope in control of diabetes mellitus and its sequel to ensure quality life.
Keywords:dietary non nutrient, OHA, herbal composite, limited initial diet, Lipid profile, hepatic, renal, quality of life
As per 2016 WHO survey 422million adults are suffering with diabetes mellitus globally and is increasing rapidly and IDF predicted to be its double by 2030.1‒8 A disease of luxury today affecting more the persons of low socio economic status and is attributed to trend of urbanization, change in lifestyle, sedentary life, less physical work, changing dietary constituents and emergence of non nutrients in the diet. Presently India had more diabetics than any other country and is considered diabetic capital of the World as 62million Indians i.e.- more than 7.2% of adult population are affected with Diabetes mellitus and nearly 1 million dies of diabetes mellitus every year.9 Recent survey reveals 30% population of Bihar is affected with Diabetes mellitus which only represent the registered cases while at least 10 % cases remain unregistered and taking vague treatment or treated by non qualified doctors. Due to rampant use of fertilisers chemical insecticide and soil energisers the food and drinks constitute a non nutrient constituent due to changed soil texture and chemical status which causes various metabolic and endocrinal disorders and these days also a cause of carcinogenesis due to increased proliferation and decreased apoptosis.10 In past patients with blood sugar more than 400mg % remain unable to stand or present with hyperglycaemic coma but these days patients even with blood sugar more than 500mg remain standing and dictate the disease history which affirms the changed etiopathogenesis of diabetes mellitus i.e. combined effect of hepato pancreatic dysfunction as evidence by its incidence and changed hepatic profile in majority cases.11 Study approves the initial dietary dose effect on the prognosis of diabetes mellitus as 100 calories initial diet improves the quality of life and diabetic control.12
Material:
3770 patients of diabetes mellitus enrolled at RA Hospital & Research Centre Warisaliganj (Nawada) Bihar and Aarogyam Punarjeevan, Ram Bhawan, Ara Garden Road, Jagdeopath, Baily Road Patna 14 were considered for the proposed study.
Methods:
Enrolled patients were interrogated thoroughly for their disease history, treatment taken, their response, clinically examined and investigated for Fasting blood sugar, post prandial blood sugar, HbA1C, lipid profile, hepatic profile and renal profile. For ease of evaluation urine was also assessed for sugar and albumin. Old patients were continued with continuing therapeutics with suggestive care while newly detected cases were advised as per their glycaemic status
Patients of either group been given a follow up card to enter hypoglycaemic event or any other sequel, on hypoglycaemic manifestation patients are warned to take sugar candy and taper the dose of continuing Insulin dose by 25% and visit the centre for evaluation or contact the project in charge for evaluation.
Each Cap of Meta Reg constitutes active ingredient of:
|
Each capsule of 500mg constituents |
|
|---|---|
|
Ficus bengalensis (Bad ka chhal) |
90mg |
|
Gymnema sylvestre (Gudmar) |
40mg |
|
Syzgium cumini (Jamun) |
40mg |
|
Coccinia grandis (Kundru) |
40mg |
|
Tribulus terristeris (Bada gokshuru ) |
40mg |
|
Calotropis gigantea (Ark root ) |
20mg |
|
Opuntia dilenii (Thhuhar) |
4mg |
|
Picrorhiza kuroo( Kutki ) |
20mg |
|
Terminalia arjuna (Arjun ) |
40mg |
|
Sida rhombifolia ( Mahavala) |
40mg |
|
Momordica charantia (Karela ) |
40mg |
|
Rubia cordifolia (Manjishtha ) |
40mg |
|
Aegle marmelos (Vel patra ) |
20mg |
|
Tigonella foenum graecum ( Methi seed ) |
6mg |
During each visit diabetic, lipid, renal and hepattic profile been repeated to adjudge the response of therapeutics, diet and life style changes, in addition safety profile.
Among the 3770 selected patients , 2250 and 1520 were male and female respectively of age group 22-52years while among them 2520 were old diabetics taking various i.e. Insulin, OHA and OHA combination (Table 1, Figures 1‒3) Out of all old cases 1230patients were having no diabetic sequel while 545, 540 and 205 patients were with associated hypertension, neuropathy and nephropathy respectively (Figure 4) 322 old and 120 new cases were with fasting blood sugar 130-150mg% though 220 old and 34 new cases had fasting blood sugar >290mg% while post prandial blood sugar in 264 old and 780 new cases were with 200-250mg% though 119 old and 18 new cases were with >500mg%. HbA1C was 7-9 in 428 old and 156 new cases while >13in 361 old and 119 new cases (Table 2). Out of all 245 old and 10 new cases had haemoglobin <10gm% 2094 old and 80 new cases were with altered hepatic function while 205 and 165 old cases were with altered renal and lipid profile respectively (Table 3).
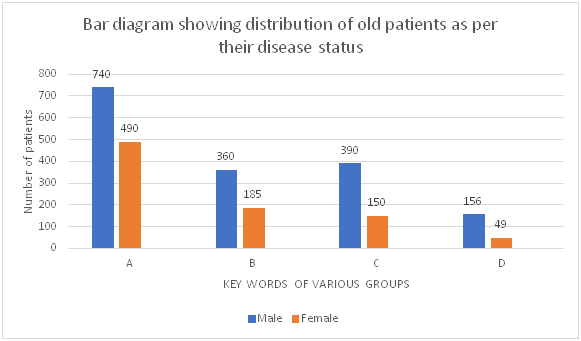
Figure 4 Distribution of patients as per their disease status.
Key words: Non complicated diabetes mellitus, A; Diabetes with hypertension, B; Diabetes with Neuropathy, C; Diabetes with Nephropathy, D.
Number of patients |
||
|---|---|---|
Male |
Female |
|
22-27 |
130 |
80 |
27-32 |
260 |
120 |
32-37 |
480 |
210 |
37-42 |
490 |
250 |
42-47 |
520 |
390 |
47-52 |
370 |
470 |
Table 1 Distribution of patients as per age and sex
Parameters |
Number of patients |
|
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Old patients |
New patients |
|||||
|
Male |
Female |
Total |
Male |
Female |
Total |
HbA1C: |
||||||
7-9 |
210 |
218 |
428 |
98 |
58 |
156 |
9-11 |
640 |
310 |
950 |
250 |
260 |
510 |
11-13 |
511 |
270 |
781 |
236 |
229 |
465 |
>13 |
245 |
116 |
361 |
60 |
59 |
119 |
Blood sugar(mg%): |
||||||
Fasting: |
||||||
130-150 |
213 |
109 |
322 |
60 |
60 |
120 |
150-170 |
196 |
132 |
328 |
102 |
110 |
212 |
170-190 |
243 |
108 |
351 |
114 |
129 |
243 |
190-210 |
132 |
72 |
204 |
80 |
70 |
150 |
210-230 |
149 |
69 |
218 |
72 |
60 |
132 |
230-250 |
280 |
138 |
418 |
64 |
52 |
116 |
250-270 |
120 |
86 |
206 |
76 |
60 |
136 |
270-290 |
129 |
124 |
253 |
54 |
53 |
107 |
>290 |
144 |
76 |
220 |
22 |
12 |
34 |
Post prandial: |
||||||
200-250 |
176 |
88 |
264 |
38 |
40 |
78 |
250-300 |
332 |
249 |
581 |
162 |
134 |
296 |
300-350 |
310 |
188 |
498 |
148 |
144 |
292 |
350-400 |
295 |
105 |
400 |
134 |
130 |
264 |
400-450 |
248 |
168 |
416 |
102 |
49 |
151 |
450-500 |
160 |
82 |
242 |
48 |
53 |
101 |
>500 |
85 |
34 |
119 |
12 |
6 |
18 |
Table 2 Showing Diabetic profile of the patients on admission
Parameters |
Number of patients |
|
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Old patients |
New patients |
|||||
|
Male |
Female |
Total |
Male |
Female |
Total |
Haematological: |
||||||
Haemoglobin: |
||||||
< 10 gm % |
156 |
89 |
245 |
6 |
4 |
10 |
>10 gm % |
1450 |
825 |
2275 |
638 |
602 |
1240 |
Hepatic profile: |
||||||
Serum bilirubin |
; |
|||||
<1mg% |
320 |
106 |
426 |
600 |
570 |
1170 |
>1mg% |
1286 |
808 |
2094 |
44 |
36 |
80 |
SGOT: |
||||||
<30 IU |
320 |
106 |
426 |
440 |
210 |
650 |
>30 IU |
1286 |
808 |
2094 |
204 |
396 |
600 |
SGPT: |
||||||
<30 IU |
320 |
106 |
426 |
440 |
210 |
650 |
>30 IU |
1286 |
808 |
2094 |
204 |
296 |
600 |
Renal profile: |
||||||
Serum creatinine |
||||||
<1.5 mg |
1450 |
865 |
2315 |
639 |
599 |
1238 |
>1.5 mg |
156 |
49 |
205 |
5 |
7 |
12 |
Blood Urea |
||||||
<26mg |
1450 |
865 |
2315 |
639 |
599 |
1238 |
>26mg |
156 |
49 |
205 |
5 |
7 |
12 |
Urine: |
||||||
Albumin |
||||||
Present |
156 |
49 |
205 |
3 |
2 |
5 |
Absent |
1450 |
865 |
2315 |
641 |
604 |
1245 |
RBC |
||||||
Absent |
1450 |
865 |
2315 |
641 |
604 |
1245 |
Present |
156 |
49 |
205 |
3 |
2 |
5 |
Lipid profile: |
||||||
Total Serum Cholestrol |
||||||
<200mg |
1246 |
749 |
1995 |
629 |
576 |
1205 |
>200mg |
360 |
165 |
525 |
15 |
30 |
45 |
Table 3 Distribution of patients as per basic bio parameters
All patients of both group show progressive decline in fasting and post prandial blood sugar HbA1C and lipid profile and attains normoglycemic state by 6th month of therapy (Table 4&5, Figure 6‒8). In addition all old cases on Insulin shows progressive decline in insulin dose and completely withdrawn by 6th month of therapy (Figure 9), in addition all cases also had decline in OHA dose with complete normalisation of haematological, hepatic and renal profile with improved quality of life. No patients had any withdrawal presentation (Table 6)
Bio parameters |
Number of patients |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Old cases |
New cases |
BLOOD SUGAR (mg%) |
||
Fasting : |
||
80-100 |
2230 |
980 |
100-120 |
290 |
270 |
120-140 |
Non |
Non |
>140 |
Non |
Non |
Post prandiol |
||
140—150 |
2190 |
1160 |
150- -160 |
330 |
90 |
160-170 |
Non |
Non |
170-180 |
Non |
Non |
180-200 |
Non |
Non |
>200 |
Non |
Non |
LIPID PROFILE (mg%) |
||
Serum Cholestrol : |
||
150-170 |
225 |
131 |
170-190 |
2170 |
1060 |
190-210 |
125 |
59 |
>210 |
Non |
Non |
RENAL PROFILE |
||
Blood Urea : |
||
<26mg% |
2520 |
1250 |
>26mg% |
||
Serum creatine |
||
<1.5mg% |
2520 |
1250 |
>1.5mg% |
Non |
Non |
Urine : |
||
Albumin |
||
Present : |
Non |
Non |
Absent : |
2520 |
1250 |
RBC: |
||
Present |
Non |
Non |
Absent |
2520 |
1250 |
HEPATIC PROFILE |
||
SGOT: |
||
<30 IU |
2520 |
1250 |
>30IU |
Non |
Non |
SGPT: |
||
<30 IU |
2520 |
1250 |
>30 IU |
Non |
Non |
Alkaline phosphatase : |
||
<140 |
||
>140 |
Non |
Non |
Table 4 Outcome of the study
|
HbA1C |
Number of patients |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
1st |
2nd |
3rd |
4th |
5th |
6th |
|
>13 |
480 |
56 |
45 |
38 |
12 |
0 |
|
11-13 |
1246 |
944 |
870 |
620 |
324 |
0 |
|
9-11 |
1460 |
1010 |
960 |
540 |
402 |
0 |
|
7-9 |
984 |
903 |
395 |
890 |
1120 |
0 |
|
5-7 |
0 |
655 |
1020 |
1012 |
884 |
330 |
|
3-5 |
0 |
202 |
480 |
670 |
1028 |
3440 |
Table 5 Showing pattern of HbA1C
Response in clinical presentation improvement: |
|
Particulars |
Remarks |
Diabetic triad: |
None |
Hypertension |
|
Completely controlled |
All |
Neuropathic manifestation |
|
Tingling numbness |
None |
Burning hand & feet |
None |
Pain in extremity |
None |
Nephrological manifestation |
|
Polyuria |
None |
Oliguria |
None |
Swelling of the body |
None |
Puffiness of face |
None |
Exertional dyspnoea |
None |
Obesity |
None |
Table 6 No patients had any withdrawal presentation
Increasing incidence of diabetes mellitus among Indian due to changed life style, dietary habits, emergence of non nutrient in dietary products and economical burden induced stress, designated India as World capital of Diabetes. In addition current survey of 2019 more than 30% Bihar population is affected with Diabetes mellitus.1‒4 Increasing tolerance to high blood sugar created doubt of multifocal pathogenesis of hyperglycaemia and been approved as hepatopancreatic etiopathogenesis. In spite of increasing incidence and its sequel even with OHA and Insulin supplementation,13‒19 pose a challenge to healthy longevity, but in present study with modified life style, 100 calories initial diet, restriction of fast food and unconscious eating with supplementation of herbal composite Cap META Reg in 3770patients shows marked decline in blood sugar, serum lipid , HbA1C. Progressive decline in Insulin supplementation achieving complete withdrawal of Insulin and declined OHA dose with normoglycemic status in 6months therapy with better quality of life without any adversity and reversal of lipid, hepatic, and renal profile. This marked clinical efficacy can be explained as – Minimal initial diet prompt secretion of incretin (GLP), and GIP which induce Insulin secretion from Pancreatic Beta Cells, restricted dietary allowance and food grain rice and potato decreases amount of non nutrient enzyme inhibitor (Figures 8&9) while constituent of META Reg20 – Gymnema sylvestre, Sygium cumini, Coccinia grandis, and Trigonella foenum graceum invigorate Pancreatic Beta cells to synthesize Insulin, Ficus bengalensis, Tribulus terresteris, Calotropis gigantea, and Picrorhiza kurroo modulate hepatic parenchyma to increase glucose utilization and glycogenesis Terminalia arjuna and Sida rhombifolia modulate lipid metabolism and helps decline raised lipid profile, increase cardiac blood supply and its tonicity, thus takes care of cardiac healthy state. Momordica charantia, and Rubia cordifolia increases insulin receptor sensitivity, Aegle marmelos decline absorption of carbohydrate and lipid from intestine while Opuntia delleni modulate neuro endocrinal path way for needed insulin release (Figure 10). Thus this combo prescription ensure diabetic control with improved quality of life.
Though diabetic incidence is increasing in geometric progression and failure of existing modern molecule, change in life style, dietary intake and its regime, moderate exercise and Cap META Reg in dose of 1 cap 30 minutes before breakfast, lunch and dinner, a new hope for diabetic control and better control of quality of life.
None.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
None.

©2019 Shankar, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.